Abstract
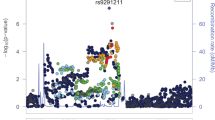
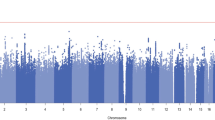
Opioids are very effective analgesics, but they are also highly addictive. Methadone is used to treat opioid dependence (OD), acting as a selective agonist at the μ-opioid receptor encoded by the gene OPRM1. Determining the optimal methadone maintenance dose is time consuming; currently, no biomarkers are available to guide treatment. In methadone-treated OD subjects drawn from a case and control sample, we conducted a genome-wide association study of usual daily methadone dose. In African-American (AA) OD subjects (n=383), we identified a genome-wide significant association between therapeutic methadone dose (mean=68.0 mg, s.d.=30.1 mg) and rs73568641 (P=2.8 × 10−8), the nearest gene (306 kilobases) being OPRM1. Each minor (C) allele corresponded to an additional ~20 mg day−1 of oral methadone, an effect specific to AAs. In European-Americans (EAs) (n=1027), no genome-wide significant associations with methadone dose (mean=77.8 mg, s.d.=33.9 mg) were observed. In an independent set of opioid-naive AA children being treated for surgical pain, rs73568641-C was associated with a higher required dose of morphine (n=241, P=3.9 × 10−2). Similarly, independent genomic loci previously shown to associate with higher opioid analgesic dose were associated with higher methadone dose in the OD sample (AA and EA: n=1410, genetic score P=1.3 × 10−3). The present results in AAs indicate that genetic variants influencing opioid sensitivity across different clinical settings could contribute to precision pharmacotherapy for pain and addiction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okie S . A flood of opioids, a rising tide of deaths. N Engl J Med 2010; 363: 1981–1985.
Volkow ND, Frieden TR, Hyde PS, Cha SS . Medication-assisted therapies—tackling the opioid-overdose epidemic. N Engl J Med 2014; 370: 2063–2066.
Dowell D, Haegerich TM, Chou R . CDC Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Chronic Pain—United States, 2016. JAMA 2016; 315: 1624–1645.
Dole VP . Implications of methadone maintenance for theories of narcotic addiction. JAMA 1988; 260: 3025–3029.
Dole VP, Nyswander M . A medical treatment for diacetylmorphine (heroin) addiction. A clinical trial with methadone hydrochloride. JAMA 1965; 193: 646–650.
Kreek MJ, LaForge KS, Butelman E . Pharmacotherapy of addictions. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2002; 1: 710–726.
Harding-Pink D . Methadone: one person's maintenance dose is another's poison. Lancet 1993; 341: 665–666.
Maxwell S, Shinderman MS . Optimizing long-term response to methadone maintenance treatment: a 152-week follow-up using higher-dose methadone. J Addict Dis 2002; 21: 1–12.
Berridge V . Heroin prescription and history. N Engl J Med 2009; 361: 820–821.
Courtwright DT . Preventing and treating narcotic addiction—century of Federal Drug Control. N Engl J Med 2015; 373: 2095–2097.
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. National Survey of Substance Abuse Treatment Services (N-SSATS): 2013. Data on Substance Abuse Treatment Facilities. BHSIS Series S-73, HHS Publication No. (SMA) 14-489. Rockville, MD: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 2014.
Crist RC, Berrettini WH . Pharmacogenetics of OPRM1. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2014; 123: 25–33.
Zhang H, Luo X, Kranzler HR, Lappalainen J, Yang BZ, Krupitsky E et al. Association between two mu-opioid receptor gene (OPRM1) haplotype blocks and drug or alcohol dependence. Hum Mol Genet 2006; 15: 807–819.
Hung CC, Chiou MH, Huang BH, Hsieh YW, Hsieh TJ, Huang CL et al. Impact of genetic polymorphisms in ABCB1, CYP2B6, OPRM1, ANKK1 and DRD2 genes on methadone therapy in Han Chinese patients. Pharmacogenomics 2011; 12: 1525–1533.
