Abstract
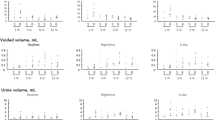
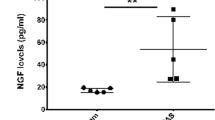
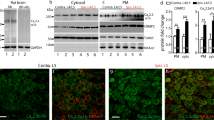
We investigated the effects of replication-defective herpes simplex virus (HSV) vector expression of interleukin-4 (IL-4) on bladder overactivity and nociception. HSV vector expressing murine interleukin-4 (S4IL4) or the control vector expressing β-galactosidase (SHZ) were injected to the rat bladder wall. At 1 week after viral injection, in cystometry performed under urethane anesthesia, the S4IL4-treated group did not show the intercontraction intervals reduction during intravesical administration of 10 nM resiniferatoxin (RTx). At 2 weeks after viral injection, behavioral studies were performed on vector-injected animals in an awakened state. Freezing behavior induced by 3 μM RTx, administered for 1 min into the bladder, was significantly suppressed in the S4IL4 group compared with the SHZ group. Murine IL-4 levels examined by ELISA were significantly increased in bladder and bladder afferent dorsal root ganglia at 2 weeks after viral injection. The expression of IL-1β and IL-2 and bladder inflammatory responses were significantly suppressed in the RTx-irritated bladder of S4IL4-injected rats. These results indicate that HSV vector-mediated interleukin-4 expression in the bladder and bladder afferent pathways reduces the inflammatory response, bladder overactivity and nociceptive behavior induced by bladder irritation in the rat model. Therefore, IL-4 gene therapy could be a new strategy for treating urinary frequency and/or bladder pain.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keay S . Cell signaling in interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Cell Signal 2008; 20: 2174.
Erickson DR, Xie SX, Bpavanandan VP, Wheeler MA, Hurst RE, Demers LM et al. A comparison of multiple urine markers for interstitial cystitis. J Urol 2002; 167: 2461.
Peters KM, Diokno AC, Steinert BW . Preliminary study on urinary cytokine levels in interstitial cystitis: does intravesical bacille Calmette-Guerin treat interstitial cystitis by altering the immune profile in the bladder? Urology 1999; 54: 450.
Ogawa T, Homma T, Igawa Y, Seki S, Ishizuka O, Imamura T et al. CXCR3 binding chemokine and TNFSF14 over expression in bladder urothelium of patients with ulcerative interstitial cystitis. J Urol 2010; 183: 1206.
te Velde AA, Hujijbens RJ, Heije K, de Vries JE, Figdor CG . Interleukin-4 (IL-4) inhibits secretion of IL-1 beta, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and IL-6 by human monocytes. Blood 1990; 76: 1392.
Mijatovic T, Kruys V, Caput D, Defrance P, Huez G . Interleukin-4 and -13 inhibit tumor necrosis factor –alpha mRNA translational activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced mouse macrophages. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 14394.
Gautam S, Tebo JM, Hamilton TA . IL-4 suppresses cytokine gene expression induced by IFN-gamma and/or IL-2 in murine peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol 1992; 148: 1725.
Ueda T, Tamaki M, Ogawa O, Yamauchi T, Yoshimura N . Improvement of interstitial cystitis symptoms and problems that developed during treatment with oral IPD-1151T. J Urol 2000; 164: 1917.
Bouchelouche K, Andresen L, Alvarez S, Nordling J, Nielsen OH, Bouchelouche P . Interleukin-4 and 13 induce the expression and release of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, interleukin-6 and stem cell factor from human detrusor smooth muscle cells: synergy with interleukin 1β and tumor necrosis factor-α. J Urol 2006; 175: 760.
Fink DJ, DeLuca NA, Goins WF, Glorioso JC . Gene transfer to neurons using herpes simplex virus-based vectors. Annu Rev Neurosci 1996; 19: 265.
Glorioso JC, Fink DJ . Herpes vector-mediated gene transfer in the treatment of chronic pain. Mol Ther 2009; 17: 13.
Goss JR, Mata M, Goins WF, Wu HH, Glorioso JC, Fink DJ . Antinociceptive effect of a genomic herpes simplex virus-based vector expressing human proenkephalin in rat dorsal root ganglion. Gene Therapy 2001; 8: 551.
Hao S, Mata M, Wolfe D, Huang S, Glorioso JC, Fink DJ . HSV-mediated gene transfer of the glial cell derived neurotrophic factor (GNDF) provides an anti-allodynic effect in neuropathic pain. Mol Ther 2003; 8: 367.
Hao S, Mata M, Glorioso JC, Fink DJ . HSV-mediated expression of interleukin-4 in dorsal root ganglion neurons reduces neuropathic pain. Mol Pain 2006; 2: 6.
Yokoyama H, Sasaki K, Franks ME, Goins WF, Goss JR, de Groat WC et al. Gene therapy for bladder overactivity and nociception with herpes simplex virus vectors expressing preproenkephalin. Hum Gene Ther 2009; 20: 63.
Miyazato M, Sugaya K, Saito S, Chancellor MB, Goins WF, Goss JR et al. Suppression of detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia by herpes simplex virus vector mediated gene delivery of glutamic acid decarboxylase in spinal cord injured rats. J Urol 2010; 184: 1204.
Sasaki K, Chancellor MB, Goins WF, Phelan MW, Glorioso JC, de Groat WC et al. Gene therapy using replication-defective herpes simplex expressing nerve growth factor in a rat model of diabetic cystopathy. Diabetes 2004; 53: 2723.
Goins WF, Yoshimura N, Pheian MW, Yokoyama T, Fraser MO, Ozawa H et al. Herpes simplex virus mediated nerve growth factor expression in bladder and afferent neurons: potential treatment for diabetic bladder dysfunction. J Urol 2001; 165: 1748.
