Abstract
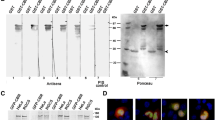
We have developed monoclonal antibodies against the human aurora-A serine/threonine kinase. After immunization of a mouse, a fusion was performed to obtain hybridomas that were selected because they produced immunoglobulin positively reacting against the protein used for immunization. We isolated one particular monoclonal that we named 35C1 using a series of selective assays. The first criteria of the screen for monoclonals was an Elisa (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbant Assay) assay performed in 96-well plates against the purified recombinant histidine-tagged aurora-A. The second was a positive Western blot against the same recombinant protein. The third criteria was a positive western blot against an HeLa cell extract, the selected monoclonal should detect only one protein migrating at 46 kDa (kiloDalton) on SDS (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate)-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Finally, the monoclonal had to bind to duplicated centrosomes and spindle poles in human MCF7 cultured cells by indirect immunofluorescence. At this stage several monoclonals were still positive. We then increased the selectivity by searching for antibodies that were able to cross-react with the mouse aurora-A kinase both by western blot and indirect immunofluorescence. We selected and cloned the 35C1 hybridoma to produce the antibody. Further characterization of the 35C1 antibody revealed that it was able to immunoprecipitate the kinase, that it did not inhibit the aurora-A kinase activity and consequently could be used to measure the aurora-A kinase activity in vivo after immunoprecipitation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nigg EA: Mitotic kinases as regulators of cell division and its checkpoints. Nature reviews. Mol Cell Biol 2: 21-32, 2001
Glover DM, Leibowitz MH, McLean DA, Parry H: Mutations in aurora prevent centrosome separation leading to the formation of monopolar spindles. Cell 81: 95-105, 1995
Bischoff JR, Plowman GD: The Aurora/Ip11p kinase family: Regulators of chromosome segregation and cytokinesis. Trends Cell Biol 9: 454-459, 1999
Giet R, Prigent C: Aurora/Ip11p-related kinases, a new oncogenic family of mitotic serine-threonine kinases. J Cell Sci 112: 3591-3601, 1999
Bischoff JR, Anderson L, Zhu Z, Mossie K, Ng L, Souza B, Schryver B, Flanagan P, Clairvoyant F, Ginther C, Chan CS, Novotny M, Slamon DJ, Plowman GD: A homologue of Drosophila aurora kinase is oncogenic and amplified in human colorectal cancers. EMBO J 17: 3052-3065, 1998
Zhou H, Kuang J, Zhong L, Kuo WL, Gray JW, Sahin A, Brinkley BR, Sen S: Tumour amplified kinase STK15/BTAK induces centrosome amplification, aneuploidy and transformation. Nat Genet 20: 189-193, 1998
Takahashi T, Futamura M, Yoshimi N, Sano J, Katada M, Takagi Y, Kimura M, Yoshioka T, Okano Y, Saji S: Centrosomal kinases, HsAIRK1 and HsAIRK3, are overexpressed in primary colorectal cancers. Jpn J Cancer Res 91: 1007-1014, 2000
Kaitna S, Mendoza M, Jantsch-Plunger V, Glotzer M: Incenp and an aurora-like kinase form a complex essential for chromosome segregation and efficient completion of cytokinesis. Curr Biol 10: 1172-1181, 2000
Adams RR, Wheatley SP, Gouldsworthy AM, Kandels-Lewis SE, Carmena M, Smythe C, Gerloff DL, Earnshaw WC: INCENP binds the Aurora-related kinase AIRK2 and is required to target it to chromosomes, the central spindle and cleavage furrow. Curr Biol 10: 1075-1078, 2000
Severson AF, Hamill DR, Carter JC, Schumacher J, Bowerman B: The aurora-related kinase AIR-2 recruits ZEN-4/CeMKLP1 to the mitotic spindle at metaphase and is required for cytokinesis. Curr Biol 10: 1162-1171, 2000
Wheatley SP, Carvalho A, Vagnarelli P, Earnshaw WC: INCENP is required for proper targeting of Survivin to the centromeres and the anaphase spindle during mitosis. Curr Biol 11: 886-890, 2001
Adams RR, Maiato H, Earnshaw WC, Carmena M: Essential roles of Drosophila inner centromere protein (INCENP) and aurora B in histone H3 phosphorylation, metaphase chromosome alignment, kinetochore disjunction, and chromosome segregation. J Cell Biol 153: 865-880, 2001
Giet R, Glover DM: Drosophila aurora B kinase is required for histone H3 phosphorylation and condensin recruitment during chromosome condensation and to organize the central spindle during cytokinesis. J Cell Biol 152: 669-682, 2001
