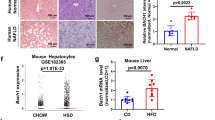
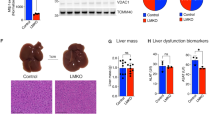
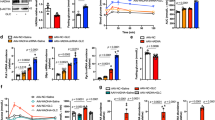
Abstract
Type 2 diabetes is a complex disease that is marked by the dysfunction of glucose and lipid metabolism. Hepatic insulin resistance is especially pathogenic in type 2 diabetes, as it dysregulates fasting and postprandial glucose tolerance and promotes systemic dyslipidemia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease1,2. Mitochondrial dysfunction is closely associated with insulin resistance and might contribute to the progression of diabetes3,4. Here we used previously generated mice5 with hepatic insulin resistance owing to the deletion of the genes encoding insulin receptor substrate-1 (Irs-1) and Irs-2 (referred to here as double-knockout (DKO) mice) to establish the molecular link between dysregulated insulin action and mitochondrial function. The expression of several forkhead box O1 (Foxo1) target genes increased in the DKO liver, including heme oxygenase-1 (Hmox1), which disrupts complex III and IV of the respiratory chain and lowers the NAD+/NADH ratio and ATP production. Although peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α (Ppargc-1α) was also upregulated in DKO liver, it was acetylated and failed to promote compensatory mitochondrial biogenesis or function. Deletion of hepatic Foxo1 in DKO liver normalized the expression of Hmox1 and the NAD+/NADH ratio, reduced Ppargc-1α acetylation and restored mitochondrial oxidative metabolism and biogenesis. Thus, Foxo1 integrates insulin signaling with mitochondrial function, and inhibition of Foxo1 can improve hepatic metabolism during insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edgerton, D.S., Johnson, K.M. & Cherrington, A.D. Current strategies for the inhibition of hepatic glucose production in type 2 diabetes. Front. Biosci. 14, 1169–1181 (2009).
Postic, C. & Girard, J. Contribution of de novo fatty acid synthesis to hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance: lessons from genetically engineered mice. J. Clin. Invest. 118, 829–838 (2008).
Lowell, B.B. & Shulman, G.I. Mitochondrial dysfunction and type 2 diabetes. Science 307, 384–387 (2005).
Kim, J.A., Wei, Y. & Sowers, J.R. Role of mitochondrial dysfunction in insulin resistance. Circ. Res. 102, 401–414 (2008).
Dong, X.C. et al. Inactivation of hepatic Foxo1 by insulin signaling is required for adaptive nutrient homeostasis and endocrine growth regulation. Cell Metab. 8, 65–76 (2008).
Kubota, N. et al. Dynamic functional relay between insulin receptor substrate 1 and 2 in hepatic insulin signaling during fasting and feeding. Cell Metab. 8, 49–64 (2008).
Matsumoto, M., Pocai, A., Rossetti, L., DePinho, R.A. & Accili, D. Impaired regulation of hepatic glucose production in mice lacking the forkhead transcription factor foxo1 in liver. Cell Metab. 6, 208–216 (2007).
Matsumoto, M., Han, S., Kitamura, T. & Accili, D. Dual role of transcription factor FoxO1 in controlling hepatic insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 2464–2472 (2006).
Kamei, Y. et al. Regulation of SREBP1c gene expression in skeletal muscle: role of retinoid X receptor/liver X receptor and forkhead-O1 transcription factor. Endocrinology 149, 2293–2305 (2008).
Kamagate, A. et al. FoxO1 mediates insulin-dependent regulation of hepatic VLDL production in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 118, 2347–2364 (2008).
van der Horst, A. & Burgering, B.M. Stressing the role of FoxO proteins in lifespan and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 440–450 (2007).
Wallace, D.C. Mitochondrial diseases in man and mouse. Science 283, 1482–1488 (1999).
Gottlieb, E., Armour, S.M. & Thompson, C.B. Mitochondrial respiratory control is lost during growth factor deprivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 12801–12806 (2002).
Leone, T.C. et al. PGC-1α deficiency causes multi-system energy metabolic derangements: muscle dysfunction, abnormal weight control and hepatic steatosis. PLoS Biol. 3, e101 (2005).
Wu, Z. et al. Mechanisms controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and respiration through the thermogenic coactivator PGC-1. Cell 98, 115–124 (1999).
Rodgers, J.T. & Puigserver, P. Fasting-dependent glucose and lipid metabolic response through hepatic sirtuin 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 12861–12866 (2007).
Converso, D.P. et al. HO-1 is located in liver mitochondria and modulates mitochondrial heme content and metabolism. FASEB J. 20, 1236–1238 (2006).