Oslin DW, Leong SH, Lynch KG, Berrettini W, O'Brien CP, Gordon AJ et al. Naltrexone vs placebo for the treatment of alcohol dependence: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2015; 72: 430–437.
Gelernter J, Gueorguieva R, Kranzler HR, Zhang H, Cramer J, Rosenheck R et al. Opioid receptor gene (OPRM1, OPRK1, and OPRD1) variants and response to naltrexone treatment for alcohol dependence: results from the VA Cooperative Study. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2007; 31: 555–563.
Schwantes-An TH, Zhang J, Chen LS, Hartz SM, Culverhouse RC, Chen X et al. Association of the OPRM1 variant rs1799971 (A118G) with non-specific liability to substance dependence in a collaborative de novo meta-analysis of European-ancestry cohorts. Behav Genet 2016; 46: 151–169.
Hancock DB, Levy JL, Gaddis NC, Glasheen C, Saccone NL, Page GP et al. Cis-expression quantitative trait loci mapping reveals replicable associations with heroin addiction in OPRM1. Biol Psychiatry 2015; 78: 474–484.
Kharasch ED, Regina KJ, Blood J, Friedel C . Methadone pharmacogenetics: CYP2B6 polymorphisms determine plasma concentrations, clearance, and metabolism. Anesthesiology 2015; 123: 1142–1153.
Eap CB, Broly F, Mino A, Hämmig R, Déglon JJ, Uehlinger C et al. Cytochrome P450 2D6 genotype and methadone steady-state concentrations. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2001; 21: 229–234.
Crettol S, Déglon JJ, Besson J, Croquette-Krokar M, Hämmig R, Gothuey I et al. ABCB1 and cytochrome P450 genotypes and phenotypes: influence on methadone plasma levels and response to treatment. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2006; 80: 668–681.
Leavitt SB, Shinderman M, Maxwell S, Eap CB, Paris P . When ‘enough’ is not enough: new perspectives on optimal methadone maintenance dose. Mt Sinai J Med 2000; 67: 404–411.
Dennis BB, Bawor M, Thabane L, Sohani Z, Samaan Z . Impact of ABCB1 and CYP2B6 genetic polymorphisms on methadone metabolism, dose and treatment response in patients with opioid addiction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2014; 9: e86114.
Gelernter J, Kranzler HR, Sherva R, Koesterer R, Almasy L, Zhao H et al. Genome-wide association study of opioid dependence: multiple associations mapped to calcium and potassium pathways. Biol Psychiatry 2014; 76: 66–74.
Nelson EC, Agrawal A, Heath AC, Bogdan R, Sherva R, Zhang B et al. Evidence of CNIH3 involvement in opioid dependence. Mol Psychiatry 2016; 21: 608–614.
Bosker FJ, Hartman CA, Nolte IM, Prins BP, Terpstra P, Posthuma D et al. Poor replication of candidate genes for major depressive disorder using genome-wide association data. Mol Psychiatry 2011; 16: 516–532.
Gelernter J, Kranzler HR, Sherva R, Almasy L, Koesterer R, Smith AH et al. Genome-wide association study of alcohol dependence:significant findings in African- and European-Americans including novel risk loci. Mol Psychiatry 2014; 19: 41–49.
Gelernter J, Sherva R, Koesterer R, Almasy L, Zhao H, Kranzler HR et al. Genome-wide association study of cocaine dependence and related traits: FAM53B identified as a risk gene. Mol Psychiatry 2014; 19: 717–723.
Pierucci-Lagha A, Gelernter J, Feinn R, Cubells JF, Pearson D, Pollastri A et al. Diagnostic reliability of the Semi-structured Assessment for Drug Dependence and Alcoholism (SSADDA). Drug Alcohol Depend 2005; 80: 303–312.
