Abstract
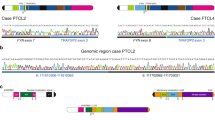
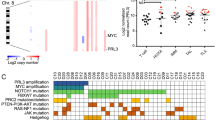
PTPN2 (protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 2, also known as TC-PTP) is a cytosolic tyrosine phosphatase that functions as a negative regulator of a variety of tyrosine kinases and other signaling proteins1,2,3. In agreement with its role in the regulation of the immune system, PTPN2 was identified as a susceptibility locus for autoimmune diseases4,5. In this work, we describe the identification of focal deletions of PTPN2 in human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). Deletion of PTPN2 was specifically found in T-ALLs with aberrant expression of the TLX1 transcription factor oncogene6, including four cases also expressing the NUP214-ABL1 tyrosine kinase7. Knockdown of PTPN2 increased the proliferation and cytokine sensitivity of T-ALL cells. In addition, PTPN2 was identified as a negative regulator of NUP214-ABL1 kinase activity. Our study provides genetic and functional evidence for a tumor suppressor role of PTPN2 and suggests that expression of PTPN2 may modulate response to treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doody, K.M., Bourdeau, A. & Tremblay, M.L. T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase is a key regulator in immune cell signaling: lessons from the knockout mouse model and implications in human disease. Immunol. Rev. 228, 325–341 (2009).
van Vliet, C. et al. Selective regulation of tumor necrosis factor-induced Erk signaling by Src family kinases and the T cell protein tyrosine phosphatase. Nat. Immunol. 6, 253–260 (2005).
Shields, B.J., Hauser, C., Bukczynska, P.E., Court, N.W. & Tiganis, T. DNA replication stalling attenuates tyrosine kinase signaling to suppress S phase progression. Cancer Cell 14, 166–179 (2008).
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 447, 661–678 (2007).
Todd, J.A. et al. Robust associations of four new chromosome regions from genome-wide analyses of type 1 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 39, 857–864 (2007).
Ferrando, A.A. et al. Gene expression signatures define novel oncogenic pathways in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell 1, 75–87 (2002).
Graux, C. et al. Fusion of NUP214 to ABL1 on amplified episomes in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat. Genet. 36, 1084–1089 (2004).
De Keersmaecker, K., Marynen, P. & Cools, J. Genetic insights in the pathogenesis of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 90, 1116–1127 (2005).
Grabher, C., von Boehmer, H. & Look, A.T. Notch 1 activation in the molecular pathogenesis of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 6, 347–359 (2006).
Aifantis, I., Raetz, E. & Buonamici, S. Molecular pathogenesis of T-cell leukaemia and lymphoma. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8, 380–390 (2008).
Lahortiga, I. et al. Duplication of the MYB oncogene in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat. Genet. 39, 593–595 (2007).
Dik, W.A. et al. New insights on human T cell development by quantitative T cell receptor gene rearrangement studies and gene expression profiling. J. Exp. Med. 201, 1715–1723 (2005).
Soulier, J. et al. HOXA genes are included in genetic and biologic networks defining human acute T-cell leukemia (T-ALL). Blood 106, 274–286 (2005).
Mullighan, C.G. et al. BCR-ABL1 lymphoblastic leukaemia is characterized by the deletion of Ikaros. Nature 453, 110–114 (2008).
ten Hoeve, J. et al. Identification of a nuclear Stat1 protein tyrosine phosphatase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 5662–5668 (2002).
Simoncic, P.D., Lee-Loy, A., Barber, D.L., Tremblay, M.L. & McGlade, C.J. The T cell protein tyrosine phosphatase is a negative regulator of Janus family kinases 1 and 3. Curr. Biol. 12, 446–453 (2002).
Lu, X. et al. T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase, distinctively expressed in activated-B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphomas, is the nuclear phosphatase of STAT6. Mol. Cell. Biol. 27, 2166–2179 (2007).
Leonard, W.J. Cytokines and immunodeficiency diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 1, 200–208 (2001).
Blanchetot, C., Chagnon, M., Dube, N., Halle, M. & Tremblay, M.L. Substrate-trapping techniques in the identification of cellular PTP targets. Methods 35, 44–53 (2005).
