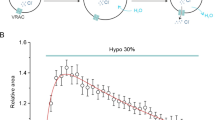
Abstract
Mammals perceive the five different taste qualities: bitter, sweet, umami, sour, and salty. At least two different mechanisms contribute to salt taste in rodents. One is elicited by various cations and sensitive to cetylpyridinium chloride, whereas another is selectively stimulated by Na+ and inhibited by amiloride. The latter pathway has been suggested to involve the epithelial sodium channel, ENaC. In humans, the presence of amiloride-sensitive salt taste transduction is being disputed. In this paper, we addressed the question whether ENaC may have a role in human salt taste perception. Immunohistochemistry revealed that β-, γ-, and δ-ENaC subunits are present in subsets of circumvallate and fungiform taste bud cells, whereas α-ENaC was confined to cells of circumvallate taste buds. Alpha-, β-, and γ-subunits were observed in basolateral intracellular compartments, while δ-ENaC was exclusively found in all taste pores of both types of papillae consistent with a function in taste transduction. To further assess the involvement of ENaC in salt taste transduction, we combined sensory studies and functional expression of ENaC in oocytes. With the exception of l-homoarginine, choline chloride, l-arginine, l-lysine, and l-argininyl-l-arginine enhanced both salt taste perception in subjects and sodium currents recorded in αβγ- or δβγ-ENaC expressing oocytes, whereas l-glutamine did neither show salt-taste-enhancing activity nor did it influence the sodium currents in the oocyte assay. Taken together, our data make ENaC an interesting molecule possibly involved in salty taste transduction.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler E, Hoon MA, Mueller KL, Chandrashekar J, Ryba NJ, Zuker CS (2000) A novel family of mammalian taste receptors. Cell 100:693–702
Anand KK, Zuniga JR (1997) Effect of amiloride on suprathreshold NaCl, LiCl, and KCl salt taste in humans. Physiol Behav 62:925–929
Avenet P, Lindemann B (1988) Amiloride-blockable sodium currents in isolated taste receptor cells. J Membr Biol 105:245–255
Beauchamp GK, Bertino M, Burke D, Engelman K (1990) Experimental sodium depletion and salt taste in normal human volunteers. Am J Clin Nutr 51:881–889
Behrens M, Stähler F, Shi P, Bufe B, Meyerhof W (2007) Taste: topics in chemical biology. Wiley Encyclopedia of Chemical Biology
Boughter JD Jr., Gilbertson TA (1999) From channels to behavior: an integrative model of NaCl taste. Neuron 22:213–215
Brand JG, Teeter JH, Silver WL (1985) Inhibition by amiloride of chorda tympani responses evoked by monovalent salts. Brain Res 334:207–214
Brouard M, Casado M, Djelidi S, Barrandon Y, Farman N (1999) Epithelial sodium channel in human epidermal keratinocytes: expression of its subunits and relation to sodium transport and differentiation. J Cell Sci 112(Pt 19):3343–3352
Bufe B, Hofmann T, Krautwurst D, Raguse JD, Meyerhof W (2002) The human TAS2R16 receptor mediates bitter taste in response to beta-glucopyranosides. Nat Genet 32:397–401
Contreras RJ, Catalanotto FA (1980) Sodium deprivation in rats: salt thresholds are related to salivary sodium concentrations. Behav Neural Biol 29:303–314
Denton D (1982) The hunger for salt. An anthropological, physiological and medical analysis. Springer, Berlin
DeSimone JA, Heck GL, Mierson S, Desimone SK (1984) The active ion transport properties of canine lingual epithelia in vitro. Implications for gustatory transduction. J Gen Physiol 83:633–656
DeSimone JA, Lyall V, Heck GL, Phan TH, Alam RI, Feldman GM, Buch RM (2001) A novel pharmacological probe links the amiloride-insensitive NaCl, KCl, and NH(4)Cl chorda tympani taste responses. J Neurophysiol 86:2638–2641
Doolin RE, Gilbertson TA (1996) Distribution and characterization of functional amiloride-sensitive sodium channels in rat tongue. J Gen Physiol 107:545–554
Feldman GM, Mogyorosi A, Heck GL, DeSimone JA, Santos CR, Clary RA, Lyall V (2003) Salt-evoked lingual surface potential in humans. J Neurophysiol 90:2060–2064