Pierucci-Lagha A, Gelernter J, Chan G, Arias A, Cubells JF, Farrer L et al. Reliability of DSM-IV diagnostic criteria using the semi-structured assessment for drug dependence and alcoholism (SSADDA). Drug Alcohol Depend 2007; 91: 85–90.
Price AL, Patterson NJ, Plenge RM, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA, Reich D . Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 904–909.
Patterson N, Price AL, Reich D . Population structure and eigenanalysis. PLoS Genet 2006; 2: e190.
R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2016.
Locke AE, Kahali B, Berndt SI, Justice AE, Pers TH, Day FR et al. Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology. Nature 2015; 518: 197–206.
Abecasis GR, Auton A, Brooks LD, DePristo MA, Durbin RM, Handsaker RE et al. An integrated map of genetic variation from 1,092 human genomes. Nature 2012; 491: 56–65.
Howie BN, Donnelly P, Marchini J . A flexible and accurate genotype imputation method for the next generation of genome-wide association studies. PLoS Genet 2009; 5: e1000529.
Delaneau O, Marchini J, Zagury J . A linear complexity phasing method for thousands of genomes. Nat Methods 2012; 9: 179–181.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Willer CJ, Li Y, Abecasis GR . METAL: fast and efficient meta-analysis of genomewide association scans. Bioinformatics 2010; 26: 2190–2191.
Pruim RJ, Welch RP, Sanna S, Teslovich TM, Chines PS, Gliedt TP et al. LocusZoom: regional visualization of genome-wide association scan results. Bioinformatics 2010; 26: 2336–2337.
Cook-Sather SD, Li J, Goebel TK, Sussman EM, Rehman MA, Hakonarson H . TAOK3, a novel genome-wide association study locus associated with morphine requirement and postoperative pain in a retrospective pediatric day surgery population. Pain 2014; 155: 1773–1783.
Marchini J, Howie B, Myers S, McVean G, Donnelly P . A new multipoint method for genome-wide association studies by imputation of genotypes. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 906–913.
Wigginton JE, Cutler DJ, Abecasis GR . A note on exact tests of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Am J Hum Genet 2005; 76: 887–893.
Somogyi AA, Barratt DT, Ali RL, Coller JK . Pharmacogenomics of methadone maintenance treatment. Pharmacogenomics 2014; 15: 1007–1027.
Nishizawa D, Fukuda K, Kasai S, Hasegawa J, Aoki Y, Nishi A et al. Genome-wide association study identifies a potent locus associated with human opioid sensitivity. Mol Psychiatry 2014; 19: 55–62.
Aoki Y, Nishizawa D, Hasegawa J, Kasai S, Yoshida K, Koukita Y et al. Association between the rs1465040 single-nucleotide polymorphism close to the transient receptor potential subfamily C member 3 (TRPC3) gene and postoperative analgesic requirements. J Pharmacol Sci 2015; 127: 391–393.
Vestal C . In fighting an opioid epidemic, medication-assisted treatment is effective but underused. Health Aff (Millwood) 2016; 35: 1052–1057.
Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, Davoli M . Buprenorphine maintenance versus placebo or methadone maintenance for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014; 2: CD002207.
Johnson RE, Chutuape MA, Strain EC, Walsh SL, Stitzer ML, Bigelow GE . A comparison of levomethadyl acetate, buprenorphine, and methadone for opioid dependence. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 1290–1297.
Strain EC, Bigelow GE, Liebson IA, Stitzer ML . Moderate- vs high-dose methadone in the treatment of opioid dependence: a randomized trial. JAMA 1999; 281: 1000–1005.
D'Aunno T, Pollack HA, Frimpong JA, Wuchiett D . Evidence-based treatment for opioid disorders: a 23-year national study of methadone dose levels. J Subst Abuse Treat 2014; 47: 245–250.
Bell JR, Butler B, Lawrance A, Batey R, Salmelainen P . Comparing overdose mortality associated with methadone and buprenorphine treatment. Drug Alcohol Depend 2009; 104: 73–77.
