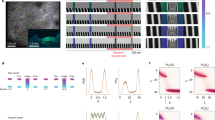
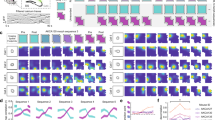
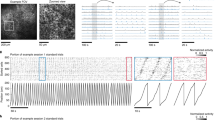
Abstract
The hippocampus is widely believed to be involved in the storage or consolidation of long-term memories1,2,3,4. Several reports have shown short-term changes in single hippocampal unit activity during memory and plasticity experiments5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12, but there has been no experimental demonstration of long-term persistent changes in neuronal activity in any region except primary cortical areas13,14,15,16. Here we report that, in rats repeatedly exposed to two differently shaped environments, the hippocampal-place-cell representations of those environments gradually and incrementally diverge; this divergence is specific to environmental shape, occurs independently of explicit reward, persists for periods of at least one month, and transfers to new enclosures of the same shape. These results indicate that place cells may be a neural substrate for long-term incidental learning, and demonstrate the long-term stability of an experience-dependent firing pattern in the hippocampal formation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scoville, W. B. & Milner, B. Loss of recent memory after bilateral hippocampal lesions. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat. 20, 11–21 (1957).
O'Keefe, J. & Nadel, L. The Hippocampus as a Cognitive Map (Clarendon, Oxford, 1978).
Squire, L. R. Memory and Brain (Oxfrord Univ. Press, New York, 1987).
Cohen, N. J. & Eichenbaum, H. Memory, Amnesia and the Hippocampal System (MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1993).
Bostock, E., Muller, R. U. & Kubie, J. L. Experience-dependent modifications of hippocampal place cell firing. Hippocampus 1, 193–205 (1991).
Kentros, C. et al. Abolition of long-term stability of new hippocampal place cell maps by NMDA receptor blockade. Science 280, 2121–2126 (1998).
Muller, R. U. & Kubie, J. L. The effects of changes in the environment on the spatial firing of hippocampal complex-spike cells. J. Neurosci. 7, 1951–1968 (1987).
Wilson, M. A. & McNaughton, B. L. Dynamics of the hippocampal ensemble code for space. Science 261, 1055–1058 (1993).
O'Keefe, J. & Speakman, A. Single unit activity in the rat hippocampus during a spatial memory task. Exp. Brain Res. 68, 1–27 (1987).
Mehta, M. R., Barnes, C. A. & McNaughton, B. L. Experience-dependent, asymmetric expansion of hippocampal place fields. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 8918–8921 (1997).
Mehta, M. R., Quirk, M. C. & Wilson, M. A. Experience-dependent asymmetric fields. Neuron 25, 707–715 (2000).
Jeffery, K. J. in Neuronal Mechanisms of Memory Formation (ed. Holscher, C.) 100–121 (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 2000).
Merzenich, M. M. et al. Topographic reorganization of somatosensory cortical areas 3b and 1 in adult monkeys following restricted deafferentiation. Neuroscience 8, 33–55 (1983).
Clark, S. A., Allard, T., Jenkins, W. J. & Merzenich, M. M. Receptive fields in the body-surface map in adult cortex defined by temporally correlated inputs. Nature 332, 444–445 (1988).
Wang, X., Merzenich, M. M., Sameshina, K. & Jenkins, W. M. Remodelling of hand representation in adult cortex determined by timing of tactile stimulation. Nature 378, 71–75 (1995).
Weinberger, N. M., Javid, R. & Lepan, B. Long-term retention of learning-induced receptive-field plasticity in the auditory cortex. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 2394–2398 (1993).
O'Keefe, J., Nadel, L., Keightley, S. & Kill, D. Fornix lesions selectively abolish place learning in the rat. Exp. Neurol. 48, 152–166 (1975).
Morris, R. G., Garrud, P., Rawlins, J. N. & O'Keefe, J. Place navigation impaired in rats with hippocampal lesions. Nature 297, 681–683 (1982).
Sutherland, R. J., Kolb, B. & Whishaw, I. Spatial mapping: definitive disruption by hippocampal or medial frontal cortical damage in the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 31, 271–276 (1982).
Barnes, C. A. Spatial learning and memory processes: the search for their neurobiological mechanisms in the rat. Trends Neurosci. 11, 163–169 (1988).
O'Keefe, J. & Burgess, N. Geometric determinants of the place fields of hippocampal neurons. Nature 381, 425–428 (1996).
Hartley, T., Burgess, N., Lever, C., Cacucci, F. & O'Keefe, J. Modeling place fields in terms of the cortical inputs to the hippocampus. Hippocampus 10, 369–379 (2000).
Quirk, G. J., Muller, R. U., Kubie, J. L. & Ranck, J. B. The positional firing properties of medial entorhinal neurons: description and comparison with hippocampal place cells. J. Neurosci. 12, 1945–1963 (1992).
Sharp, P. E. Subicular cells generate similar spatial firing patterns in two geometrically and visually distinctive environments: comparison with hippocampal place cells. Behav. Brain. Res. 85, 71–92 (1997).
Wood, E. R., Dudchenko, P. A. & Eichenbaum, H. The global record of memory in hippocampal neuronal activity. Nature 397, 613–616 (1999).
Frank, L. M., Brown, E. M. & Wilson, M. Trajectory encoding in the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex. Neuron 27, 169–178 (2000).
Tanila, H., Shapiro, M., Gallagher, M. & Eichenbaum, H. Brain aging: Changes in the nature of information coding by the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 17, 5155–5166 (1997).
Hollup, S. A., Molden, S., Donnett, J. G., Moser, M. B. & Moser, E. I. Accumulation of hippocampal place fields at the goal location in an annular watermaze task. J. Neurosci. 21, 1635–1644 (2001).
O'Keefe, J. & Recce, M. L. Phase relationship between hippocampal place units and the EEG theta rhythm. Hippocampus 3, 317–330 (1993).
Jeffery, K. J. & O'Keefe, J. Learned interaction of visual and idiothetic cues in the control of place field orientation. Exp. Brain Res. 127, 151–161 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Huxter, T. Hartley and K. Jeffery for discussion, S. Burton for reviewing the manuscript, C. Parker for technical assistance, and J. Donnett for the recording system. This work was supported by a Medical Research Council (UK) programme grant to J.O.K., MRC Advanced Studentships to C.L. and T.W., a Wellcome Trust Studentship to F.C., and Royal Society and MRC Senior Fellowships to N.B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lever, C., Wills, T., Cacucci, F. et al. Long-term plasticity in hippocampal place-cell representation of environmental geometry. Nature 416, 90–94 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/416090a
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/416090a
This article is cited by
-
Subicular neurons encode concave and convex geometries
Nature (2024)
-
Heterosynaptic plasticity-induced modulation of synapses
The Journal of Physiological Sciences (2023)
-
Sensory cortex plasticity supports auditory social learning
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Experience-dependent changes in hippocampal spatial activity and hippocampal circuit function are disrupted in a rat model of Fragile X Syndrome
Molecular Autism (2022)
-
Neural circuit dynamics of drug-context associative learning in the mouse hippocampus
Nature Communications (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.