Saitoh C, Chancellor MB, de Groat WC, Yoshimura N . Effects of intravesical instillation of resiniferatoxin on bladder function and nociceptive behavior in freely moving, conscious rats. J Urol 2008; 179: 359.
Lecci A, Gliuliani S, Lazzeri M, Benaim G, Turini D, Maggi CA . The behavioral response induced by intravesical instillation of capsaicin rats is mediated by pudental urethral sensory fibers. Life Sci 1994; 55: 429.
Fraser MO, Levelle JP, Sacks MS, Chancellor MB . The future of bladder control- intravesical drug delivery, a pinch of pepper, and gene therapy. Rev Urol 2002; 4: 1.
Kuklin NA, Daheshia M, Marconi PC, Krisky DM, Rouse RJ, Glorioso JC et al. Modulation of mucosal and systemic immunity by enteric administration of nonreplicating herpes simplex virus expressing cytokines. Virology 1998; 240: 245.
Ghiasi H, Osorio Y, Perng G, Nesburn AB, Wechsler SL . Recombinant herpes simplex virus type 1 expressing murine interleukin-4 is less virulent than wild-tiype virus in mice. J Virol 2001; 75: 9029.
Mott KR, Wechsler SL, Ghiasi H . Ocular infection of mice with an avirulent recombinant HSV-1 strain generates virulent recombinants in vivo. Mol Vis 2010; 16: 2153.
Poliani PL, Brok H, Furlan R, Ruffini F, Bergami A, Desina G et al. Delivery to the central nervous system of a nonreplicative herpes simplex type 1 vector engineered with the interleukin 4 gene protects rhesus monkeys from hyperacute autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Hum Gene Ther 2001; 12: 905.
Furlan R, Poliani PL, Galbiati F, Bergami A, Grimaldi LM, Comi G et al. Central nervous system delivery of interleukin 4 by a nonreplicative herpes simplex type 1 viral vector ameliorates autoimmune demyelination. Hum Gene Ther 1998; 9: 2605–2617.
Furlan R, Poliani PL, Marconi PC, Bergami A, Ruffini F, Adorini L et al. Central nervous system gene therapy with interleukin-4 inhibits progression of ongoing relapsing- remitting autoimmune encephalomyelitis in Biozzi AB/H mice. Gene Therapy 2001; 8: 13.
Broberg EK, Salmi AA, Hukkanen V . IL-4 is the key regulator in herpes simplex virus-based gene therapy BALB/c experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neurosci Lett 2004; 364: 173.
Broberg E, Setala N, Roytta M, Salmi A, Erälinna JP, He B et al. Expression of interleukin-4 but not of interleukin-10 from a replicative herpes simplex virus type 1 viral vector precludes experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Gene Therapy 2001; 8: 769.
Frazer ME, Hughes JE, Mastrangelo MA, Tibbens JL, Federoff HJ, Bowers WJ . Reduced pathology and impreoved behavioral performance in Alzheimer’s disease mice vaccinated with HSV amplicons expressing amyloid-β and interleukin-4. Mol Ther 2008; 16: 845.
Watkins LR, Milligan ED, Maier SF . Glial activation: a driving force for pathological pain. Trends Neurosci 2001; 24: 450.
Sweitzer SM, Colburn RW, Rutkowski M, DeLeo JA . Acute peripheral inflammation induces moderate glial activation and spinal IL-1 beta expression that correlates with pain behavior in the rat. Brain Res 1999; 829: 209.
Watkins LR, Milligan ED, Maier SF . Spinal cord glia: new players in pain. Pain 2001; 93: 201.
Schafer M . Cytokines and peripheral analgesia. Adv Exp Med Biol 2003; 521: 40.
Benarroch EE . Central neuron-glia interactions and neuropathic pain: overview of recent concepts and clinical implications. Neurology 2010; 75: 273.
Bradesi S . Role of spinal cord glia in the central processing of peripheral pain perception. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2010; 22: 499.
Sommer C, Petrausch S, Lindenlaub T, Toyka KV . Neutralizing antibodies to interleukin 1- receptor reduce pain-associated behavior in mice with experimental neuropathy. Neurosci Lett 1999; 270: 25.
Vannier E, Miller LC, Dinarello CA . Coordinated anti-inflammatory effects of interleukin 4: interleukin 4 suppresses interleukin 1 production but up-regulates gene expression and synthesis of interleukin 1 receptor antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Aci USA 1992; 89: 4076.
Hart PH, Vitti GF, Burgess DR, Whitty GA, Piccoli DS, Hamilton JA . Potential anti-inflammatory effects of interleukin 4: suppression of human monocyte tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1, and prostaglandin E2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1989; 86: 3803.
Cunha FQ, Poole S, Lorenzetti BB, Veiga FH, Ferreira SH . Cytokine-mediated inflammatory hyperalgesia limited by interleukin-4. Br J Pharmacol 1999; 126: 45.
Vale ML, Marques JB, Moreira CA, Rocha FA, Ferreira SH, Poole S et al. Antinociceptive effects of interleukin-4, -10, and -13 on the writhing response in mice and zymosan-induced knee joint incapacitation in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2003; 304: 102.
Shepard AA, DeLuca NA . A second-site revertant of a defective herpes simplex virus ICP4 protein with restored regulatory activities and impaired DNA-binding properties. J Virol 1991; 65: 787.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by National Institutes of Health grants (DK057267, DK088836 and P01 DK044935) and the Samuel Wilan Research Fund for Interstitial Cystitis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oguchi, T., Funahashi, Y., Yokoyama, H. et al. Effect of herpes simplex virus vector-mediated interleukin-4 gene therapy on bladder overactivity and nociception. Gene Ther 20, 194–200 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2012.24
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2012.24