Abstract
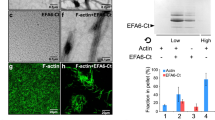
A C-terminal region of human endothelial actin-binding protein-280 (ABP-280 or ABP, non-muscle filamin) was subcloned and efficiently expressed in a mammalian cells system as indicated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting analysis. As predicted by the aminoacid sequence, the fragment, a 79 kD peptide (residues 1671–2361, plus 3.9 kD from an N-terminal fusion peptide included in the expression plasmid), contained the two potential cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) phosphorylation sites (serine 2152 and threonine 2336) predicted to be present in this region of the molecule. Incubation of cells in the presence of cAMP-elevating agents enhanced 32P uptake into the fragment. Site-directed mutagenesis analysis indicated that serine 2152 is the unique substrate in the C-terminal region of ABP for endogenously activated PKA. The functional implications of phosphorylation of this residue, which belongs to a serine-proline motif, are discussed in terms of the role of filamin in cytoskeleton reorganization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gorlin JB, Yamin R, Egam S, Stewart M, Stossel TP, Kwiatkowski DJ, Hartwig JH: Human endothelial actin-binding protein (ABP-280, non-muscle filamin): A molecular leaf spring. J Cell Biol 111: 1089-1105, 1990
Zhuang QQ, Rosenberg S, Lawrence J, Stracher A: Role of actin binding protein phosphorylation in platelet cytoskeleton assembly. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 118: 508-513, 1984
Chen M, Stracher A: In situ phosphorylation of platelet actin-binding protein by cAMP-dependent protein kinase stabilizes it against proteolysis by calpain. J Biol Chem 264: 14282-14289, 1989
Wu MP, Jay D, Stracher A: Existence of multiple phosphorylated forms of human platelet actin binding protein. Cell Mol Biol Res 40: 351-357, 1994
Jay D, Stracher A: Expression in Escherichia coli and phosphorylation with camp-dependent protein kinase of the N-terminal region of human endothelial actin-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 202: 764-771, 1994
Jay D, Stracher A: Expression in Escherichia coli, phosphorylation with camp-dependent protein kinase and proteolysis by calpain of a 71 kD domain of human endothelial actin binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 232: 555-558, 1997
Jay D, García EJ, Lara JE, Medina MA, Ibarra M de la L: Determination of a cAMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation site in the C-terminal region of human endothelial actin-binding protein. Arch Biochem Biophys 377: 80-84, 2000
Tabor S, Richardson CC: A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 1074-1078, 1985
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T: In: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 1989
Harlow E, Lane D: Antibodies. In: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1988, pp 421-470
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680-685, 1970
Lindberg U, Markey F: In: D.E. MacIntyre, J.L. Gordon (eds), Platelets in Biology and Pathology III. Elsevier Science Publishers B.V., Amsterdam, 1987, pp 220-248
Schutkowski M, Bernhardt A, Zhou XZ, Shen M, Reimer U, Rahfeld JU, Lu KP, Fischer G: Role of phosphorylation in determining the backbone dynamics of the serine/threonine-proline motif and Pin1 substrate recognition. Biochemistry 37: 5566-5575, 1998
Gothel SF, Marahiel MA: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerases, a superfamily of ubiquitous folding catalysts. Cell Mol Life Sci 55: 423-436, 1999
Gustke N, Steiner B, Mandelkow EM, Biernat J, Meyer HE, Goedert M, Mandelkow E: The Alzheimer-like phosphorylation of tau protein reduces microtubule binding and involves Ser-Pro and Thr-Pro motifs. FEBS Lett 307: 199-205, 1992
Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E: Tau as a marker for Alzheimer's disease. Trends Biochem Sci 18: 480-483, 1993
Mandelkow EM, Schweers O, Drewes G, Biernat J, Gustke N, Trinczek B, Mandelkow E: Structure, microtubule interactions, and phosphorylation of tau protein. Ann NY Acad Sci 777: 96-106, 1996
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jay, D., García, E.J. & de la Luz Ibarra, M. In situ determination of a PKA phosphorylation site in the C-terminal region of filamin. Mol Cell Biochem 260, 49–53 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MCBI.0000026052.76418.55
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MCBI.0000026052.76418.55