Abstract
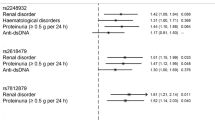
We targeted LYN, a src-tyosine kinase involved in B-cell activation, in case–control association studies using populations of European-American, African-American and Korean subjects. Our combined European-derived population, consisting of 2463 independent cases and 3131 unrelated controls, shows significant association with rs6983130 in a female-only analysis with 2254 cases and 2228 controls (P=1.1 × 10−4, odds ratio (OR)=0.81 (95% confidence interval: 0.73–0.90)). This single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) is located in the 5′ untranslated region within the first intron near the transcription initiation site of LYN. In addition, SNPs upstream of the first exon also show weak and sporadic association in subsets of the total European-American population. Multivariate logistic regression analysis implicates rs6983130 as a protective factor for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) susceptibility when anti-dsDNA, anti-chromatin, anti-52 kDa Ro or anti-Sm autoantibody status were used as covariates. Subset analysis of the European-American female cases by American College of Rheumatology classification criteria shows a reduction in the risk of hematological disorder with rs6983130 compared with cases without hematological disorders (P=1.5 × 10−3, OR=0.75 (95% CI: 0.62−0.89)). None of the 90 SNPs tested show significant association with SLE in the African American or Korean populations. These results support an association of LYN with European-derived individuals with SLE, especially within autoantibody or clinical subsets.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lahita RG . Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, 4th edn. Academic Press: New York, 2004.
Fessel WJ . Systemic lupus erythematosus in the community. Incidence, prevalence, outcome, and first symptoms; the high prevalence in black women. Arch Intern Med 1974; 134: 1027–1035.
Siegel M, Lee S . The epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum 1973; 3: 1–54.
Hart HH, Grigor RR, Caughey DE . Ethnic difference in the prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rhuem Dis 1983; 42: 529–532.
Michet CJ, Mc Kenna CH, Elveback CR, Kaslow RA, Kurland LT . Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus and other connective tissue diseases in Rochester, Minnesota 1950 through 1979. Mayo Clin Proc 1985; 60: 105–113.
Serdula MK, Rhoads GG . Frequency of systemic lupus erythematosus in different ethnic groups in Hawaii. Arthritis Rheum 1979; 22: 328–333.
Harley JB, Kelly JA, Kaufman KM . Unraveling the genetics of systemic lupus erythematosus. Springer Semin Immunopathol 2006; 28: 119–130.
Sestak AL, Nath SK, Harley JB . Genetics of systemic lupus erythematosus: how far have we come? Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2005; 31: 223–244 v.
Nath SK, Kilpatrick J, Harley JB . Genetics of human systemic lupus erythematosus: the emerging picture. Curr Opin Immunol 2004; 16: 794–800.
Hom G, Graham RR, Modrek B, Taylor KE, Ortmann W, Garnier S et al. Association of systemic lupus erythematosus with C8orf13-BLK and ITGAM-ITGAX. N Engl J Med 2008.
Kozyrev SV, Abelson AK, Wojcik J, Zaghlool A, Linga Reddy MV, Sanchez E et al. Functional variants in the B-cell gene BANK1 are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 211–216.
Liossis SN, Solomou EE, Dimopoulos MA, Panayiotidis P, Mavrikakis MM, Sfikakis PP . B-cell kinase Lyn deficiency in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Investig Med 2001; 49: 157–165.
Flores-Borja F, Kabouridis PS, Jury EC, Isenberg DA, Mageed RA . Decreased Lyn expression and translocation to lipid raft signaling domains in B lymphocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2005; 52: 3955–3965.
Hibbs ML, Tarlinton DM, Armes J, Grail D, Hodgson G, Maglitto R et al. Multiple defects in the immune system of Lyn-deficient mice, culminating in autoimmune disease. Cell 1995; 83: 301–311.
Chan VW, Lowell CA, DeFranco AL . Defective negative regulation of antigen receptor signaling in Lyn-deficient B lymphocytes. Curr Biol 1998; 8: 545–553.
Nishizumi H, Taniuchi I, Yamanashi Y, Kitamura D, Ilic D, Mori S et al. Impaired proliferation of peripheral B cells and indication of autoimmune disease in Lyn-deficient mice. Immunity 1995; 3: 549–560.
DeFranco AL, Chan VW, Lowell CA . Positive and negative roles of the tyrosine kinase Lyn in B cell function. Semin Immunol 1998; 10: 299–307.
Sillman AL, Monroe JG . Surface IgM-stimulated proliferation, inositol phospholipid hydrolysis, Ca2+ flux, and tyrosine phosphorylation are not altered in B cells from p59fyn-1-mice. J Leukoc Biol 1994; 56: 812–816.
Texido G, Su IH, Mecklenbrauker I, Saijo K, Malek SN, Desiderio S et al. The B-cell-specific Src-family kinase Blk is dispensable for B-cell development and activation. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20: 1227–1233.
Wang J, Koizumi T, Watanabe T . Altered antigen receptor signaling and impaired Fas-mediated apoptosis of B cells in Lyn-deficient mice. J Exp Med 1996; 184: 831–838.
Cornall RJ, Cyster JG, Hibbs ML, Dunn AR, Otipoby KL, Clark EA et al. Polygenic autoimmune traits: Lyn, CD22, and SHP-1 are limiting elements of a biochemical pathway regulating BCR signaling and selection. Immunity 1998; 8: 497–508.
