Abstract
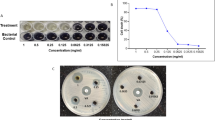
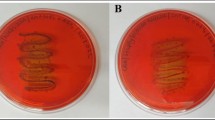
The present study was undertaken with objectives of; a) to investigate and compare Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from two dairies for biofilm formation potential and, b) to compares three common biocides for biofilm eradication efficiencies. Amongst the isolates from commercial dairy, 70 % were strong and/or moderate biofilm former in comparison to 40 % isolates from small scale dairy. All isolates, irrespective of source, exhibited higher susceptibility to biocides in planktonic stage than in biofilm. Antibiofilm efficiencies of three biocides i.e. benzalkonium chloride, sodium hypochlorite and iodophore were determined in terms of their microbial biofilms eradicating concentration (MBEC). Our findings show that the three biocides were ineffective against preformed biofilms at recommended in-use concentrations. Biofilms were the most resistant to benzalkonium chloride and least against iodophore. A trend of decreasing MBECs was observed with extended contact time. The findings of present study warrant for a systematic approach for selecting types and concentrations of biocide for application as antibiofilm agent in food industry.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bridier A, Dubois-Brissonnet F, Greub G, Thomas V, Briandet R (2011) Dynamics of the action of biocides in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55(6):2648–2654
Byun MW, Kim JH, Kim DH, Kim HJ, Jo C (2007) Effects of irradiation and sodium hypochlorite on the micro-organisms attached to a commercial food container. Food Microbiol 24(5):544–548
Campanac C, Pineau L, Payard A, Baziard-Mouysset G, Roques C (2002) Interactions between biocide cationic agents and bacterial biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46(5):1469–1474
Chmielewski RAN, Frank JF (2003) Biofilm formation and control in food processing facilities. Compr Rev Food Sci F 2:23–32
DeQueiroz GA, Day DF (2007) Antimicrobial activity and effectiveness of a combination of sodium hypochlorite and hydrogen peroxide in killing and removing Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms from surfaces. J App Microbiol 103(4):794–802
Dynes JJ, Lawrence JR, Korber DR, Swerhone GD, Leppard GG, Hitchcock AP (2009) Morphological and biochemical changes in Pseudomonas fluorescens biofilms induced by sub-inhibitory exposure to antimicrobial agents. Can J Microbiol 55(2):163–178
Franzetti L, Scarpellini M (2007) Characterisation of Pseudomonas spp. isolated from foods. Ann Microbiol 57(1):39–47
Leung CY, Chan YC, Samaranayake LP, Seneviratne CJ (2012) Biocide resistance of Candida and Escherichia coli biofilms is associated with higher antioxidative capacities. J Hosp Infect 81:79–86
Martin NH, Murphy SC, Ralyea RD, Wiedmann M, Boor KJ (2011) When cheese gets the blues Pseudomonas fluorescens as the causative agent of cheese spoilage. J Dairy Sci 94(6):3176–3183
Pagedar A, Singh J, Batish VK (2010) Surface hydrophobicity, nutritional contents affect Staphylococcus aureus biofilms and temperature influences its survival in preformed biofilms. J Basic Microbiol 50(S1):S98–S106
Pagedar A, Singh J, Batish VK (2011) Efflux mediated adaptive and cross resistance to ciprofloxacin and benzalkonium chloride in Pseudomonas aeruginosa of dairy origin. J Basic Microbiol 51(3):289–295
Pagedar A, Singh J, Batish VK (2012) Adaptation to benzalkonium chloride and ciprofloxacin affects biofilm formation potential, efflux pump and haemolysin activity of Escherichia coli of dairy origin. J Dairy Res 79(4):383–389
Sagripanti JL, Bonifacino A (2000) Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to liquid disinfectants on contaminated surfaces before formation of biofilms. J AOAC Int 83(6):1415–1422
Smith K, Hunter IS (2008) Efficacy of common hospital biocides with biofilms of multi-drug resistant clinical isolates. J Med Microbiol 57:966–973
Stepanovic S, Vukovic D, Dakic I, Savic B, Svabic-Vlahovic MA (2000) modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J Microbiol Methods 40(2):175–179
Toté K, Horemans T, Vanden Berghe D, Maes L, Cos P (2010) Inhibitory effect of biocides on the viable masses and matrices of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(10):3135–3142
van der Horst MA, Schuurmans JM, Smid MC, Koenders BB, Ter Kuile BH (2011) De novo acquisition of resistance to three antibiotics by Escherichia coli. Microb Drug Resist 17:141–147
Van Tassell JA, Martin NH, Murphy SC, Wiedmann M, Boor KJ, Ivy RA (2012) Evaluation of various selective media for the detection of Pseudomonas species in pasteurized milk. J Dairy Sci 95(3):1568–1574
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pagedar, A., Singh, J. Evaluation of antibiofilm effect of benzalkonium chloride, iodophore and sodium hypochlorite against biofilm of Pseudomonas aeruginosa of dairy origin. J Food Sci Technol 52, 5317–5322 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1575-4
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1575-4