Abstract
The monoclonal antibody 1A1D-2 has been shown to strongly neutralize dengue virus serotypes 1, 2 and 3, primarily by inhibiting attachment to host cells. A crystal structure of its antigen binding fragment (Fab) complexed with domain III of the viral envelope glycoprotein, E, showed that the epitope would be partially occluded in the known structure of the mature dengue virus. Nevertheless, antibody could bind to the virus at 37 °C, suggesting that the virus is in dynamic motion making hidden epitopes briefly available. A cryo-electron microscope image reconstruction of the virus:Fab complex showed large changes in the organization of the E protein that exposed the epitopes on two of the three E molecules in each of the 60 icosahedral asymmetric units of the virus. The changes in the structure of the viral surface are presumably responsible for inhibiting attachment to cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Main
Dengue, yellow fever and West Nile viruses are major human pathogens that are members of the flavivirus genus of the Flaviviridae1 family. Dengue virus (DENV) is the causative agent for dengue fever and the more severe dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF). Although DENV infects approximately 50–100 million people each year2, no effective vaccine has been licensed for human use. Vaccine development has been hampered by the potential complications following secondary DENV infections, which can result in DHF3,4. This frequently occurs when the secondary infection is of a serotype different from the first, possibly because cross-reactive non-neutralizing antibodies from the first infection bind to the virus and promote antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE) of infection in cells expressing Fc-γ receptors. To avoid ADE, a tetravalent vaccine would need to elicit strongly neutralizing antibodies against all four serotypes of DENV.
Flaviviruses consist of an icosahedrally symmetric ectodomain, containing 180 copies of the envelope (E) glycoprotein and 180 copies of the membrane (M) protein anchored in and surrounding a lipid membrane5. The nucleocapsid core within the membrane consists of a positive-sense, 11-kb RNA genome and multiple copies of the capsid protein. In the mature virus, the E protein is arranged into 30 rafts of three parallel dimers5. Crystal structures of the dimeric E protein6,7,8 have been determined for DENV serotypes 2 and 3. The E-protein monomer has three domains, E-DI, E-DII and E-DIII, of which E-DIII is probably involved in recognition of the principal cell receptor9,10,11,12. However, E-DII can also participate in the initial binding to an ancillary receptor, DC-SIGN, thereby possibly enhancing the local concentration of the primary receptor in the vicinity of the virus required for cell entry13.
Neutralizing epitopes are clustered at the tip of E-DII (which is also the location of the fusion peptide9,14), the hinge region between E-DI and E-DII, and the lateral surface of E-DIII7,15. The hinge regions, between E-DI and E-DII and between E-DI and E-DIII, participate in structural rearrangements that occur at low pH as the immature virus is converted into infectious particles8 and in the initial stages of infection when the virus fuses with an endosomal membrane16,17.
Before the fusion of the virus to endosomal membranes, the E dimers dissociate and then reassociate as trimers18. This conformational change can be blocked in West Nile virus (WNV) infection by the monoclonal antibody (mAb) E16 binding to E-DIII19,20. The postfusion, trimeric E-protein structures of tick-borne encephalitis virus16 and DENV17 show that E-DIII rotates by about 70° closer to E-DI relative to its position in the dimeric prefusion structure.
The mAb 1A1D-2 strongly neutralizes DENV serotypes 1, 2 and 3 (Supplementary Fig. 1 online) but does not bind to serotype 4 (ref. 21). We report here the crystal structure of the Fab fragment of the mAb 1A1D-2 complexed with recombinant E-DIII of DENV serotype 2. Interpretation of a cryo-electron microscopy (cryoEM) image reconstruction of Fab 1A1D-2 complexed with DENV, made by using this crystal structure, showed that Fab 1A1D-2 bound to only two of the three E proteins in each of the 60 icosahedral asymmetric units and resulted in the rearrangement of E proteins, thus preventing viral infection.
Results
Crystal structure of the Fab–1A1D-2:E-DIII complex
The recombinant E-DIII protein of DENV serotype 2 was complexed with Fab 1A1D-2. The structures were determined for two crystal forms of the complex (Table 1 and Supplementary Fig. 2a online). Both forms had one complex per crystallographic asymmetric unit. Crystal form 1 diffracted to only 3.8-Å resolution, whereas form 2 diffracted to 3.0-Å resolution. The r.m.s. deviation between equivalent Cα atoms of the two structures using only the constant domain of Fab, the variable domain of Fab or E-DIII were 1.2 Å, 1.7 Å and 1.2 Å, respectively. In addition, the E-DIII structure in the complex was similar to the E-DIII structure in crystallized DENV E protein6,8, with an r.m.s. difference of only 1.1 Å between equivalent Cα atoms. The main difference between the two crystal forms is a 20° change in the elbow angle of the Fab molecule (Supplementary Fig. 2b), consistent with previous observations that the hinge angle in Fab fragments is flexible19,22.
