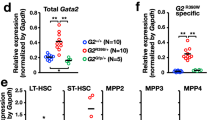
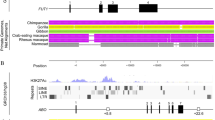
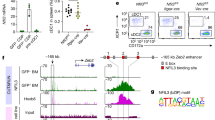
Abstract
The mRNA for the Duffy blood group antigen, the erythrocyte receptor for the Plasmodium vivax malaria parasite, has recently been cloned and shown to encode a widely expressed chemokine receptor. Here, we show that the Duffy antigen/chemokine receptor gene (DARC) is composed of a single exon and that most Duffy–negative blacks carry a silent FY*B allele with a single T to C substitution at nucleotide −46. This mutation impairs the promoter activity in erythroid cells by disrupting a binding site for the GATA1 erythroid transcription factor. With the recent characterization of the FY*A and FY*B alleles, these findings provide the molecular basis of the Duffy blood group system and an explanation for the erythroid–speeific repression of the DARC gene in Duffy–negative individuals.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hadley, J.T., Ktotz, W. & Miller, L.H. Invasion of erythrocytes by malaria parasites: a cellular and molecular approach. A. Rev. Microbiol. 40, 451–477 (1986).
Chaudhuri, A. et al. Expression of the Duffy Antigen in K562 cells. J. biol. Chem. 269, 10793–10797 (1994).
Neote, K., Mak, J.Y., Kdakowski, L.F. & Schall, T.J. Functional and biochemical analysis of the cloned Duffy antigen: identity with the red blood cell chemokine receptor. Blood. 84, 44–52 (1994).
Darbonne, W.C. et al. Red blood cells as sink for interleukin-8, a leukocyte chemotaxin. J. clin. Invest. 88, 1362–1369 (1991).
Chaudhuri, A. Purification and characterization of a erythrocyte membrane protein complex carrying Duffy blood group antigen. J. biol. Chem. 264, 13770–13774 (1989).
Chaudhuri, A. et al. Cloning of glycoprotein D cDNA, which encodes the major subunit of the Duffy blood group system and the receptor for the Plasmodium vivax malaria parasite. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 10793–10797 (1993).
Dohlman, H.G., Thorner, J., Caron, M.G. & Lefkowitz, R.J. Model systems for the study of seven tansmembrane-segment receptors. A. Rev. Biochem. 60, 653–688 (1991).
Chrtnis, C.E. & Miller, L.H Identification of the erythrocyte binding domains of Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium knowlesi proteins involved in erythrocyte invasion. J. exp. Med. 180, 497–506 (1994).
Toumamilte, C., Le Van Kim, C., Gane, P., Cartron, J.P. & Colin, Y. Molecular basis and PCR-DNA typing of the Pya/Pyb blood group polymorphism. Hum. Genet. 85, 407–410 (1995).
Race, R.R. & Sanger, R. Blood Groups in Man, 6th edn (Blackwell, Oxford, 1975).
Miller, L.H., Mason, S.J., Dvorack., J.A., McGinnis, M.H. & Rothman, K.I. Erythrocyte receptors for (Plasmodium knowlesi) malaria: Duffy blood group determinants. Science 189, 561–563 (1975).
Miller, L.H., Aikawa, M., Johnson, J.G. & Shiroishi, T., Interaction, between cytochalasin B-treated malarian parasites and erythrocytes Attachment and junction formation. J. exp. Med. 149, 172–185 (1979).
Barnwell, J.H., Nicholls, M.E. & Rubinstein, P. In vitro evaluation of the role of the Duffy blood group in erythrocyte invasion by Plasmodium vivax. J. exp. Med. 169, 1795–1799 (1989).
Miller, L.H., Mason, S.J., Clyde, D.F. & McGinnis, M.H. The resistance factor to Plasmodium vivax in blacks. The Duffy blood group phenotype, FyFy. New Engl. J. Med. 295, 302–305 (1976).
Hadley, T.J. et al. Postcapillary venule endothelial cells in kidney express a multispecific chemokine receptor that is structurally and fonctionally identical to the erythroid isoform, which is the duffy blood group antigene. J. clin. Invest. 88, 985–991 (1994).
Wasniowska, K. & Hadley, T.J. The duffy blood group antigen: an update. Trans. Med. Rev. 8, 281–288 (1994).