Formaker BK, Hill DL (1991) Lack of amiloride sensitivity in SHR and WKY glossopharyngeal taste responses to NaCl. Physiol Behav 50:765–769
Gilbertson TA, Fontenot DT (1998) Distribution of amiloride-sensitive sodium channels in the oral cavity of the hamster. Chem Senses 23:495–499
Gilbertson TA, Kinnamon SC (1996) Making sense of chemicals. Chem Biol 3:233–237
Guitard M, Leyvraz C, Hummler E (2004) A nonconventional look at ionic fluxes in the skin: lessons from genetically modified mice. News Physiol Sci 19:75–79
Hager H, Kwon TH, Vinnikova AK, Masilamani S, Brooks HL, Frokiaer J, Knepper MA, Nielsen S (2001) Immunocytochemical and immunoelectron microscopic localization of alpha-, beta-, and gamma-ENaC in rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 280:F1093–F1106
Halpern BP (1998) Amiloride and vertebrate gustatory responses to NaCl. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:5–47
Halpern BP, Darlington RB (1998) Effects of amiloride on gustatory quality descriptions and temporal patterns produced by NaCl. Chem Senses 23:501–511
Heck GL, Mierson S, DeSimone JA (1984) Salt taste transduction occurs through an amiloride-sensitive sodium transport pathway. Science 223:403–405
Hubbard TJ, Aken BL, Beal K, Ballester B, Caccamo M, Chen Y, Clarke L, Coates G, Cunningham F, Cutts T, Down T, Dyer SC, Fitzgerald S, Fernandez-Banet J, Graf S, Haider S, Hammond M, Herrero J, Holland R, Howe K, Johnson N, Kahari A, Keefe D, Kokocinski F, Kulesha E, Lawson D, Longden I, Melsopp C, Megy K, Meidl P, Ouverdin B, Parker A, Prlic A, Rice S, Rios D, Schuster M, Sealy I, Severin J, Slater G, Smedley D, Spudich G, Trevanion S, Vilella A, Vogel J, White S, Wood M, Cox T, Curwen V, Durbin R, Fernandez-Suarez XM, Flicek P, Kasprzyk A, Proctor G, Searle S, Smith J, Ureta-Vidal A, Birney E (2007) Ensembl 2007. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D610–D617
Ji HL, Bishop LR, Anderson SJ, Fuller CM, Benos DJ (2004) The role of Pre-H2 domains of alpha- and delta-epithelial Na+ channels in ion permeation, conductance, and amiloride sensitivity. J Biol Chem 279:8428–8440
Ji HL, Su XF, Kedar S, Li J, Barbry P, Smith PR, Matalon S, Benos DJ (2006) Delta-subunit confers novel biophysical features to alpha beta gamma-human ENaC via a physical interaction. J Biol Chem 281:8233–8241
Kitada Y, Mitoh Y, Hill DL (1998) Salt taste responses of the IXth nerve in Sprague–Dawley rats: lack of sensitivity to amiloride. Physiol Behav 63:945–949
Kretz O, Barbry P, Bock R, Lindemann B (1999) Differential expression of RNA and protein of the three pore-forming subunits of the amiloride-sensitive epithelial sodium channel in taste buds of the rat. J Histochem Cytochem 47:51–64
Kuhn C, Bufe B, Winnig M, Hofmann T, Frank O, Behrens M, Lewtschenko T, Slack JP, Ward CD, Meyerhof W (2004) Bitter taste receptors for saccharin and acesulfame K. J Neurosci 24:10260–10265
Li WY, Huey CL, Yu AS (2004) Expression of claudin-7 and -8 along the mouse nephron. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 286:F1063–F1071
Liman ER, Tytgat J, Hess P (1992) Subunit stoichiometry of a mammalian K+ channel determined by construction of multimeric cDNAs. Neuron 9:861–871
Lin W, Finger TE, Rossier BC, Kinnamon SC (1999) Epithelial Na+ channel subunits in rat taste cells: localization and regulation by aldosterone. J Comp Neurol 405:406–420
Lindemann B (1996) Taste reception. Physiol Rev 76:718–766
Locke KW, Fielding S (1994) Enhancement of salt intake by choline chloride. Physiol Behav 55:1039–1046
McCaughey SA, Scott TR (1998) The taste of sodium. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 22:663–676
McDonald FJ, Snyder PM, McCray PB, Jr., Welsh MJ (1994) Cloning, expression, and tissue distribution of a human amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel. Am J Physiol 266:L728–L734
McDonald FJ, Price MP, Snyder PM, Welsh MJ (1995) Cloning and expression of the beta- and gamma-subunits of the human epithelial sodium channel. Am J Physiol 268:C1157–C1163
Michlig S, Damak S, Le Coutre J (2007) Claudin-based permeability barriers in taste buds. J Comp Neurol 502:1003–1011
