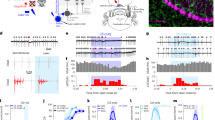
Abstract
Retinal bipolar cells have been assumed to generate purely graded responses to light. To test this idea we imaged the presynaptic calcium transient in live zebrafish. We found that ON, OFF, transient and sustained bipolar cells are all capable of generating fast 'all-or-none' calcium transients modulated by visual stimulation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Masland, R.H. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 877–886 (2001).
Protti, D.A., Flores-Herr, N. & von Gersdorff, H. Neuron 25, 215–227 (2000).
Palmer, M.J. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 572, 747–762 (2006).
Dreosti, E., Odermatt, B., Dorostkar, M. & Lagnado, L. Nat. Methods 6, 883–889 (2009).
Dorostkar, M.M., Dreosti, E., Odermatt, B. & Lagnado, L. J. Neurosci. Methods 188, 141–150 (2010).
Neves, G., Gomis, A. & Lagnado, L. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 15282–15287 (2001).
Burrone, J., Neves, G., Gomis, A., Cooke, A. & Lagnado, L. Neuron 33, 101–112 (2002).
Burrone, J. & Lagnado, L. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 505, 571–584 (1997).
Pan, Z.H. & Hu, H.J. J. Neurophysiol. 84, 2564–2571 (2000).
Zenisek, D., Henry, D., Studholme, K., Yazulla, S. & Matthews, G. J. Neurosci. 21, 4543–4550 (2001).
Cui, J. & Pan, Z.H. Vis. Neurosci. 25, 635–645 (2008).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all of the members of the Lagnado laboratory for discussions that contributed to this work. We also thank the Wellcome Trust for funding (grant 083220).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Experiments were designed by E.D., F.E. and L.L. and performed by E.D., F.E. and L.L. Analysis was carried out by E.D., F.E. and L.L. The manuscript was written by F.E., T.B. and L.L.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figure 1, Supplementary Methods and Algorithm (PDF 234 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dreosti, E., Esposti, F., Baden, T. et al. In vivo evidence that retinal bipolar cells generate spikes modulated by light. Nat Neurosci 14, 951–952 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2841
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2841
This article is cited by
-
An amplitude code transmits information at a visual synapse
Nature Neuroscience (2019)
-
In vivo measurement of afferent activity with axon-specific calcium imaging
Nature Neuroscience (2018)
-
Designed cell consortia as fragrance-programmable analog-to-digital converters
Nature Chemical Biology (2017)
-
Inhibition decorrelates visual feature representations in the inner retina
Nature (2017)
-
Correction-free remotely scanned two-photon in vivo mouse retinal imaging
Light: Science & Applications (2016)