The surface area of the interface between the Fab molecule and E-DIII is 940 Å2, typical of antibody-antigen interactions23. The binding surface on the Fab molecule consists of five of the six complementary determining regions L1, L2, H1, H2 and H3. The E-DIII binding surface is predominantly on one β-strand (residues 305–312), but residues 325, 364, 388 and 390 also contact the Fab molecule (Fig. 1a and Supplementary Table 1a online). There are likely to be about eight hydrogen bonds, three salt bridges and some hydrophobic interactions in the interface. The relative importance of the residues in the contact area was examined by investigating whether site-specific mutant forms of E-DIII (Supplementary Fig. 3 online) could bind to mAb 1A1D-2 using a yeast surface-display system. Mutations of K305E, K307E or K310E completely abolished antibody binding24, consistent with the crystal structure, which showed that these residues participate in making salt bridges and hydrogen bonds with the Fab molecule.
(a) Stereo diagram of the interface between E-DIII and Fab 1A1D-2 in the crystal structure complex. Residues of Fab 1A1D-2 and E-DIII are colored yellow and cyan, respectively. The light (L) and heavy (H) chain of the Fab molecule are indicated in the residue label with subscripts. Oxygen and nitrogen atoms are colored red and blue, respectively. Putative hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines. (b) Footprints of Fab 1A1D-2 (cyan) and E16 (pink) on E-DIII. Residues recognized by both Fabs are colored purple. (c) Ribbon diagram of the E molecule onto which the E-DIII components of the Fab 1A1D-2 and E16 complex crystal structures have been superimposed. E-DI, E-DII and E-DIII are colored red, yellow and blue, respectively. The Fab 1A1D-2 (cyan) and Fab E16 (pink) molecules are shown as Cα backbones. (d) The pseudo atomic–resolution structure of the E-protein arrangement in mature dengue virus (DENV)31. The E-protein molecules at the A, B and C sites in the asymmetric unit of the virus are shaded.
The importance of the β-strand, formed by residues 305–312 (β-strand A9), to the binding of various other neutralizing antibodies against DENV is evident in that several escape mutations to neutralizing antibodies are located within the strand25,26. This region is also recognized by the antibody 4E11, which cross-reacts with and neutralizes all DENV serotypes27,28.
Comparison of the amino acids in the 1A1D-2 DENV2 epitope with other serotypes (Supplementary Table 1b calculated using the program ClustalW, http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/clustalw/), indicated that the DENV2 epitope is closely similar to DENV1 and DENV3, but not DENV4 (similarity score of 45, 45 and 18, respectively). This is consistent with the inability of the antibody to bind DENV4 (ref. 21).
Comparison of mAb 1A1D-2 and E16 binding sites on E-DIII
The neutralizing mAb E16 inhibits WNV infection at a step after attachment, but before fusion20, whereas the mAb 1A1D-2 neutralizes DENV infection of Vero cells, in part by preventing viral attachment10. Although both antibodies bind E-DIII, their footprints barely overlap one another (Fig. 1b,c). Presumably, this difference, at least in part, is likely to account for the difference in their mechanisms of neutralization. The surface accessibility of the E16 and 1A1D-2 epitopes on E-DIII, as determined by crystallography, are different for each of the three E molecules in the native virus icosahedral asymmetric unit, identified as A, B and C in Figure 1d. The epitope recognized by E16 has an area of 1,550 Å2 and is fully exposed on E-DIIIB (E-DIII at B site) and E-DIIIC (E-DIII at C site) of the mature virus, whereas only 54% of the epitope is exposed for the potential binding site on E-DIIIA (E-DIII at A site). This is consistent with the cryoEM reconstruction map of Fab E16 complexed with WNV19, which shows Fab molecules binding only to E-DIIIB and E-DIIIC, but not to E-DIIIA.
In contrast to Fab E16, 18% of the binding surface of Fab 1A1D-2 is buried at all three E-DIIIs in the icosahedral asymmetric unit of the mature virus. This raises the question of how the antibody could bind to any of the E-DIII epitopes. Temperature was found to be crucial in the binding of the antibody (Fig. 2). Inspection of cryoEM micrographs showed that fewer than one-third of the particles were bound by Fab 1A1D-2 when incubated for 30 min at room temperature, whereas nearly all the particles bound Fab at 37 °C. This suggested that higher temperature promotes increased mobility of the E proteins on the surface of the virus, thus transiently exposing the previously hidden part of the epitope and making it available for antibody binding.
Structure of dengue virus 2 complexed with Fab 1A1D-2
The cryoEM reconstruction of Fab 1A1D-2 complexed with DENV2 incubated at 37 °C was determined to 24-Å resolution (Fig. 3). Interpretation of the cryoEM map showed that the E glycoproteins on the viral surface had undergone a major rearrangement (Fig. 4). Such large quaternary structural changes are not uncommon in flaviviruses, as occurs in the maturation of virions29 and in the fusion of virions to cell membranes17,18.