Hibbs ML, Harder KW, Armes J, Kountouri N, Quilici C, Casagranda F et al. Sustained activation of Lyn tyrosine kinase in vivo leads to autoimmunity. J Exp Med 2002; 196: 1593–1604.
Dorner T, Lipsky PE . Signalling pathways in B cells: implications for autoimmunity. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2006; 305: 213–240.
Harley JB, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Criswell LA, Jacob CO, Kimberly RP, Moser KL et al. Genome-wide association scan in women with systemic lupus erythematosus identifies susceptibility variants in ITGAM, PXK, KIAA1542 and other loci. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 204–210.
Graham RR, Cotsapas C, Davies L, Hackett R, Lessard CJ, Leon JM et al. Genetic variants near TNFAIP3 on 6q23 are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 1059–1061.
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF et al. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 1982; 25: 1271–1277.
Hochberg MC, Wallace DJ HBH . The epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Anonymous (ed.) Dubois, Äô Lupus Erythematosus. Williams and Wilkins: Baltimore, 1997, pp 49–65.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Price AL, Patterson NJ, Plenge RM, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA, Reich D . Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 904–909.
Acknowledgements
We thank the participants, both patients and controls, who graciously agreed to take part in these studies by donating samples to the various collections, including the Lupus Family Registry and Repository (http://lupus.omrf.org), PROFILE, BIOLUPUS and many other individual or multicenter collaborator initiated collections. We also thank the recruitment and technical teams at each of the sample procurement sites for their important contributions. We thank the Wake Forest University Health Sciences Center for Public Health Genomics for support of the data analysis efforts of our Wake Forest University collaborators. Finally, we thank the various funding sources as outlined on the title page for their continued support for the collection of samples and the conduct of this research.
Members of BIOLUPUS who have provided samples to this study are: Peter Junker, Ann Voss and Helle Laustrup (Odense, Denmark), Bernard Lawerys and Fredric Houssieau (Louvain, Belgium), Carlos Vasconcelos and Berta Martins Da Silva (Porto, Portugal), Carmen Gutierrez and Ana Suárez (Oviedo, Spain), Torsten Witte (Hannover, Germany), Sandra D'Alfonso, Sergio Migliaresi, Mauro Galeazzi and Gian Domenico Sebastiani (Novara, Naples, Siena and Rome, Italy), Bernardo Pons-Estel and the members of GENLES (Rosario, Argentina) and Emoke Endreffy (Szeged, Hungary). Peter K Gregersen from the Feinstein Institute of Medical Research and Jorge R Oksenberg from the University of California at San Francisco graciously provided controls used in this study. Members of PROFILE who have provided samples to this study are Graciela S Alarcón, Elizabeth E Brown, Robert P Kimberly, Jeffery C Edberg and Gerald McGwin, Jr (University of Alabama Birmingham, Birmingham, AL, USA), Rosalind Ramsey-Goldman (Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, IL, USA), John D Reveille (University Texas Health Science Center, Houston, TX, USA), Luis M Vilá (University of Puerto Rico Medical Sciences Campus, San Juan, PR, USA) and Michelle A Petri (Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, MD, USA). This project was funded by National Institutes of Health RR020143 (JMG and JBH), RR015577 (JMG, JBH, JAJ), NIAID-HHSN266200500026C (JMG and JAJ), AI031584 (JBH, JMG, JAJ), AR053483 (JMG, SKN and JAJ), AR48940 (JBH, JAJ), AI063622 (SKN), Kirkland Scholar awards (JBH and JAJ), AR049084 (SKN, JBH, RPK, RRG, JDR, MAP, LMV, GSA, JCE, GMcG Jr), AR42460 (JBH), AR12253 (JBH), AR62277 (JBH), AI24717 (JBH), AI063274 (PMG), AR052125 (PMG), AR043247 (KLM), DEO15223 (JBH), Alliance for Lupus Research (JBH), the US Department of Veterans Affairs (JBH), Swedish Research Council (MEAR), the Korea Healthcare technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, Republic of Korea. (A010252, A080588) (SCB), the Torsten & Ragnar Söderbergs Foundation (MEAR), the Swedish Foundation Against Rheumatism (MEAR), the Gustaf Vth-80th-Year Foundation (MEAR), Plan Nacional de I+D, Spain (SAF06-00398) (JM), the Junta de Andalucía, grupo CTS-180 (JM) and OHRS award # HR08-037 from the Oklahoma Center for the Advancement of Science & Technology (JMG). Dr Harley has received consulting fees, speaking fees and/or director's fees from Bio-Rad Laboratories, Merck, UCB Inc., ImmunoVision Inc., IVAX Diagnostics and JK Autoimmunity and owns stock or stock options in IVAX Diagnostics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Genes and Immunity website (http://www.nature.com/gene)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, R., Vidal, G., Kelly, J. et al. Genetic associations of LYN with systemic lupus erythematosus. Genes Immun 10, 397–403 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2009.19
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2009.19
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition as an Emerging Therapy in Systemic Autoimmune Disease
Drugs (2021)
-
Altered B cell signalling in autoimmunity
Nature Reviews Immunology (2017)
-
BLK pathway-associated rs13277113 GA genotype is more frequent in SLE patients and associated with low gene expression and increased flares
Clinical Rheumatology (2017)
-
Intracellular B Lymphocyte Signalling and the Regulation of Humoral Immunity and Autoimmunity
Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology (2017)
-
Genetics and pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis
Nature Reviews Nephrology (2015)