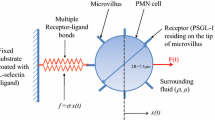
Abstract
Molecular dissociation rates have long been known to be sensitive to applied force. We use a laser trap to provide evidence that rates of association may also be force-dependent. We use the thermal fluctuation assay to study single bonds between E-selectin and sialyl Lewisa (sLea), the sugar on PSGL-1 to which the three selectins bind. Briefly, an E-selectin-coated bead is held in a laser trap and pressed with various compressive loads against the vertical surface of a bead coated with sLea. The time it takes for a bond to form is used to calculate a specific two-dimensional on-rate, \( k_{\text{on}}^{\text{o}} . \) We observe an increase in \( k_{\text{on}}^{\text{o}} \) with increasing compressive force, providing single molecule evidence that on-rate, in addition to off-rate, is influenced by load. By measuring bond lifetimes at known tensile loads, we show that E-selectin, like its family members L- and P-selectin, is capable of forming catch bonds. Our data support a reverse Bell model, in which compressive forces lower the activation energy for binding. Load-dependent on-rates may be a general feature of all intermolecular bonds.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alon, R., S. Chen, K. D. Puri, E. B. Finger, and T. A. Springer. The kinetics of L-selectin tethers and the mechanics of selectin-mediated rolling. J. Cell Biol. 138:1169–1180, 1997.
Alon, R., D. A. Hammer, and T. A. Springer. Lifetime of the P-selectin-carbohydrate bond and its response to tensile force in hydrodynamic flow. Nature 374:539–542, 1995.
Bell, G. I. Models for the specific adhesion of cells to cells. Science 200:618–627, 1978.
Beste, M. T., and D. A. Hammer. Selectin catch-slip kinetics encode shear threshold adhesive behavior of rolling leukocytes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105:20716–20721, 2008.
Brunk, D. K., and D. A. Hammer. Quantifying rolling adhesion with a cell-free assay: E-selectin and its carbohydrate ligands. Biophys. J. 72:2820–2833, 1997.
Chen, S., and T. A. Springer. Selectin receptor-ligand bonds: formation limited by shear rate and dissociation governed by the Bell model. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98:950–955, 2001.
Chen, W., E. A. Evans, R. P. McEver, and C. Zhu. Monitoring receptor-ligand interactions between surfaces by thermal fluctuations. Biophys. J. 94:694–701, 2008.
Chesla, S. E., P. Selvaraj, and C. Zhu. Measuring two-dimensional receptor-ligand binding kinetics by micropipette. Biophys. J. 75:1553–1572, 1998.
Dembo, M., D. C. Torney, K. Saxman, and D. Hammer. The reaction-limited kinetics of membrane-to-surface adhesion and detachment. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 234:55–83, 1988.
Evans, E., A. Leung, V. Heinrich, and C. Zhu. Mechanical switching and coupling between two dissociation pathways in a P-selectin adhesion bond. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101:11281–11286, 2004.
Finger, E. B., K. D. Puri, R. Alon, M. B. Lawrence, U. H. von Andrian, and T. A. Springer. Adhesion through L-selectin requires a threshold hydrodynamic shear. Nature 379:266–269, 1996.
Florin, E. L., V. T. Moy, and H. E. Gaub. Adhesion forces between individual ligand-receptor pairs. Science 264:415–417, 1994.
Fritz, J., A. G. Katopodis, F. Kolbinger, and D. Anselmetti. Force-mediated kinetics of single P-selectin/ligand complexes observed by atomic force microscopy. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95:12283–12288, 1998.
Graves, B. J., R. L. Crowther, C. Chandran, J. M. Rumberger, S. Li, K. S. Huang, D. H. Presky, P. C. Familletti, B. A. Wolitzky, and D. K. Burns. Insight into E-selectin/ligand interaction from the crystal structure and mutagenesis of the lec/EGF domains. Nature 367:532–538, 1994.
