Abstract
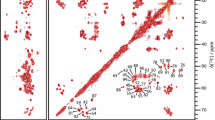
Parkinson’s disease is a neurological human proteinopathy, which is caused by the accumulation of protein aggregates of high molecular mass. α-Synuclein is a major component of these fibrillar, β-sheet rich, insoluble assemblies and is deposited in the form of amyloids. Structural characterization of amyloids is possible by solid-state NMR, although no atomic-resolution structure is available as of today. α-Synuclein, as many other pathology-related fibril-forming proteins, can form a number of different polymorphs that are sometimes tricky to obtain in pure form. Here, we describe the chemical shifts and secondary structure analysis of a polymorph that also adopts mainly β-sheet conformation, with a fibrillar core ranging from residues 38 to 94. In addition, residues 15–20 from the N-terminus found to be part of a rigid ordered β-sheet. The chemical shifts differ substantially from the polymorph we previously assigned.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Böckmann A, Gardiennet C, Verel R, Hunkeler A, Loquet A, Pintacuda G, Emsley L, Meier BH, Lesage A (2009) Characterization of different water pools in solid-state NMR protein samples. J Biomol NMR 45(3):319–327
Cohlberg JA, Li J, Uversky VN, Fink AL (2002) Heparin and other glycosaminoglycans stimulate the formation of amyloid fibrils from α-synuclein in vitro. Biochemistry 41(5):1502–1511
Comellas G, Lemkau LR, Nieuwkoop AJ, Kloepper KD, Ladror DT, Ebisu R, Woods WS, Lipton AS, George JM, Rienstra CM (2011) Structured regions of α-synuclein fibrils include the early-onset Parkinsons disease mutation sites. J Mol Biol 411(4):881–895
Gath J, Habenstein B, Bousset L, Melki R, Meier BH, Böckmann A (2012) Solid-state NMR sequential assignments of α-synuclein. Biomol NMR Assign 6(1):51–55
Habenstein B, Wasmer C, Bousset L, Sourigues Y, Schütz A, Loquet A, Meier BH, Melki R, Böckmann A (2011) Extensive de novo solid-state NMR assignments of the 33 kDa C-terminal domain of the Ure2 prion. J Biomol NMR 51(3):235–243
Hansen C, Angot E, Bergström A-L, Steiner JA, Pieri L, Paul G, Outeiro TF, Melki R, Kallunki P, Fog K, Li J-Y, Brundin P (2011) α-Synuclein propagates from mouse brain to grafted dopaminergic neurons and seeds aggregation in cultured human cells. J Clin Invest 121(2):715–725
Heise H, Hoyer W, Becker S, Andronesi O, Riedel D, Baldus M (2005) Molecular-level secondary structure, polymorphism, and dynamics of full-length α-synuclein fibrils studied by solid-state NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(44):15871–15876
Kim H-Y, Cho M-K, Kumar A, Maier E, Siebenhaar C, Becker S, Fernández CO, Lashuel HA, Benz R, Lange A, Zweckstetter M (2009) Structural properties of pore-forming oligomers of α-synuclein. J Am Chem Soc 131(47):17482–17489
Lv G, Kumar A, Giller K, Orcellet ML, Riedel D, Fernandez CO, Becker S, Lange A (2012) Structural comparison of mouse and human α-synuclein amyloid fibrils by solid-state NMR. J Mol Biol 420(1–2):99–111
Schuetz A, Wasmer C, Habenstein B, Verel R, Greenwald J, Riek R, Böckmann A, Meier BH (2010) Protocols for the sequential solid-state NMR spectroscopic assignment of a uniformly labeled 25 kDa protein: HET-s(1-227). ChemBioChem 11(11):1543–1551
Stevens TJ, Fogh RH, Boucher W, Higman VA, Eisenmenger F, Bardiaux B, van Rossum B-J, Oschkinat H, Laue ED (2011) A software framework for analysing solid-state MAS NMR data. J Biomol NMR 51(4):437–447
Vranken W, Boucher W, Stevens T, Fogh R, Pajon A, Llinas P, Ulrich E, Markley J, Ionides J, Laue E (2005) The CCPN data model for NMR spectroscopy: development of a software pipeline. Proteins 59(4):687–696
Wishart DS, Sykes BD (1994) The 13C Chemical-Shift Index: a simple method for the identification of protein secondary structure using 13C chemical-shift data. J Biomol NMR 4(2):171–180
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR-11-BSV8-021-01), the ETH Zurich, the Swiss National Science Foundation (Grant 200020_124611), the Era-Net Neuron (project MIPROTRAN, ANR-08-NEUR-001-01) and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique. We also acknowledge support from the European Commission under the Seventh Framework Programme (FP7), contract Bio-NMR 261863.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Julia Gath and Luc Bousset have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gath, J., Bousset, L., Habenstein, B. et al. Yet another polymorph of α-synuclein: solid-state sequential assignments. Biomol NMR Assign 8, 395–404 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-013-9526-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-013-9526-y