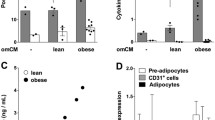
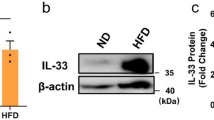
Abstract
Adipose tissue remodeling in obesity involves macrophage infiltration and chronic inflammation. NF-kB-mediated chronic inflammation of the adipose tissue is directly implicated in obesity-associated insulin resistance. We have investigated the effect of growth hormone (GH) on NF-kB activity in preadipocytes (3T3-F442A) and macrophages (J774A.1). Our studies indicate that whereas GH increases NF-kB activity in preadipocytes, it decreases NF-kB activity in macrophages. This differential response of NF-kB activity to GH correlates with the GH-dependent expression of a cadre of NF-kB-activated cytokines in these two cell types. Activation of NF-kB by GH in preadipocytes heightens inflammatory response by stimulating production of multiple cytokines including TNF-α, IL-6, and MCP-1, the mediators of both local and systemic insulin resistance and chemokines that recruit macrophages. Our studies also suggest differential regulation of miR132 and SIRT1 expression as a mechanism underlying the observed variance in GH-dependent NF-kB activity and altered cytokine profile in preadipocytes and macrophages. These findings further our understanding of the complex actions of GH on adipocytes and insulin sensitivity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arkan MC, Hevener AL, Greten FR, Maeda S, Li ZW, Long JM et al (2005) IKK-beta links inflammation to obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nat Med 11:191–198
Bjorntorp P (1974) Size, number and function of adipose tissue cells in human obesity. Horm Metab Res Suppl 4:77–83
Cai D, Yuan M, Frantz DF, Melendez PA, Hansen L, Lee J et al (2005) Local and systemic insulin resistance resulting from hepatic activation of IKK-beta and NF-kappaB. Nat Med 11:183–190
Etherton TD (2000) The biology of somatotropin in adipose tissue growth and nutrient partitioning. J Nutr 130:2623–2625
Fujisaka S, Usui I, Bukhari A, Ikutani M, Oya T, Kanatani Y et al (2009) Regulatory mechanisms for adipose tissue M1 and M2 macrophages in diet-induced obese mice. Diabetes 58:2574–2582
Goldsby RKT, Osborne B, Kuby J. Edited by: Goldsby R. New York: Freeman & Co, a (2002) Mononuclear Phagocytes. Immunology. 5th edition, p 38–19
Hausman DB, DiGirolamo M, Bartness TJ, Hausman GJ, Martin RJ (2001) The biology of white adipocyte proliferation. Obes Rev 2:239–254
Heilbronn LK, Campbell LV (2008) Adipose tissue macrophages, low grade inflammation and insulin resistance in human obesity. Curr Pharm Des 14:1225–1230
Hirsch J, Fried SK, Edens NK, Leibel RL (1989) The fat cell. Med Clin North Am 73:83–96
Ikeda A, Chang KT, Matsumoto Y, Furuhata Y, Nishihara M, Sasaki F et al (1998) Obesity and insulin resistance in human growth hormone transgenic rats. Endocrinology 139:3057–3063
Johansen T, Laurino C, Barreca A, Malmlof K (2005) Reduction of adiposity with prolonged growth hormone treatment in old obese rats: effects on glucose handling and early insulin signaling. Growth Horm IGF Res 15:55–63
Lacasa D, Taleb S, Keophiphath M, Miranville A, Clement K (2007) Macrophage-secreted factors impair human adipogenesis: involvement of proinflammatory state in preadipocytes. Endocrinology 148:868–877
Louveau I, Gondret F (2004) Regulation of development and metabolism of adipose tissue by growth hormone and the insulin-like growth factor system. Domest Anim Endocrinol 27:241–255
Lu C, Kumar PA, Fan Y, Sperling MA, Menon RK (2010) A novel effect of growth hormone on macrophage modulates macrophage-dependent adipocyte differentiation. Endocrinology 151:2189–2199
Lu C, Kumar PA, Sun J, Aggarwal A, Fan Y, Sperling MA et al (2013) Targeted deletion of growth hormone (GH) receptor in macrophage reveals novel osteopontin-mediated effects of GH on glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity in diet-induced obesity. J Biol Chem 288:15725–15735
Lumeng CN, Bodzin JL, Saltiel AR (2007) Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J Clin Invest 117:175–184
Maury E, Brichard SM (2010) Adipokine dysregulation, adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic syndrome. Mol Cell Endocrinol 314:1–16
Murphy AJ, Guyre PM, Pioli PA (2010) Estradiol suppresses NF-kappa B activation through coordinated regulation of let-7a and miR-125b in primary human macrophages. J Immunol 184:5029–5037
Richelsen B (1997) Action of growth hormone in adipose tissue. Horm Res 48(Suppl 5):105–110
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Shoelson SE, Herrero L, Naaz A (2007) Obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Gastroenterology 132:2169–2180
Sica A, Mantovani A (2012) Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest 122:787–795
Strum JC, Johnson JH, Ward J, Xie H, Feild J, Hester A et al (2009) MicroRNA 132 regulates nutritional stress-induced Chemokine production through repression of SirT1. Mol Endocrinol 23:1876–1884
Tai PK, Liao JF, Chen EH, Dietz J, Schwartz J, Carter-Su C (1990) Differential regulation of two glucose transporters by chronic growth hormone treatment of cultured 3 T3-F442A adipose cells. J Biol Chem 265:21828–21834
Victor WH, Ho LMS (2009) Derivation and characterization of murine alternatively activated (M2) macrophages. Methods Mol Biol 531:173–185
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL, Ferrante AW Jr (2003) Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 112:1796–1808
Wellen KE, Hotamisligil GS (2003) Obesity-induced inflammatory changes in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 112:1785–1788
Wentworth JM, Naselli G, Brown WA, Doyle L, Phipson B, Smyth GK et al (2010) Pro-inflammatory CD11c + CD206+ adipose tissue macrophages are associated with insulin resistance in human obesity. Diabetes 59:1648–1656
Yin D, Clarke SD, Peters JL, Etherton TD (1998) Somatotropin-dependent decrease in fatty acid synthase mRNA abundance in 3 T3-F442A adipocytes is the result of a decrease in both gene transcription and mRNA stability. Biochem J 331(Pt 3):815–820
Yuan M, Konstantopoulos N, Lee J, Hansen L, Li ZW, Karin M et al (2001) Reversal of obesity- and diet-induced insulin resistance with salicylates or targeted disruption of ikkbeta. Science 293:1673–1677
Zeyda M, Stulnig TM (2007) Adipose tissue macrophages. Immunol Lett 112:61–67
Zipf WB (1999) Glucose homeostasis in Prader-Willi syndrome and potential implications of growth hormone therapy. Acta Paediatr Suppl 88:115–117
Acknowledgments
Work in the authors’ laboratory was supported by the DST-INSPIRE Faculty Programme, INDIA (PAK) and NIH, USA (RKM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, P.A., Chitra, P.S., Lu, C. et al. Growth hormone (GH) differentially regulates NF-kB activity in preadipocytes and macrophages: implications for GH’s role in adipose tissue homeostasis in obesity. J Physiol Biochem 70, 433–440 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-014-0321-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-014-0321-8