Angst MS, Phillips NG, Drover DR, Tingle M, Ray A, Swan GE et al. Pain sensitivity and opioid analgesia: a pharmacogenomic twin study. Pain 2012; 153: 1397–1409.
Williams JT, Ingram SL, Henderson G, Chavkin C, von Zastrow M, Schulz S et al. Regulation of μ-opioid receptors: desensitization, phosphorylation, internalization, and tolerance. Pharmacol Rev 2013; 65: 223–254.
Yang HC, Chu SK, Huang CL, Kuo HW, Wang SC, Liu SW et al. Genome-wide pharmacogenomic study on methadone maintenance treatment identifies SNP rs17180299 and multiple haplotypes on CYP2B6, SPON1, and GSG1L associated with plasma concentrations of methadone R- and S-enantiomers in heroin-dependent patients. PLoS Genet 2016; 12: e1005910.
Wang JS, DeVane CL . Involvement of CYP3A4, CYP2C8, and CYP2D6 in the metabolism of (R)- and (S)-methadone in vitro. Drug Metab Dispos 2003; 31: 742–747.
Coller JK, Joergensen C, Foster DJ, James H, Gillis D, Christrup L et al. Lack of influence of CYP2D6 genotype on the clearance of (R)-, (S)- and racemic-methadone. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 2007; 45: 410–417.
Fonseca F, de la Torre R, Díaz L, Pastor A, Cuyàs E, Pizarro N et al. Contribution of cytochrome P450 and ABCB1 genetic variability on methadone pharmacokinetics, dose requirements, and response. PLoS One 2011; 6: e19527.
Siegle I, Fritz P, Eckhardt K, Zanger UM, Eichelbaum M . Cellular localization and regional distribution of CYP2D6 mRNA and protein expression in human brain. Pharmacogenetics 2001; 11: 237–245.
Britto MR, Wedlund PJ . Cytochrome P-450 in the brain. Potential evolutionary and therapeutic relevance of localization of drug-metabolizing enzymes. Drug Metab Dispos 1992; 20: 446–450.
Levran O, Peles E, Hamon S, Randesi M, Adelson M, Kreek MJ . CYP2B6 SNPs are associated with methadone dose required for effective treatment of opioid addiction. Addict Biol 2013; 18: 709–716.
Kagimoto M, Heim M, Kagimoto K, Zeugin T, Meyer UA . Multiple mutations of the human cytochrome P450IID6 gene (CYP2D6) in poor metabolizers of debrisoquine. Study of the functional significance of individual mutations by expression of chimeric genes. J Biol Chem 1990; 265: 17209–17214.
CONVERGE consortium. Sparse whole-genome sequencing identifies two loci for major depressive disorder. Nature 2015; 523: 588–591.
Dickson SP, Wang K, Krantz I, Hakonarson H, Goldstein DB . Rare variants create synthetic genome-wide associations. PLoS Biol 2010; 8: e1000294.
Polimanti R, Yang C, Zhao H, Gelernter J . Dissecting ancestry genomic background in substance dependence genome-wide association studies. Pharmacogenomics 2015; 16: 1487–1498.
Pletcher MJ, Kertesz SG, Kohn MA, Gonzales R . Trends in opioid prescribing by race/ethnicity for patients seeking care in US emergency departments. JAMA 2008; 299: 70–78.
Goyal MK, Kuppermann N, Cleary SD, Teach SJ, Chamberlain JM . Racial disparities in pain management of children with appendicitis in emergency departments. JAMA Pediatr 2015; 169: 996–1002.
Zhou HH, Sheller JR, Nu H, Wood M, Wood AJ . Ethnic differences in response to morphine. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1993; 54: 507–513.
Daly AK . Genome-wide association studies in pharmacogenomics. Nat Rev Genet 2010; 11: 241–246.
Mieda T, Nishizawa D, Nakagawa H, Tsujita M, Imanishi H, Terao K et al. Genome-wide association study identifies candidate loci associated with postoperative fentanyl requirements after laparoscopic-assisted colectomy. Pharmacogenomics 2016; 17: 133–145.