Guilford, W. H., D. E. Dupuis, G. Kennedy, J. Wu, J. B. Patlak, and D. M. Warshaw. Smooth muscle and skeletal muscle myosins produce similar unitary forces and displacements in the laser trap. Biophys. J. 72:1006–1021, 1997.
Guilford, W. H., J. A. Tournas, D. Dascalu, and D. S. Watson. Creating multiple time-shared laser traps with simultaneous displacement detection using digital signal processing hardware. Anal. Biochem. 326:153–166, 2004.
Guo, B., and W. H. Guilford. Mechanics of actomyosin bonds in different nucleotide states are tuned to muscle contraction. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103:9844–9849, 2006.
Ham, A. S., D. J. Goetz, A. L. Klibanov, and M. B. Lawrence. Microparticle adhesive dynamics and rolling mediated by selectin-specific antibodies under flow. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 96:596–607, 2007.
Hanley, W., O. McCarty, S. Jadhav, Y. Tseng, D. Wirtz, and K. Konstantopoulos. Single molecule characterization of P-selectin/ligand binding. J. Biol. Chem. 278:10556–10561, 2003.
Hanley, W. D., D. Wirtz, and K. Konstantopoulos. Distinct kinetic and mechanical properties govern selectin-leukocyte interactions. J. Cell Sci. 117:2503–2511, 2004.
Hulme, E. C., and N. J. M. Birdsall. Strategy and Tactics in Receptor-Binding Studies. Oxford, UK: IRL Press, pp. 63–176, 1992.
Johnson, K. L. Contact Mechanics (2nd ed.). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 1985.
Kimura, N., C. Mitsuoka, A. Kanamori, N. Hiraiwa, K. Uchimura, T. Muramatsu, T. Tamatani, G. S. Kansas, and R. Kannagi. Reconstitution of functional L-selectin ligands on a cultured human endothelial cell line by cotransfection of alpha1→3 fucosyltransferase VII and newly cloned GlcNAcbeta:6-sulfotransferase cDNA. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96:4530–4535, 1999.
Kong, F., A. J. Garcia, A. P. Mould, M. J. Humphries, and C. Zhu. Demonstration of catch bonds between an integrin and its ligand. J. Cell Biol. 185:1275–1284, 2009.
Lawrence, M. B., G. S. Kansas, E. J. Kunkel, and K. Ley. Threshold levels of fluid shear promote leukocyte adhesion through selectins (CD62L, P, E). J. Cell Biol. 136:717–727, 1997.
Lou, J., T. Yago, A. G. Klopocki, P. Mehta, W. Chen, V. I. Zarnitsyna, N. V. Bovin, C. Zhu, and R. P. McEver. Flow-enhanced adhesion regulated by a selectin interdomain hinge. J. Cell Biol. 174:1107–1117, 2006.
Lowe, J. B., L. M. Stoolman, R. P. Nair, R. D. Larsen, T. L. Berhend, and R. M. Marks. ELAM-1-dependent cell adhesion to vascular endothelium determined by a transfected human fucosyltransferase cDNA. Cell 63:475–484, 1990.
Lubarsky, G. V., M. R. Davidson, and R. H. Bradley. Elastic modulus, oxidation depth and adhesion force of surface modified polystyrene studied by AFM and XPS. Surf. Sci. 558:135–144, 2004.
Marshall, B. T., M. Long, J. W. Piper, T. Yago, R. P. McEver, and C. Zhu. Direct observation of catch bonds involving cell-adhesion molecules. Nature 423:190–193, 2003.
Mody, N. A., O. Lomakin, T. A. Doggett, T. G. Diacovo, and M. R. King. Mechanics of transient platelet adhesion to von Willebrand factor under flow. Biophys. J. 88:1432–1443, 2005.
Moore, K. L., K. D. Patel, R. E. Bruehl, F. Li, D. A. Johnson, H. S. Lichenstein, R. D. Cummings, D. F. Bainton, and R. P. McEver. P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 mediates rolling of human neutrophils on P-selectin. J. Cell Biol. 128:661–671, 1995.
