Abstract
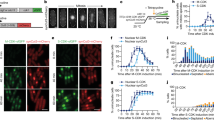
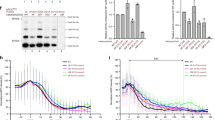
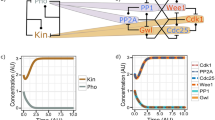
Cyclin B1–Cdk1 is the key initiator of mitosis, but when and where activation occurs has not been precisely determined in mammalian cells. Activation may occur in the nucleus or cytoplasm, as just before nuclear envelope breakdown, Polo-like kinase1 (Plk1) is proposed to phosphorylate cyclin B1 in its nuclear export sequence (NES), to trigger rapid nuclear import. We raised phospho-specific antibodies against cyclin B1 that primarily recognise the active form of the complex. We show that cyclin B1 is initially phosphorylated on centrosomes in prophase and that Plk1 phosphorylates cyclin B1, but not in the NES. Furthermore, phosphorylation by Plk1 does not cause cyclin B1 to move into the nucleus. We conclude that cyclin B1–Cdk1 is first activated in the cytoplasm and that centrosomes may function as sites of integration for the proteins that trigger mitosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nurse, P. Nature 344, 503–508 (1990).
Pines, J. Nature Cell Biol. 1, E73–E79 (1999).
Pines, J. & Hunter, T. J. Cell Biol. 115, 1–17 (1991).
Bailly, E., Pines, J., Hunter, T. & Bornens, M. J. Cell Sci. 101, 529–545 (1992).
Hagting, A., Karlsson, C., Clute, P., Jackman, M. & Pines, J. EMBO J. 17, 4127–4138 (1998).
Yang, J. et al. Genes Dev. 12, 2131–2143 (1998).
Toyoshima, F., Moriguchi, T., Wada, A., Fukuda, M. & Nishida, E. EMBO J. 17, 2728–2735 (1998).
Li, J., Meyer, A.N. & Donoghue, D.J. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 502–507 (1997).
Pines, J. & Hunter, T. EMBO J. 13, 3772–3781 (1994).
Hagting, A., Jackman, M., Simpson, K. & Pines, J. Curr. Biol. 9, 680–689 (1999).
Yang, J., Song, H., Walsh, S., Bardes, E.S. & Kornbluth, S. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 3604–3609 (2001).
Toyoshima-Morimoto, F., Taniguchi, E., Shinya, N., Iwamatsu, A. & Nishida, E. Nature 410, 215–220 (2001).
Borgne, A., Ostvold, A.C., Flament, S. & Meijer, L. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 11977–11986 (1999).
Meijer, L. et al. EMBO J. 8, 2275–2282 (1989).
Ookata, K., Hisanaga, S., Okano, T., Tachibana, K. & Kishimoto, T. EMBO J. 11, 1763–1772 (1992).
Kelm, O., Wind, M., Lehmann, W.D. & Nigg, E.A. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 25247–25256. (2002).
Hendzel, M.J. et al. Chromosoma 106, 348–360 (1997).
Wei, Y., Mizzen, C.A., Cook, R.G., Gorovsky, M.A. & Allis, C.D. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 7480–7484 (1998).
Clute, P. & Pines, J. Nature Cell Biol. 1, 82–87 (1999).
Kudo, N. et al. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 9112–9117 (1999).
Masui, Y. & Markert, C.L. J. Exp. Zool. 177, 129–145 (1971).
Hara, K., Tydeman, P. & Kirschner, M. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77, 462–466 (1980).
Gerhart, J., Wu, M. & Kirschner, M. J. Cell Biol. 98, 1247–1255 (1984).
Picard, A., Labbe, J.C., Barakat, H., Cavadore, J.C. & Doree, M. J. Cell Biol. 115, 337–344 (1991).
Newport, J.W. & Kirschner, M.W. Cell 37, 731–742 (1984).
Perez-Mongiovi, D., Beckhelling, C., Chang, P., Ford, C.C. & Houliston, E. J. Cell Biol. 150, 963–974 (2000).
Picard, A., Karsenti, E., Dabauvalle, M. & Doree, M. Nature 327, 170–172 (1987).
Hinchcliffe, E.H., Miller, F.J., Cham, M., Khodjakov, A. & Sluder, G. Science 291, 1547–1550 (2001).
Peter, M. et al. EMBO Reports 3, 551–556 (2002).
Bridge, A.J., Morphew, M., Bartlett, R. & Hagan, I.M. Genes Dev. 12, 927–942 (1998).
Grallert, A. & Hagan, I.M. EMBO J. 21, 3096–3107 (2002).
Pines, J. & Hunter, T. Cell 58, 833–846 (1989).
Lindon, C., Albagli, O., Domeyne, P., Montarras, D. & Pinset, C. Mol. Cell Biol. 20, 8923–8932 (2000).
Krude, T., Jackman, M.R., Pines, J.N. & Laskey, R.A. Cell 87, 109–119 (1997).
Kumagai, A. & Dunphy, W.G. Science 273, 1377–1380 (1996).
Boyle, W.J., van der Geer, P. & Hunter, T. in Methods Enzymol. (eds Hunter, T. & Sefton, B.M.) 110–149 (Academic Press, San Diego, 1991).
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to C. Broad for help with the cell culture. We are grateful to S. Kornbluth for discussing results before publication, to J. Gannon and T. Hunt for anti-Cdk1 antibodies, and K. Lee and R. Erikson (Havard, USA) for the Plk1 baculovirus. We thank E. Nishida (Kyoto, Japan) for sending us anti-phospho-Ser 147 serum. This work was supported by a Wellcome Trust Training Fellowship to CL, by the Association for International Cancer Research [AICR], and by a programme grant to JP from Cancer Research UK (CRC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Figures
Figure S1 S126-P antibody staining focuses at centrosomes. (PDF 470 kb)
Figure S2 PLK1 preferentially phosphorylates S133 and not S147 in cyclin B1
Figure S3 Plk1 accumulates in the nucleus at prophase before cyclin B1.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jackman, M., Lindon, C., Nigg, E. et al. Active cyclin B1–Cdk1 first appears on centrosomes in prophase. Nat Cell Biol 5, 143–148 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb918
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb918
This article is cited by
-
On the assembly of the mitotic spindle, bistability and hysteresis
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)
-
Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases: from biology to tumorigenesis and therapeutic opportunities
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2023)
-
An updated view on the centrosome as a cell cycle regulator
Cell Division (2022)
-
Pyrrolizidine alkaloids cause cell cycle and DNA damage repair defects as analyzed by transcriptomics in cytochrome P450 3A4-overexpressing HepG2 clone 9 cells
Cell Biology and Toxicology (2022)
-
In silico analysis of a Skp1 protein homolog from the human pathogen E. histolytica
Journal of Parasitic Diseases (2022)