Abstract
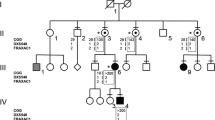
The vast majority of patients with fragile X syndrome show a folate–sensitive fragile site at Xq27.3 (FRAXA) at the cytogenetic level, and both amplification of the (CGG)n repeat and hypermethylation of the CpG island in the 5′ fragile X gene (FMR–1) at the molecular level. We have studied the FMR–1 gene of a patient with the fragile X phenotype but without cytogenetic expression of FRAXA, a (CGG)n repeat of normal length and an unmethylated CpG island. We find a single point mutation in FMR–1 resulting in an Ne367Asn substitution. This de novo mutation is absent in the patient's family and in 130 control X chromosomes, suggesting that the mutation causes the clinical abnormalities. Our results suggest that mutations in FMR–1 are directly responsible for fragile X syndrome, irrespective of possible secondary effects caused by FRAXA
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Verkerk, A.J.M.H. et al. Identification of a gene (FMR-1) containing a CGG repeat coincident with a breakpoint cluster region exhibiting length variation in fragile X syndrome. Cell 65, 905–914 (1991).
Kremer, E. et al. Mapping of DNA instability at the fragile X to a trinucleotide repeat sequence p(GCG)n . Science 252, 1711–1714 (1991).
Yu, S. et al. Fragile X genotype characterized by an unstable region of DNA. Science 252, 1179–1181 (1991).
Fu, Y.H. et al. Variation of the CGG repeat at the fragile X site results in genetic instability: resolution of the Sherman paradox. Cell 67, 1047–1058 (1991).
Rousseau, F. et al. Direct diagnosis by DNA analysis of the fragile X syndrome of mental retardation. New Engl. J. Med. 325, 1673–1681 (1991).
Bell, M.V. et al. Physical mapping across the fragile X: Hypermethylation and clinical expression of the fragile X syndrome. Cell 64, 861–866 (1991).
Heitz, D. et al. Isolation of sequences that span the fragile X and identification of a fragile X-related CpG Island. Science 251, 1236–1239 (1991).
Oberlé, I. et al. Instability of a 550-base pair DNA segment and abnormal methylation in fragile X syndrome. Science 252, 1097–1102 (1991).
Vincent, A. et al. Abnormal pattern detected in fragile X patients by pulsed-field gel etectrophoresis. Nature 349, 624–626 (1991).
Gedeon, A.K. et al. Fragile X syndrome without CGG amplification has an FMR-1 deletion. Nature Genet. 1, 341–344 (1992).
Wöhrle, D. et al. A microdeletion of less than 250 kb, including the proximal part of the FMR-1 gene and the fragile X site, in a male with the clinical phenotype of the fragile X syndrome. Am. J. hum. Genet. 51, 299–306 (1992).
Verkerk, A.J.M.H., Eussen, B.H.J., Van Hemel, J.O. & Oostra, B.A. Limited size of the fragile X site shown by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Am. J. med. Genet. 43, 187–191 (1992).
Brook, J.D. et al. Molecular basis of myotpnic dystrophy: Expansion of trinucleotide (CTG) repeat at the 3′ end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member. Cell 68, 799–808 (1992).
Fu, Y.-H. et al. An unstable triplet repeat in a gene related to myotonic muscular dystrophy. Science 255, 1256–1258 (1992).
Mahadevan, M. et al. Myotonic dystrophy mutation: An unstable CTG repeat in the 3′ untranslated region of the gene. Science 255, 1253–1255 (1992).
La Spada, A.R. et al. Androgen receptor gene mutation in X-linked spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Nature 352, 77–79 (1991).
Pieretti, M. et al. Absence of expression of the FMR-1 gene in fragile X syndrome. Cell 66, 817–822 (1991).
Clarke, A. et al. Fragile X mental retardation and the iduronate sulphatase locus: Testing Laird's model of Fra(X) inheritance. Am. J. med. Genet. 43, 299–306 (1992).
Willems, P.J. et al. Mapping of the gene for X-linked liver glycogenosis due to phosphorylase kinase deficiency to human chromosome region Xp22. Genomics 9, 565–569 (1991).
Willems, P.J., Gerver, W.J.M., Berger, R. & Fernandes, J. The natural history of liver glycogenosis due to phosphorylase kinase deficiency: A longitudinal study of 41 patients. Eur. J. Pediatr. 149, 268–271 (1990).
Wauters, J.G. et al. Regional mapping of a liver α-subunit gene of phosphorylase kinase to the distal region of chromosome Xp. Cytogen. Cell Genet. 60, 194–196 (1992).
Davidson, J.J. et al. cDNA cloning of a liver isoform of the phosphorylase kinase α-subunit and mapping of the gene to Xp22.2-p22.1, the region of human X-linked liver glycogenosis. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 2096–2100 (1992).
Hendrickx, J. et al. Hum. molec. Genet. (in the press).
Chou, P.Y. & Fasman, G.D. Prediction of the secondary structure of protein from their amino acid sequence. Adv. Enzym. 47, 45–147 (1978).
Van Roy, B.C., De Smedt, M.C., Raes, R.A., Dumon, J.E. & Leroy, J.G. Fragile X trait in a large kindred: transmission also through normal males. J. med. Genet. 20, 286–289 (1983).
McLean, D.A. & Faed, M.J.W. Improved fragile site detection with trimethoprim. Hum. Genet. 85, 241–243 (1990).
Oostra, B.A. & Verkerk, A.J.M.H. The fragile X syndrome: Isolation of the FMR-1 gene and characterization of the fragile X mutation. Chromosoma 101, 381–387 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Boulle, K., Verkerk, A., Reyniers, E. et al. A point mutation in the FMR-1 gene associated with fragile X mental retardation. Nat Genet 3, 31–35 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0193-31
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0193-31
This article is cited by
-
Dynamic FMR1 granule phase switch instructed by m6A modification contributes to maternal RNA decay
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Interaction networks from discrete event data by Poisson multivariate mutual information estimation and information flow with applications from gene expression data
Applied Network Science (2022)
-
Missense mutation of Fmr1 results in impaired AMPAR-mediated plasticity and socio-cognitive deficits in mice
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Post-translational modifications of the Fragile X Mental Retardation Protein in neuronal function and dysfunction
Molecular Psychiatry (2020)
-
Prevalence of fragile X syndrome among patients with mental retardation in the west of Iran
Frontiers in Biology (2018)