Faisst, S. & Meyer, S. Compilation of vertebrate-encoded transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 20, 3–26 (1992).
Orkin, S.H. GATA-binding transcription factors in hematopoietic cells. Blood 80, 575–580 (1992).
Rahuel, C., Vinit, M.H., Lemarchandel, V., Cartron, J.P. & Roméo, P.M. Erythroid specific activity of the glycophorin B promoter requires GATA-1 mediated displacement of a represser. EMBO J. 11, 4095–4102 (1992).
Orkin, S.H. Globin gene regulation and switching. Cell 63, 665–668 (1990).
Horuk, R., Zi-xuan, W., Peiper, S.C. & Hesselgesser, J. Identification and characterization of a promiscuous chemokine-binding protein in a human erythroleukemic cell line. J. biol. Chem. 269, 17730–17733 (1994).
Ahuja, S.K., Ozcelik, T., Milatovitch, A., Francke, U. & Murphy, P.M. Molecular evolution of ther human interleukin-8 receptor gene cluster. Nature Genet. 2, 31–36 (1992).
Benz, E.J.J., Tang, T.K., Baklouti, F., Huang, H., Cho, J. & Marchesi, V.T. Tissue specific selection of alternatively spliced exons of the protein 4. 1 gene generates multiple isoforms with altered spectrin actin binding domains. Blood 78, 83a (1991).
Conboy, J.G., Chan, J., Chasis, J.A., Kan, Y.W. & Mohandas, N. Tissue and developement-specific alternative RNA splicing regulates isoforms of erythroid membrane protein 4. 1. J. biol. Chem. 266, 8273–8280 (1991).
Matsuda, M., Sakamoto, N. & Fukumaki, Y. δ-thalassemia caused by disruption of the site for an erythroid-specific transcription factor, GATA-1, in the δ-globin gene promoter. Blood 80, 1347–1351 (1992).
Conboy, J.G. et al. An isoform-specific mutation in the protein 4.1 gene results in hereditary elliptosis and complexe deficiency of protein 4.1 in erythrocytes but not in nonerythroid cells. J. Clin. Invest. 91, 77–82 (1993).
Chérif-Zahar, B. et al. Organization of the gene (RHCE) encoding the human blood gbroup RhCcEe antigens and characteriztion of the promoter region. Genomics. 19, 68–74 (1994).
Colin, Y., Joulin, V., Le Van Kim, C., Roméo, P.H. & Cartron, J.P. Characterization of a new erythroid/megakaryocyte-specific nuclear factor that binds the promoter of the housekeeping human glycophorin C gene. J. biol. Chem. 265, 16729–16732 (1990).
Luckow, B. & Schütz, G. CAT constructions with multiple restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucl. Acids Res. 15, 5490 (1987).
Iwamoto, S., Omi, T., Kajii, E. & Ikemoto, S. Genomic organization of the glycoprotein D gene: Duffy blood group Fya/Fyb Albantigen system is associated with a polymorphism at the 44-amino acid residue. Blood 85, 622–626 (1995).
Chaudhuri, A., Polyakova, J., Zbrzezna, V. & Pogo, O. The coding sequence of Duffy blood group gene in humans and simians: restriction fragment length polymorphism, antibody and malarial parasite specificities, and expression in nonerythroid tissues in Duffy-negative individuals. Blood 85, 615–621 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tournamille, C., Colin, Y., Cartron, J. et al. Disruption of a GATA motif in the Duffy gene promoter abolishes erythroid gene expression in Duffy–negative individuals. Nat Genet 10, 224–228 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0695-224
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0695-224
This article is cited by
-
Genetic differentiation of Plasmodium vivax duffy binding protein in Ethiopia and comparison with other geographical isolates
Malaria Journal (2024)
-
New genetic and epigenetic insights into the chemokine system: the latest discoveries aiding progression toward precision medicine
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2023)
-
Alloimmune hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn: genetics, structure, and function of the commonly involved erythrocyte antigens
Journal of Perinatology (2023)
-
Elucidation of the low-expressing erythroid CR1 phenotype by bioinformatic mining of the GATA1-driven blood-group regulome
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Duffy blood system and G6PD genetic variants in vivax malaria patients from Manaus, Amazonas, Brazil
Malaria Journal (2022)