Taillé, C. et al. Induction of heme oxygenase-1 inhibits NAD(P)H oxidase activity by down-regulating cytochrome b558 expression via the reduction of heme availability. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 28681–28688 (2004).
González-Halphen, D., Lindorfer, M.A. & Capaldi, R.A. Subunit arrangement in beef heart complex III. Biochemistry 27, 7021–7031 (1988).
Alam, J., Cai, J. & Smith, A. Isolation and characterization of the mouse heme oxygenase-1 gene. Distal 5′ sequences are required for induction by heme or heavy metals. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 1001–1009 (1994).
Baur, J.A. et al. Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet. Nature 444, 337–342 (2006).
Howitz, K.T. et al. Small molecule activators of sirtuins extend Saccharomyces cerevisiae lifespan. Nature 425, 191–196 (2003).
Liu, Y. et al. A fasting inducible switch modulates gluconeogenesis via activator/coactivator exchange. Nature 456, 269–273 (2008).
Kitamura, Y.I. et al. FoxO1 protects against pancreatic beta cell failure through NeuroD and MafA induction. Cell Metab. 2, 153–163 (2005).
Soriano, F.X. et al. Evidence for a mitochondrial regulatory pathway defined by peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1α, estrogen-related receptor-α, and mitofusin 2. Diabetes 55, 1783–1791 (2006).
Brown, M.S. & Goldstein, J.L. Selective versus total insulin resistance: a pathogenic paradox. Cell Metab. 7, 95–96 (2008).
Kunz, W.S. Evaluation of electron-transfer flavoprotein and α-lipoamide dehydrogenase redox states by two-channel fluorimetry and its application to the investigation of β-oxidation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 932, 8–16 (1988).
Lumeng, L., Bremer, J. & Davis, E.J. Suppression of the mitochondrial oxidation of (−)-palmitylcarnitine by the malate-aspartate and α-glycerophosphate shuttles. J. Biol. Chem. 251, 277–284 (1976).
Hwang, J.H. et al. Pharmacological stimulation of NADH oxidation ameliorates obesity and related phenotypes in mice. Diabetes 58, 965–974 (2009).
Kelley, D.E., He, J., Menshikova, E.V. & Ritov, V.B. Dysfunction of mitochondria in human skeletal muscle in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 51, 2944–2950 (2002).
Stump, C.S., Short, K.R., Bigelow, M.L., Schimke, J.M. & Nair, K.S. Effect of insulin on human skeletal muscle mitochondrial ATP production, protein synthesis and mRNA transcripts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 7996–8001 (2003).
Manfredi, G., Yang, L., Gajewski, C.D. & Mattiazzi, M. Measurements of ATP in mammalian cells. Methods 26, 317–326 (2002).
Peterside, I.E., Selak, M.A. & Simmons, R.A. Impaired oxidative phosphorylation in hepatic mitochondria in growth-retarded rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 285, E1258–E1266 (2003).
Friedman, J.R. et al. Orthogonal analysis of C/EBPβ targets in vivo during liver proliferation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 12986–12991 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We thank B. Spiegelman and L.M. Rohas for help with respiration assays, S. Orkin for help with fluorescent assays and R. de Cabo for the communication on flow cytometric assay. We are also grateful to Y. Long for his valuable comments and discussion. This project was supported by US National Institutes of Health grants DK38712 and DK55326 (M.F.W.), American Diabetes Association Mentor-Based Postdoctoral Fellowship 7-08-MN-63 (M.F.W. and Z.C.) and American Diabetes Association Junior Faculty Grant JF-7-07-27 (S.G.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.C. and M.F.W. designed this study. Z.C., S.G., K.C., X.D., R.K. and J.T.R. performed the experiments. Z.C. and M.F.W. analyzed the data. Z.C. and M.F.W. communicated with R.A.D. and P.P. about data interpretation and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–6, Supplementary Table 1 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 875 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Z., Guo, S., Copps, K. et al. Foxo1 integrates insulin signaling with mitochondrial function in the liver. Nat Med 15, 1307–1311 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2049
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2049
This article is cited by
-
FOXO transcription factors as mediators of stress adaptation
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2024)
-
Intermittent dietary methionine deprivation facilitates tumoral ferroptosis and synergizes with checkpoint blockade
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Glycemic Control and Bone in Diabetes
Current Osteoporosis Reports (2022)
-
Sirt1 coordinates with ERα to regulate autophagy and adiposity
Cell Death Discovery (2021)
-
The Role of Mitochondrial Adaptation and Metabolic Flexibility in the Pathophysiology of Obesity and Insulin Resistance: an Updated Overview
Current Obesity Reports (2021)