Miyamoto T, Miyazaki T, Fujiyama R, Okada Y, Sato T (2001) Differential transduction mechanisms underlying NaCl- and KCl-induced responses in mouse taste cells. Chem Senses 26:67–77
Ninomiya Y (1998) Reinnervation of cross-regenerated gustatory nerve fibers into amiloride-sensitive and amiloride-insensitive taste receptor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:5347–5350
Ogawa T, Nakamura T, Tsuji E, Miyanaga Y, Nakagawa H, Hirabayashi H, Uchida T (2004) The combination effect of L-arginine and NaCl on bitterness suppression of amino acid solutions. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 52:172–177
Ossebaard CA, Smith DV (1995) Effect of amiloride on the taste of NaCl, Na-gluconate and KCl in humans: implications for Na+ receptor mechanisms. Chem Senses 20:37–46
Rossier O, Cao J, Huque T, Spielman AI, Feldman RS, Medrano JF, Brand JG, le Coutre J (2004) Analysis of a human fungiform papillae cDNA library and identification of taste-related genes. Chem Senses 29:13–23
Rotzoll N, Dunkel A, Hofmann T (2006) Quantitative studies, taste reconstitution, and omission experiments on the key taste compounds in morel mushrooms (Morchella deliciosa Fr.). J Agric Food Chem 54:2705–2711
Schiffman SS, Lockhead E, Maes FW (1983) Amiloride reduces the taste intensity of Na+ and Li+ salts and sweeteners. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:6136–6140
Shigemura N, Islam AA, Sadamitsu C, Yoshida R, Yasumatsu K, Ninomiya Y (2005) Expression of amiloride-sensitive epithelial sodium channels in mouse taste cells after chorda tympani nerve crush. Chem Senses 30:531–538
Smith DV, Ossebaard CA (1995) Amiloride suppression of the taste intensity of sodium chloride: evidence from direct magnitude scaling. Physiol Behav 57:773–777
Smith DV, van der Klaauw NJ (1995) The perception of saltiness is eliminated by NaCl adaptation: implications for gustatory transduction and coding. Chem Senses 20:545–557
Sollars SI, Bernstein IL (1994) Amiloride sensitivity in the neonatal rat. Behav Neurosci 108:981–987
Tennissen AM (1992) Amiloride reduces intensity responses of human fungiform papillae. Physiol Behav 51:1061–1068
Tennissen AM, McCutcheon NB (1996) Anterior tongue stimulation with amiloride suppresses NaCl saltiness, but not citric acid sourness in humans. Chem Senses 21:113–120
Van Itallie C, Rahner C, Anderson JM (2001) Regulated expression of claudin-4 decreases paracellular conductance through a selective decrease in sodium permeability. J Clin Invest 107:1319–1327
Waldmann R, Champigny G, Bassilana F, Voilley N, Lazdunski M (1995) Molecular cloning and functional expression of a novel amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel. J Biol Chem 270:27411–27414
Yu AS, Enck AH, Lencer WI, Schneeberger EE (2003) Claudin-8 expression in Madin–Darby canine kidney cells augments the paracellular barrier to cation permeation. J Biol Chem 278:17350–17359
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms. Elisabeth Meyer for expert technical assistance and Dr. Erwin Tareilus for the supply of cDNAs encoding α-, β- and γ-ENaC. This work was supported by grants from the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) to W.M. (0313819A) and T.H. (0313819B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Immunohistochemistry omitting primary antibodies in circumvallate and fungiform papillae. Indirect immunohistochemistry was performed without primary antibodies using 2-μm sections of paraffin-embedded human circumvallate and fungiform papillae. Detection with peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody resulted in no labeling at all. Dotted lines mark taste buds within taste papillae (GIF 103 KB).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stähler, F., Riedel, K., Demgensky, S. et al. A Role of the Epithelial Sodium Channel in Human Salt Taste Transduction?. Chem. Percept. 1, 78–90 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12078-008-9006-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12078-008-9006-4