Park, S. E., R. Ryoo, W. S. Ahn, C. W. Lee, and J. S. Chang. Nanotechnology in mesostructured materials, Vol 146: Proceedings of the 3rd International Mesostructured Materials Symposium, p. 393, 2003.
Park, E. Y., M. J. Smith, E. S. Stropp, K. R. Snapp, J. A. DiVietro, W. F. Walker, D. W. Schmidtke, S. L. Diamond, and M. B. Lawrence. Comparison of PSGL-1 microbead and neutrophil rolling: microvillus elongation stabilizes P-selectin bond clusters. Biophys. J. 82:1835–1847, 2002.
Paschall, C. D., W. H. Guilford, and M. B. Lawrence. Enhancement of L-selectin, but not P-selectin, bond formation frequency by convective flow. Biophys. J. 94:1034–1045, 2008.
Pereverzev, Y. V., O. V. Prezhdo, M. Forero, E. V. Sokurenko, and W. E. Thomas. The two-pathway model for the catch-slip transition in biological adhesion. Biophys. J. 89:1446–1454, 2005.
Phan, U. T., T. T. Waldron, and T. A. Springer. Remodeling of the lectin-EGF-like domain interface in P- and L-selectin increases adhesiveness and shear resistance under hydrodynamic force. Nat. Immunol. 7:883–889, 2006.
Phillips, M. L., E. Nudelman, F. C. Gaeta, M. Perez, A. K. Singhal, S. Hakomori, and J. C. Paulson. ELAM-1 mediates cell adhesion by recognition of a carbohydrate ligand, sialyl-Lex. Science 250:1130–1132, 1990.
Pierce, G. W. The Songs of Insects. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1948.
Puri, K. D., E. B. Finger, and T. A. Springer. The faster kinetics of L-selectin than of E-selectin and P-selectin rolling at comparable binding strength. J. Immunol. 158:405–413, 1997.
Ramachandran, V., M. U. Nollert, H. Qiu, W. J. Liu, R. D. Cummings, C. Zhu, and R. P. McEver. Tyrosine replacement in P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 affects distinct kinetic and mechanical properties of bonds with P- and L-selectin. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96:13771–13776, 1999.
Ramachandran, V., T. Yago, T. K. Epperson, M. M. Kobzdej, M. U. Nollert, R. D. Cummings, C. Zhu, and R. P. McEver. Dimerization of a selectin and its ligand stabilizes cell rolling and enhances tether strength in shear flow. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98:10166–10171, 2001.
Rinko, L. J., M. B. Lawrence, and W. H. Guilford. The molecular mechanics of P- and L-selectin lectin domains binding to PSGL-1. Biophys. J. 86:544–554, 2004.
Sarangapani, K. K., T. Yago, A. G. Klopocki, M. B. Lawrence, C. B. Fieger, S. D. Rosen, R. P. McEver, and C. Zhu. Low force decelerates L-selectin dissociation from P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 and endoglycan. J. Biol. Chem. 279:2291–2298, 2004.
Smith, M. J., E. L. Berg, and M. B. Lawrence. A direct comparison of selectin-mediated transient, adhesive events using high temporal resolution. Biophys. J. 77:3371–3383, 1999.
Somers, W. S., J. Tang, G. D. Shaw, and R. T. Camphausen. Insights into the molecular basis of leukocyte tethering and rolling revealed by structures of P- and E-selectin bound to SLe(X) and PSGL-1. Cell 103:467–479, 2000.
Spillmann, C. M., E. Lomakina, and R. E. Waugh. Neutrophil adhesive contact dependence on impingement force. Biophys. J. 87:4237–4245, 2004.
Springer, T. A. Structural basis for selectin mechanochemistry. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106:91–96, 2009.
Sun, G., Y. Zhang, B. Huo, and M. Long. Surface-bound selectin-ligand binding is regulated by carrier diffusion. Eur. Biophys. J. 38:701–711, 2009.
