Abstract
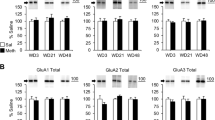
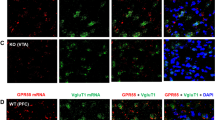
Activation of AMPA receptors (AMPARs) in the nucleus accumbens is necessary for the reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior, an animal model of drug craving and relapse. AMPARs are tetrameric protein complexes that consist of GluA1–4 subunits, of which GluA2 imparts calcium permeability. Adenosine deaminase acting on RNA 2 (ADAR2) is a nuclear enzyme that is essential for editing GluA2 pre-mRNA at Q/R site 607. Unedited GluA2(Q) subunits form calcium-permeable AMPARs (CP-AMPARs), whereas edited GluA2(R) subunits form calcium-impermeable channels (CI-AMPARs). Emerging evidence suggests that the reinstatement of cocaine seeking is associated with increased synaptic expression of CP-AMPARs in the nucleus accumbens. However, the role of GluA2 Q/R site editing and ADAR2 in cocaine seeking is unclear. In the present study, we investigated the effects of forced cocaine abstinence on GluA2 Q/R site editing and ADAR2 expression in the nucleus accumbens. Our results demonstrate that 7 days of cocaine abstinence is associated with decreased GluA2 Q/R site editing and reduced ADAR2 expression in the accumbens shell, but not core, of cocaine-experienced rats compared with yoked saline controls. To examine the functional significance of ADAR2 and GluA2 Q/R site editing in cocaine seeking, we used viral-mediated gene delivery to overexpress ADAR2b in the accumbens shell. Increased ADAR2b expression in the shell attenuated cocaine priming-induced reinstatement of drug seeking and was associated with increased GluA2 Q/R site editing and surface expression of GluA2-containing AMPARs. Taken together, these findings support the novel hypothesis that an increased contribution of accumbens shell CP-AMPARs containing unedited GluA2(Q) promotes cocaine seeking. Therefore, CP-AMPARs containing unedited GluA2(Q) represent a novel target for cocaine addiction pharmacotherapies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hollmann M, Hartley M, Heinemann S . Ca2+ permeability of KA-AMPA-gated glutamate receptor channels depends on subunit composition. Science 1991; 252: 851–853.
Hume RI, Dingledine R, Heinemann SF . Identification of a site in glutamate receptor subunits that controls calcium permeability. Science 1991; 253: 1028–1031.
Burnashev N, Monyer H, Seeburg PH, Sakmann B . Divalent ion permeability of AMPA receptor channels is dominated by the edited form of a single subunit. Neuron 1992; 8: 189–198.
Geiger JR, Melcher T, Koh DS, Sakmann B, Seeburg PH, Jonas P, et al. Relative abundance of subunit mRNAs determines gating and Ca2+ permeability of AMPA receptors in principal neurons and interneurons in rat CNS. Neuron 1995; 15: 193–204.
Melcher T, Maas S, Herb A, Sprengel R, Seeburg PH, Higuchi M . A mammalian RNA editing enzyme. Nature 1996; 379: 460–464.
Bass BL . RNA editing by adenosine deaminases that act on RNA. Annu Rev Biochem 2002; 71: 817–846.
Rueter SM, Burns CM, Coode SA, Mookherjee P, Emeson RB . Glutamate receptor RNA editing in vitro by enzymatic conversion of adenosine to inosine. Science 1995; 267: 1491–1494.
Wright A, Vissel B . The essential role of AMPA receptor GluR2 subunit RNA editing in the normal and diseased brain. Front Mol Neurosci 2012; 5: 34.
Isaac JT, Ashby MC, McBain CJ . The role of the GluR2 subunit in AMPA receptor function and synaptic plasticity. Neuron 2007; 54: 859–871.
Wiltgen BJ, Royle GA, Gray EE, Abdipranoto A, Thangthaeng N, Jacobs N, et al. A role for calcium-permeable AMPA receptors in synaptic plasticity and learning. PLoS One 2010; 5: e12818.
Pierce RC, Wolf ME . Psychostimulant-induced neuroadaptations in nucleus accumbens AMPA receptor transmission. In: Pierce RC, Kenny PJ (eds). Addiction. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2013, pp, 121–134.
Schmidt HD, Pierce RC . Cocaine-induced neuroadaptations in glutamate transmission: potential therapeutic targets for craving and addiction. Ann NY Acad Sci 2010; 1187: 35–75.
Anderson SM, Famous KR, Sadri-Vakili G, Kumaresan V, Schmidt HD, Bass CE, et al. CaMKII: a biochemical bridge linking accumbens dopamine and glutamate systems in cocaine seeking. Nat Neurosci 2008; 11: 344–353.
Famous KR, Kumaresan V, Sadri-Vakili G, Schmidt HD, Mierke DF, Cha JH, et al. Phosphorylation-dependent trafficking of GluR2-containing AMPA receptors in the nucleus accumbens plays a critical role in the reinstatement of cocaine seeking. J Neurosci 2008; 28: 11061–11070.
