Abstract
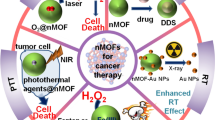
Nanoscale metal organic frameworks (NMOFs) with porous structure and inherent biodegradability are attractive nanomedicine platforms. In addition to conventional particulate NMOFs, two-dimensional (2D) NMOFs are emerging as a unique type of NMOFs which however have been relatively less explored for nanomedicine applications. Herein, 2D-NMOFs composed of Zn2+ and tetrakis(4-carboxyphenyl) porphyrin (TCPP) are fabricated and functionalized with polyethylene glycol (PEG). Compared to their particulate counterpart, such 2D-NMOFs show greatly increased drug loading capacity and enhanced light-triggered singlet oxygen production, promising for chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy (PDT), respectively. Utilizing the porphyrin structure of TCPP, our 2D-NMOFs could be labeled with a diagnostic radioisotope, 99mTc, for single photon emission computer tomography (SPECT) imaging, which reveals efficient tumor homing of those 2D-NMOFs upon intravenous injection. While offering a remarkable synergistic in vivo antitumor effect for the combined chemo-PDT, such 2D-NMOFs show efficient biodegradation and rapid renal clearance. Our work presents the great promise of 2D-NMOFs for nanomedicine applications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
He, C. B.; Liu, D. M.; Lin, W. B. Nanomedicine applications of hybrid nanomaterials built from metal-ligand coordination bonds: Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks and nanoscale coordination polymers. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11079–11108.
Della Rocca, J.; Liu, D. M.; Lin, W. B. Nanoscale metal–organic frameworks for biomedical imaging and drug delivery. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 957–968.
Li, H. L.; Eddaoudi, M.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O. M. Design and synthesis of an exceptionally stable and highly porous metal-organic framework. Nature 1999, 402, 276–279.
Furukawa, H.; Cordova, K. E.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O. M. The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks. Science 2013, 341, 1230444.
Horcajada, P.; Chalati, T.; Serre, C.; Gillet, B.; Sebrie, C.; Baati, T.; Eubank, J. F.; Heurtaux, D.; Clayette, P.; Kreuz, C. et al. Porous metal-organicframework nanoscale carriers as a potential platform for drug delivery and imaging. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 172–178.
Huxford, R. C.; Della Rocca, J.; Lin, W. B. Metal–organic frameworks as potential drug carriers. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 262–268.
Horcajada, P.; Serre, C.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Sebban, M.; Taulelle, F.; Férey, G. Metal–organic frameworks as efficient materials for drug delivery. Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 6120–6124.
McKinlay, A. C.; Morris, R. E.; Horcajada, P.; Férey, G.; Gref, R.; Couvreur, P.; Serre, C. Biomofs: Metal–organic frameworks for biological and medical applications. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6260–6266.
Tafipolsky, M.; Schmid, R. Systematic first principles parameterization of force fields for metal–organic frameworks using a genetic algorithm approach. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 1341–1352.
Morris, W.; Briley, W. E.; Auyeung, E.; Cabezas, M. D.; Mirkin, C. A. Nucleic acid–metal organic framework (MOF) nanoparticle conjugates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7261–7264.
Yang, Y.; Zhu, W. J.; Dong, Z. L.; Chao, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, M. W.; Liu, Z. 1D coordination polymer nanofibers for low–temperature photothermal therapy. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703588.
Yang, Y.; Chao, Y.; Liu, J. J.; Dong, Z. L.; He, W. W.; Zhang, R.; Yang, K.; Chen, M. W.; Liu, Z. Core-shell and co-doped nanoscale metal-organic particles (NMOPs) obtained via post-synthesis cation exchange for multimodal imaging and synergistic thermo-radiotherapy. NPG Asia Mater. 2017, 9, e344.
Yang, Y.; Liu, J. J.; Liang, C.; Feng, L. Z.; Fu, T. T.; Dong, Z. L.; Chao, Y.; Li, Y. G.; Lu, G.; Chen, M. W. et al. Nanoscale metal–organic particles with rapid clearance for magnetic resonance imaging-guided photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2774–2781.
Liu, J. J.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, W. W.; Yi, X.; Dong, Z. L.; Xu, X. N.; Chen, M. W.; Yang, K.; Lu, G.; Jiang, L. X. et al. Nanoscale metal−organic frameworks for combined photodynamic & radiation therapy in cancer treatment. Biomaterials 2016, 97, 1–9.
Lu, K. D.; He, C. B.; Lin, W. B. A chlorin-based nanoscale metal–organic framework for photodynamic therapy of colon cancers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7600–7603.
Park, J.; Jiang, Q.; Feng, D. W.; Mao, L. Q.; Zhou, H. C. Size-controlled synthesis of porphyrinic metal–organic framework and functionalization for targeted photodynamic therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3518–3525.
Yu, B.; Wei, H.; He, Q. J.; Ferreira, C. A.; Kutyreff, C. J.; Ni, D. L.; Rosenkrans, Z. T.; Cheng, L.; Yu, F. Q.; Engle, J. W. et al. Efficient uptake of 177Lu–porphyrin–PEG nanocomplexes by tumor mitochondria for multimodal-imaging-guided combination therapy. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 218–222.