Flint, A.J., Tiganis, T., Barford, D. & Tonks, N.K. Development of “substrate-trapping” mutants to identify physiological substrates of protein tyrosine phosphatases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 1680–1685 (1997).
Tiganis, T., Flint, A.J., Adam, S.A. & Tonks, N.K. Association of the T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase with nuclear import factor p97. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 21548–21557 (1997).
De Keersmaecker, K. et al. Kinase activation and transformation by NUP214–ABL1 is dependent on the context of the nuclear pore. Mol. Cell 31, 134–142 (2008).
Wright, D.D., Sefton, B.M. & Kamps, M.P. Oncogenic activation of the Lck protein accompanies translocation of the LCK gene in the human HSB2 T-cell leukemia. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14, 2429–2437 (1994).
Flex, E. et al. Somatically acquired JAK1 mutations in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 205, 751–758 (2008).
Clappier, E. et al. The C-MYB locus is involved in chromosomal translocation and genomic duplications in human T-cell acute leukemia (T-ALL), the translocation defining a new T-ALL subtype in very young children. Blood 110, 1251–1261 (2007).
Bene, M.C. et al. Proposals for the immunological classification of acute leukemias. European Group for the Immunological Characterization of Leukemias (EGIL). Leukemia 9, 1783–1786 (1995).
Jaffe, E.H.N., Stein, H. & Vardiman, J. (ed.) World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues 84–86 (International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, France, 2001).
De Keersmaecker, K. et al. Fusion of EML1 to ABL1 in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia with cryptic t(9;14)(q34;q32). Blood 105, 4849–4852 (2005).
De Keersmaecker, K. et al. In vitro validation of γ-secretase inhibitors alone or in combination with other anti-cancer drugs for the treatment of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 93, 533–542 (2008).
Lorenzen, J.A., Dadabay, C.Y. & Fischer, E.H. COOH-terminal sequence motifs target the T cell protein tyrosine phosphatase to the ER and nucleus. J. Cell Biol. 131, 631–643 (1995).
Mosinger, B. Jr, Tillmann, U., Westphal, H. & Tremblay, M.L. Cloning and characterization of a mouse cDNA encoding a cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 499–503 (1992).
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Aerts for assistance with data analysis. This work was supported by grants from the K.U. Leuven (concerted action grant to J.C., I.W. and P.V.), the FWO-Vlaanderen (G.0287.07, J.C.), the Foundation against Cancer (SCIE2006-34, J.C.), a European Research Council starting grant (J.C.), a José-Carreras Fellowship grant from the European Hematology Association (J.C.), the Interuniversity Attraction Poles granted by the Federal Office for Scientific, Technical and Cultural Affairs, Belgium (J.C. and P.V.), a grant from the French program Carte d'Identite des Tumeurs (CIT, Ligue Contre le Cancer) and from Canceropole d'Ile de France (F.S. and J.S.); a Blood Disease Research Project research grant from The New York Community Trust (A.A.F.) and the National Institutes of Health (grants CA120196 and CA129382 to A.A.F.). A.A.F. is a Leukemia and Lymphoma Society Scholar. K.D.K. is a postdoctoral researcher, and P.V. is a senior clinical investigator of FWO-Vlaanderen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the text; M.K. designed and carried out experiments and analyzed data; I.L., T.E.C., K.D.K., N.M., C.G., K.V.R. and I.W. carried out experiments and analyzed data; A.A.F., A.W.L., J.P.P.M., F.S., T.H. and P.V. collected samples, carried out experiments and analyzed data; J.S. and J.C. supervised the project and analyzed data.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–8 and Supplementary Tables 1–4 (PDF 902 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kleppe, M., Lahortiga, I., El Chaar, T. et al. Deletion of the protein tyrosine phosphatase gene PTPN2 in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat Genet 42, 530–535 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.587
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.587
This article is cited by
-
A small molecule inhibitor of PTP1B and PTPN2 enhances T cell anti-tumor immunity
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Novel targets for immunotherapy associated with exhausted CD8 + T cells in cancer
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2023)
-
LncRNAs serve as novel biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of childhood ALL
Biomarker Research (2021)
-
Overexpression of TC-PTP in murine epidermis attenuates skin tumor formation
Oncogene (2020)
-
The effect of co-occurring lesions on leukaemogenesis and drug response in T-ALL and ETP-ALL
British Journal of Cancer (2020)