Langendam MW, van Haastrecht HJ, van Ameijden EJ . The validity of drug users' self-reports in a non-treatment setting: prevalence and predictors of incorrect reporting methadone treatment modalities. Int J Epidemiol 1999; 28: 514–520.
Cooper GM, Johnson JA, Langaee TY, Feng H, Stanaway IB, Schwarz UI et al. A genome-wide scan for common genetic variants with a large influence on warfarin maintenance dose. Blood 2008; 112: 1022–1027.
Zineh I, Pacanowski M, Woodcock J . Pharmacogenetics and coumarin dosing—recalibrating expectations. N Engl J Med 2013; 369: 2273–2275.
Kimmel SE, French B, Kasner SE, Johnson JA, Anderson JL, Gage BF et al. A pharmacogenetic versus a clinical algorithm for warfarin dosing. N Engl J Med 2013; 369: 2283–2293.
Verhoef TI, Ragia G, de Boer A, Barallon R, Kolovou G, Kolovou V et al. A randomized trial of genotype-guided dosing of acenocoumarol and phenprocoumon. N Engl J Med 2013; 369: 2304–2312.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the research participants in this study. Adult subject recruitment and assessment were overseen at the Yale School of Medicine and the APT Foundation by James Poling, PhD, and Aryeh Herman, PsyD; at McLean Hospital by Roger Weiss, MD; at the Medical University of South Carolina by Kathleen Brady, MD, PhD, and Raymond Anton, MD; and at the University of Pennsylvania initially by David Oslin, MD. Genotyping services were provided by the Center for Inherited Disease Research (CIDR) and the Yale University Center for Genome Analysis. Ann Marie Lacobelle, MS and Christa Robinson, AS provided excellent technical assistance; the SSADDA interviewers devoted substantial time and effort to phenotype the study sample; and Richard Sherva, PhD, Ryan Koesterer, MA, and John Farrell, PhD, at Boston University offered valuable assistance with data cleaning and management. Robert T Malison, MD, Department of Psychiatry, Yale School of Medicine, provided thoughtful suggestions during preparation of the manuscript. This study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) (RC2 DA028909, R01 DA12690, R01 DA12849, R01 DA18432, R01 AA11330, R01 AA017535, MSTP 5T32GM007205-38, CTSA TL1 8UL1TR000142, F30 DA037665, N01-HG-65403, S10 RR19895); a Veterans Affairs VISN1 Career Development Award; the Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine at The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia through Children’s Anesthesia Associates, Ltd.; and by The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia through a grant from the Institutional Development Fund to The Center for Applied Genomics. The funding sources had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis and interpretation of the data; preparation, review or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Dr Kranzler reports being a consultant, continuing medical education (CME) speaker or advisory board member for Alkermes, Indivior, Lundbeck and Otsuka and a member of the American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology’s Alcohol Clinical Trials Initiative, which was supported in the past 3 years by AbbVie, Alkermes, Ethypharm, Indivior, Lilly, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Pfizer and XenoPort. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, A., Jensen, K., Li, J. et al. Genome-wide association study of therapeutic opioid dosing identifies a novel locus upstream of OPRM1. Mol Psychiatry 22, 346–352 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.257
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.257
This article is cited by
-
Polygenic risk scores and the need for pharmacotherapy in neonatal abstinence syndrome
Pediatric Research (2023)
-
A genome-wide association, polygenic risk score and sex study on opioid use disorder treatment outcomes
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Association of the D-amino acid oxidase gene with methadone dose in heroin dependent patients under methadone maintenance treatment
Journal of Human Genetics (2022)
-
Multi-trait genome-wide association study of opioid addiction: OPRM1 and beyond
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
A systematic review of GWAS identified SNPs associated with outcomes of medications for opioid use disorder
Addiction Science & Clinical Practice (2021)