Lebedev, O. I.; Millange, F.; Serre, C.; Van Tendeloo, G.; Férey, G. First direct imaging of giant pores of the metal–organic framework MIL-101. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 6525–6527.
Taylor, K. M. L.; Rieter, W. J.; Lin, W. B. Manganese-based nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for magnetic resonance imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14358–14359.
Taylor-Pashow, K. M. L.; Rocca, J. D.; Xie, Z. G.; Tran, S.; Lin, W. B. Postsynthetic modifications of iron-carboxylate nanoscale metal–organic frameworks for imaging and drug delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 14261–14263.
He, C. B.; Lu, J. Q.; Lin, W. B. Hybrid nanoparticles for combination therapy of cancer. J. Control. Release 2015, 219, 224–236.
Pastorin, G.; Wu, W.; Wieckowski, S.; Briand, J. P.; Kostarelos, K.; Prato, M.; Bianco, A. Double functionalisation of carbon nanotubes for multimodal drug delivery. Chem. Commun. 2006, 11, 1182–1184.
Cao, A. N.; Liu, Z.; Chu, S. S.; Wu, M. H.; Ye, Z. M.; Cai, Z. W.; Chang, Y. L.; Wang, S. F.; Gong, Q. H.; Liu, Y. F. A facile one-step method to produce graphene–CdS quantum dot nanocomposites as promising optoelectronic materials. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 103–106.
Yang, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, G. X.; Sun, X. M.; Lee, S. T.; Liu, Z. Graphene in mice: Ultrahigh in vivo tumor uptake and efficient photothermal therapy. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3318–3323.
Yang, K.; Feng, L. Z.; Shi, X. Z.; Liu, Z. Nano-graphene in biomedicine: Theranostic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 530–547.
Lv, R. T.; Robinson, J. A.; Schaak, R. E.; Sun, D.; Sun, Y. F.; Mallouk, T. E.; Terrones, M. Transition metal dichalcogenides and beyond: Synthesis, properties, and applications of single-and few-layer nanosheets. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 48, 56–64.
Naguib, M.; Mochalin, V. N.; Barsoum, M. W.; Gogotsi, Y. 25th anniversary article: Mxenes: A new family of two–dimensional materials. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 992–1005.
Yin, W. Y.; Yan, L.; Yu, J.; Tian, G.; Zhou, L. J.; Zheng, X. P.; Zhang, X.; Yong, Y.; Li, J.; Gu, Z. J. et al. High-throughput synthesis of single-layer MoS2 nanosheets as a near-infrared photothermal-triggered drug delivery for effective cancer therapy. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6922–6933.
Lai, H. Q.; Zhang, X.; Feng, P. J.; Xie, L. N.; Chen, J. J.; Chen, T. F. Enhancement of antiangiogenic efficacy of iron(II) complex by selenium substitution. Chem. Asian J. 2017, 12, 982–987.
Peng, Y.; Li, Y. S.; Ban, Y. J.; Jin, H.; Jiao, W. M.; Liu, X. L.; Yang, W. S. Metal-organic framework nanosheets as building blocks for molecular sieving membranes. Science 2014, 346, 1356–1359.
Zhao, M. T.; Wang, Y. X.; Ma, Q. L.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ping, J. F.; Zhang, Z. C.; Lu, Q. P.; Yu, Y. F.; Xu, H. et al. Ultrathin 2D metal-organic framework nanosheets. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7372–7378.
Prencipe, G.; Tabakman, S. M.; Welsher, K.; Liu, Z.; Goodwin, A. P.; Zhang, L.; Henry, J.; Dai, H. J. PEG branched polymer for functionalization of nanomaterials with ultralong blood circulation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4783–4787.
Choi, E. Y.; Wray, C. A.; Hu, C. H.; Choe, W. Highly tunable metal–organic frameworks with open metal centers. CrystEngComm 2009, 11, 553–555.
Wang, K. P.; Wang, J.; Fan, J. T.; Lotya, M.; O’Neill, A.; Fox, D.; Feng, Y. Y.; Zhang, X. Y.; Jiang, B. X.; Zhao, Q. Z. et al. Ultrafast saturable absorption of two-dimensional MoS2 nanosheets. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9260–9267.
Feng, J.; Sun, X.; Wu, C. Z.; Peng, L. L.; Lin, C. C.; Hu, S. L.; Yang, J. H.; Xie, Y. Metallic few-layered VS2 ultrathin nanosheets: High twodimensional conductivity for in-plane supercapacitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 17832–17838.
Lu, K. D.; He, C. B.; Lin, W. B. Nanoscale metal-organic framework for highly effective photodynamic therapy of resistant head and neck cancer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16712–16715.
Fan, W. P.; Yung, B.; Huang, P.; Chen, X. Y. Nanotechnology for multimodal synergistic cancer therapy. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 13566–13638.
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Research Programs from Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) of China (No. 2016YFA0201200), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51525203 and 51761145041), Collaborative Innovation Center of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, and a Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development (PAPD) of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2018_2242_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Two-dimensional metal-organic-framework as a unique theranostic nano-platform for nuclear imaging and chemo-photodynamic cancer therapy
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, W., Yang, Y., Jin, Q. et al. Two-dimensional metal-organic-framework as a unique theranostic nano-platform for nuclear imaging and chemo-photodynamic cancer therapy. Nano Res. 12, 1307–1312 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-018-2242-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-018-2242-2