Suonpaa, M., E. Markela, T. Stahlberg, and I. Hemmila. Europium-labelled streptavidin as a highly sensitive universal label indirect time-resolved immunofluorometry of FSH and TSH. J. Immunol. Methods 149:247–253, 1992.
Svoboda, K., and S. M. Block. Biological applications of optical forces. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 23:247–285, 1994.
Tees, D. F., R. E. Waugh, and D. A. Hammer. A microcantilever device to assess the effect of force on the lifetime of selectin-carbohydrate bonds. Biophys. J. 80:668–682, 2001.
Thomas, W. For catch bonds, it all hinges on the interdomain region. J. Cell Biol. 174(7):911–913, 2006.
Thomas, W. E., M. Forero, O. Yakovenko, L. M. Nilsson, P. Vicini, E. V. Sokurenko, and V. Vogel. Catch bond model derived from allostery explains force-activated bacterial adhesion. Biophys. J. 90:753–764, 2006.
Thomas, W. E., L. M. Nilsson, M. Forero, E. V. Sokurenko, and V. Vogel. Shear-dependent ‘stick-and-roll’ adhesion of type 1 fimbriated Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 53:1545–1557, 2004.
Ushakova, N. A., M. E. Preobrazhenskaya, M. I. Bird, R. Priest, A. V. Semenov, A. V. Mazurov, N. E. Nifantiev, T. V. Pochechueva, O. E. Galanina, and N. V. Bovin. Monomeric and multimeric blockers of selectins: comparison of in vitro and in vivo activity. Biochemistry (Moscow) 70:432–439, 2005.
Varki, A. Selectin ligands. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 91:7390–7397, 1994.
Vu-Quoc, L., X. Zhang, and L. Lesburg. A normal force-displacement model for contacting spheres accounting for plastic deformation: force-driven formulation. J. Appl. Mech. 67:363–371, 2000.
Waldron, T. T., and T. A. Springer. Transmission of allostery through the lectin domain in selectin-mediated cell adhesion. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106:85–90, 2009.
Wild, M. K., M. C. Huang, U. Schulze-Horsel, P. A. van der Merwe, and D. Vestweber. Affinity, kinetics, and thermodynamics of E-selectin binding to E-selectin ligand-1. J. Biol. Chem. 276:31602–31612, 2001.
Xia, L., M. Sperandio, T. Yago, J. M. McDaniel, R. D. Cummings, S. Pearson-White, K. Ley, and R. P. McEver. P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1-deficient mice have impaired leukocyte tethering to E-selectin under flow. J. Clin. Invest. 109:939–950, 2002.
Yago, T., J. Wu, C. D. Wey, A. G. Klopocki, C. Zhu, and R. P. McEver. Catch bonds govern adhesion through L-selectin at threshold shear. J. Cell Biol. 166:913–923, 2004.
Zhu, C., M. Long, S. E. Chesla, and P. Bongrand. Measuring receptor/ligand interaction at the single-bond level: experimental and interpretative issues. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 30:305–314, 2002.
Zou, X., V. R. Shinde Patil, N. M. Dagia, L. A. Smith, M. J. Wargo, K. A. Interliggi, C. M. Lloyd, D. F. Tees, B. Walcheck, M. B. Lawrence, and D. J. Goetz. PSGL-1 derived from human neutrophils is a high-efficiency ligand for endothelium-expressed E-selectin under flow. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 289:C415–C424, 2005.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Sasha Klibanov, Michael Lawrence, and Brian Schmidt of the University of Virginia for helpful discussions. The authors also acknowledge the support of the Department of Biomedical Engineering at the University of Virginia, and the National Institutes of Health (EB002185).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Snook, J.H., Guilford, W.H. The Effects of Load on E-Selectin Bond Rupture and Bond Formation. Cel. Mol. Bioeng. 3, 128–138 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-010-0110-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-010-0110-6