Abstract
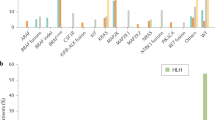
FEMALES heterozygous for the X-linked glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) locus have two populations of cells, each expressing a single phenotype corresponding to one or the other of the two alleles1–3. Where subjects are heterozygous for the A and B electrophoretic variants of G6PD4, one cell population will show only the A electrophoretic variant and the other only the B. The study of these variants has been used to throw light on the origin of certain tumours. Thus, uterine leiomyomas from Negro females heterozygous for G6PD variants A and B are of only one phenotype, although the adjacent uninvolved tissue shows both phenotypes5, which is consistent with a clonal or unicellular origin for this tumour. Similarly, chronic granulocytic leukaemia6 is probably of clonal origin, like the metastatic lesions from one patient with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia7. On the other hand, studies of metastatic lesions from a colonic malignancy7 and epider-moid carcinomas of the cervix have revealed8 the presence of both G6PD phenotypes, which implies a multiclonal origin.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davidson, R. G., Nitowsky, H. N., and Childs, B., Proc. US Nat. Acad. Sci., 50, 481 (1963).
Beutler, E., and Baluda, M. C., Lancet, i, 189 (1964).
DeMars, R., and Nance, W. E., Wistar Inst. Symp. Monog., No. 1, 35 (Wistar Institute Press, Philadelphia, 1964).
Boyer, S. H., Porter, I. H., and Weilbacher, R. G., Proc. US Nat. Acad. Sci., 48, 1868 (1962).
Linder, D., and Gartler, S. M., Science, 150, 67 (1965).
Fialkow, P. J., Gartler, S. M., and Yoshida, A., Proc. US Nat. Acad. Sci., 58, 1468 (1967).
Beutler, E., Collins, Z., and Irwin, L. E., New Engl. J. Med., 276, 389 (1967).
Park, I., and Jones, H. W., Amer J. Obstet. Gynec., 102, 106 (1968).
Allen, A. C., The Skin, a Clinicopathological Treatise, 775 (Grune and Stratton, New York, 1967).
Williams, M. G., Howatson, A. F., and Almeida, J. D., Nature, 189, 895 (1961).
Lewis, G. M., and Wheeler, C. E., Practical Dermatology, 520 (Saunders, Philadelphia, London, 1967).
Fildes, R. A., and Parr, C. W., Nature, 200, 890 (1963).
Nance, W. E., Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol., 29, 415 (1964).
Gandini, E., Gartler, S. M., Angiuni, N., Argiolas, N., and Dell'Acqua, G., Proc. US Nat. Acad. Sci., 61, 945 (1968).
Ohkawara, A., Halperin, J., Barber, P., and Halperin, K. M., Arch. Dermatol., 95, 412 (1967).
Ohno, S., Payne, H. W., Morrison, M., and Beutler, E., Science, 153, 1015 (1966).
Fialkow, P. J., Klein, G., Gartler, S. M., and Clifford, P., Lancet, i, 348 (1970).
Stanley, N. F., Lancet, i, 961 (1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MURRAY, R., HOBBS, J. & PAYNE, B. Possible Clonal Origin of Common Warts (Verruca vulgaris). Nature 232, 51–52 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1038/232051a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/232051a0
This article is cited by
-
Keratin polypeptide modifications induced by human papilloma viruses (HPV)
Archives of Dermatological Research (1981)
-
Propagation of human wart virus in tissue culture
Nature (1975)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.