Adams RR, Eckley DM, Vagnarelli P, Wheatley SP, Gerloff DL, Mackay AM, Svingen PA, Kaufmann SH, Earnshaw WC: Human INCENP colocalizes with the Aurora-B/AIRK2 kinase on chromosomes and is over-expressed in tumour cells. Chromosoma 110: 65-74, 2001
Roghi C, Giet R, Uzbekov R, Morin N, Chartrain I, Le Guellec R, Couturier A, Doree M, Philippe M, Prigent C: The Xenopus protein kinase pEg2 associates with the centrosome in a cell cycle-dependent manner, binds to the spindle microtubules and is involved in bipolar mitotic spindle assembly. J Cell Sci 111: 557-572, 1998
Miyoshi Y, Iwao K, Egawa C, Noguchi S: Association of centrosomal kinase STK15/BTAK mRNA expression with chromosomal instability in human breast cancers. Int J Cancer 92: 370-373, 2001
Sen S, Zhou Z, White RA: A putative serine/threonine kinase encoding gene BTAK on chromosome 20q13 is amplified and overexpressed in human breast cancer cell lines. Oncogene 14: 2195-2200, 1997
Tanaka T, Kimura M, Matsunaga K, Fukada D, Mori H, Okano Y: Centrosomal kinase AIK1 is overexpressed in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Cancer Res 59: 2041-2044, 1999
Sakakura C, Hagiwara A, Yasuoka R, Fujita Y, Nakanishi N, Masuda K, Shimomura K, Nakamura Y, Inazawa J, Abe T, Yamagishi H: Tumour-amplified kinase BTAK is amplified and overexpressed in gastric cancers with possible involvement in aneuploid formation. Br J Cancer 84: 824-831, 2001
Katayama H, Zhou Z, Li Q, Tatsuka M, Sen S: Interaction and feedback regulation between STK15/BTAK/Aurora-A kinase and protein phosphatase 1 through mitotic cell division cycle. J Biol Chem 276: 46219-46224, 2001
Honda K, Mihara H, Kato Y, Yamaguchi A, Tanaka H, Yasuda H, Furukawa K, Urano T: Degradation of human Aurora2 protein kinase by the anaphase-promoting complex-ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Oncogene 19: 2812-2819, 2000
Walter AO, Seghezzi W, Korver W, Sheung J, Lees E: The mitotic serine/threonine kinase Aurora2/AIK is regulated by phosphorylation and degradation. Oncogene 19: 4906-4916, 2000
Arlot-Bonnemains Y, Klotzbucher A, Giet R, Uzbekov R, Bihan R, Prigent C: Identification of a functional destruction box in the Xenopus laevis aurora-A kinase pEg2. FEBS Lett 508: 149-152, 2001
Castro A, Arlot-Bonnemains Y, Vigneron S, Labbe JC, Prigent C, Lorca T: APC/Fizzy-related targets Aurora-A kinase for proteolysis. EMBO Rep, 2002
Giet R, Prigent C: The non-catalytic domain of the Xenopus laevis auroraA kinase localises the protein to the centrosome. J Cell Sci 114: 2095-2104, 2001
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680-685, 1970
Harlow E, Lane D: Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1988, 726 pp
Kimura M, Kotani S, Hattori T, Sumi N, Yoshioka T, Todokoro K, Okano Y: Cell cycle-dependent expression and spindle pole localization of a novel human protein kinase, Aik, related to Aurora of Drosophila and yeast Ip11. J Biol Chem 272: 13766-13771, 1997
Gopalan G, Chan CS, Donovan PJ: A novel mammalian, mitotic spindle-associated kinase is related to yeast and fly chromosome segregation regulators. J Cell Biol 138: 643-656, 1997
Scrittori L, Hans F, Angelov D, Charra M, Prigent C, Dimitrov S: pEg2 aurora-A kinase, histone H3 phosphorylation, and chromosome assembly in Xenopus egg extract. J Biol Chem 276: 30002-30010, 2001
Tanner MM, Tirkkonen M, Kallioniemi A, Holli K, Collins C, Kowbel D, Gray JW, Kallioniemi OP, Isola J: Amplification of chromosomal region 20q13 in invasive breast cancer: Prognostic implications. Clin Cancer Res 1: 1455-1461, 1995
Collins C, Volik S, Kowbel D, Ginzinger D, Ylstra B, Cloutier T, Hawkins T, Predki P, Martin C, Wernick M, Kuo WL, Alberts A, Gray JW: Comprehensive genome sequence analysis of a breast cancer amplicon. Genome Res 11: 1034-1042, 2001
Meraldi P, Honda R, Nigg EA: Aurora-A overexpression reveals tetraploidization as a major route to centrosome amplification in p53-/-cells. EMBO J 21: 483-492, 2002
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cremet, J.Y., Descamps, S., Vérite, F. et al. Preparation and characterization of a human aurora-A kinase monoclonal antibody. Mol Cell Biochem 243, 123–131 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021608012253
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021608012253