Conrad KL, Tseng KY, Uejima JL, Reimers JM, Heng LJ, Shaham Y, et al. Formation of accumbens GluR2-lacking AMPA receptors mediates incubation of cocaine craving. Nature 2008; 454: 118–121.
Kawahara Y, Ito K, Sun H, Kanazawa I, Kwak S . Low editing efficiency of GluR2 mRNA is associated with a low relative abundance of ADAR2 mRNA in white matter of normal human brain. Eur J Neurosci 2003; 18: 23–33.
Paschen W, Djuricic B . Regional differences in the extent of RNA editing of the glutamate receptor subunits GluR2 and GluR6 in rat brain. J Neurosci Methods 1995; 56: 21–29.
Paxinos G, Watson C . The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997.
Sadri-Vakili G, Kumaresan V, Schmidt HD, Famous KR, Chawla P, Vassoler FM, et al. Cocaine-induced chromatin remodeling increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor transcription in the rat medial prefrontal cortex, which alters the reinforcing efficacy of cocaine. J Neurosci 2010; 30: 11735–11744.
Sommer B, Kohler M, Sprengel R, Seeburg PH . RNA editing in brain controls a determinant of ion flow in glutamate-gated channels. Cell 1991; 67: 11–19.
Schmidt HD, Sangrey GR, Darnell SB, Schassburger RL, Cha JH, Pierce RC, et al. Increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression in the ventral tegmental area during cocaine abstinence is associated with increased histone acetylation at BDNF exon I-containing promoters. J Neurochem 2012; 120: 202–209.
Neve RL, Neve KA, Nestler EJ, Carlezon WA Jr . Use of herpes virus amplicon vectors to study brain disorders. Biotechniques 2005; 39: 381–391.
Slavov D, Gardiner K . Phylogenetic comparison of the pre-mRNA adenosine deaminase ADAR2 genes and transcripts: conservation and diversity in editing site sequence and alternative splicing patterns. Gene 2002; 299: 83–94.
Peng PL, Zhong X, Tu W, Soundarapandian MM, Molner P, Zhu D, et al. ADAR2-dependent RNA editing of AMPA receptor subunit GluR2 determines vulnerability of neurons in forebrain ischemia. Neuron 2006; 49: 719–733.
Ferrario CR, Loweth JA, Milovanovic M, Ford KA, Galinanes GL, Heng LJ, et al. Alterations in AMPA receptor subunits and TARPs in the rat nucleus accumbens related to the formation of Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors during the incubation of cocaine craving. Neuropharmacology 2011; 61: 1141–1151.
Wiggins A, Smith RJ, Shen HW, Kalivas PW . Integrins modulate relapse to cocaine-seeking. J Neurosci 2011; 31: 16177–16184.
Greger IH, Khatri L, Kong X, Ziff EB . AMPA receptor tetramerization is mediated by Q/R editing. Neuron 2003; 40: 763–774.
Greger IH, Khatri L, Ziff EB . RNA editing at arg607 controls AMPA receptor exit from the endoplasmic reticulum. Neuron 2002; 34: 759–772.
Araki Y, Lin DT, Huganir RL . Plasma membrane insertion of the AMPA receptor GluA2 subunit is regulated by NSF binding and Q/R editing of the ion pore. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 11080–11085.
McCutcheon JE, Wang X, Tseng KY, Wolf ME, Marinelli M . Calcium-permeable AMPA receptors are present in nucleus accumbens synapses after prolonged withdrawal from cocaine self-administration but not experimenter-administered cocaine. J Neurosci 2011; 31: 5737–5743.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Mary O’Connell for her advice and expertise on ADAR2b antibodies. This work was supported by DA022339 (HDS, RCP and GS-V), DA033641 (HDS, RCP and GS-V), K02 DA18678 (RCP) and K01 DA030445 (HDS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, H., McFarland, K., Darnell, S. et al. ADAR2-dependent GluA2 editing regulates cocaine seeking. Mol Psychiatry 20, 1460–1466 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2014.134
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2014.134
This article is cited by
-
The Q/R editing site of AMPA receptor GluA2 subunit acts as an epigenetic switch regulating dendritic spines, neurodegeneration and cognitive deficits in Alzheimer’s disease
Molecular Neurodegeneration (2023)
-
Advances in brain epitranscriptomics research and translational opportunities
Molecular Psychiatry (2023)
-
Transcriptomics in the nucleus accumbens shell reveal sex- and reinforcer-specific signatures associated with morphine and sucrose craving
Neuropsychopharmacology (2022)
-
GLP-1 receptor signaling in the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus attenuates cocaine seeking by activating GABAergic circuits that project to the VTA
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)
-
A new mouse line with reduced GluA2 Q/R site RNA editing exhibits loss of dendritic spines, hippocampal CA1-neuron loss, learning and memory impairments and NMDA receptor-independent seizure vulnerability
Molecular Brain (2020)