(a) Stereo diagram of the cryoEM reconstruction of DENV complexed with Fab 1A1D-2 at 24-Å resolution. Surface features that are greater than 240 Å (corresponding to the external radius of the uncomplexed mature virus) from the center of the virus are colored yellow, and the remaining surface is colored red. The black triangle represents the asymmetric unit of the virus. (b) Stereo diagram of an asymmetric unit of the cryoEM structure showing the E proteins at the A and C sites complexed with Fab 1A1D-2 molecules and the uncomplexed E molecule at site B. The E molecules with bound antibody at sites A and C have their fusion peptides pointing toward the viral membrane. The Fab 1A1D-2 molecule, E-DI, E-DII, E-DIII and fusion tip are colored cyan, red, yellow, blue and green, respectively.
The interpretation of the cryoEM map (Fig. 3a) was initially guided by the two large, flat features in each icosahedral asymmetric unit, presumably representing the Fab molecules. Therefore, the first fitting operation was to manually position the 1A1D-2:E-DIII crystal structure into the appropriate densities. This showed that the elbow angle found in crystal 2 (Supplementary Fig. 2b) correlated better with the cryoEM density at both of these sites. The initial manual fitting results were optimized using the EMfit program30 (Supplementary Fig. 4 and Supplementary Table 2b online). The positions of all E-DIII domains in the antibody complex were similar to those in the native virus (Figs. 1d and 3b). Location of E-DI-DII at sites A and C (Fig. 3b) in the cryoEM map were predicted by superimposing E-DIII of the E protein as found in the mature virus31 onto the already positioned E-DIIIs complex structure. The E-DI-DII at sites A and C then had to be translated about 15 Å and 8 Å, respectively, to satisfy the nearest densities. The remaining uninterpreted density corresponded to the E molecule at site B (Supplementary Table 2b).
The resultant structure had the parallel E molecules at sites A, B and C in the mature virus (Fig. 1d) rotated counterclockwise (viewed from outside the virus) by roughly 33°, 32° and 73°, respectively (Fig. 3b). As a result, the epitopes on E-DIIIA and E-DIIIC had become completely exposed and their associated E-DIIs had their fusion tip pointing toward the viral lipid envelope (Fig. 3b and Supplementary Fig. 5a–c online). The E molecules at site C seem to make dimers by pairing across the icosahedral two-fold axes (Supplementary Fig. 5b). The E protein at site B had its Fab binding epitope turned inwards. Comparison of the E-protein structures at the A, B and C sites with the structure of the E protein in the mature virus showed that the unliganded E molecule corresponding to the B site had changed little compared to its structure in the mature virus. However, the structure of the other two E molecules with bound Fab molecules at sites A and C caused a change in the position of E-DIII relative to E-DI-DII (Supplementary Fig. 5d).
Discussion
The ability to expose the partially hidden epitope at all E-DIII sites can be explained if it is assumed that icosahedral viruses can engage in 'breathing' motions. Dynamic structural changes have been demonstrated for icosahedral nodavirus32 and rhinovirus33. The breathing exposes internal regions of rhinovirus structural proteins (VP1, VP2 and VP3), making them available for protease cleavage. The motion can be inhibited by certain antiviral compounds that bind into a cavity within VP1 (ref. 33), thereby stabilizing the virus and reducing the extent of the breathing. Apparently, in the present case, the breathing of DENV can expose the 18% of the hidden 1A1D-2 epitope for Fab attachment when incubated at an elevated temperature (Fig. 2), but is insufficient to expose 46% of the hidden surface at the WNV E-DIIIA site to allow binding of Fab E16 (ref. 19). The ability of Fab 1A1D-2 to bind to epitopes near the five-fold (the E-DIIIA site) and three-fold (the E-DIIIC site) vertices, but not elsewhere on the viral surface, suggests that the extent of the breathing motion might be greatest at these vertices.
Although, presumably, breathing exposes the epitopes required for 1A1D-2 binding to DENV, breathing also implies that, in the absence of antibody, the E proteins return to their original positions in the mature virus. Once a Fab molecule has bound, the virus would probably not be able to return to its previous range of dynamic motions because of steric hindrance between the bound Fab molecules and neighboring E proteins. Thus, the Fab molecules may capture transient viral intermediate conformations. However, there is a problem with this concept. If the observed structure were in the normal dynamic range of the viral conformations, then E16 should have captured the same state, as its epitope on E-DIII near the five-fold vertices is completely exposed in the cryoEM structure of the 1A1D-2:virus complex. However, E16 Fabs did not bind to these sites, even at 37 °C (B. Kaufmann, Purdue University, unpublished data). Thus, possibly, once a 1A1D-2 Fab molecule has bound to a transient intermediate conformation, the E proteins plus bound Fab molecules move to positions that do not occur during the normal breathing of the native virus to relieve the steric stress. One caveat is that this analysis assumes that DENV and WNV have the same breathing motion, because E16 binds to WNV and not to DENV. Another possibility is that, once E16 has bound to the fully available B and C sites, then breathing might be diminished or altered, making binding of E16 to any other normally partially hidden epitope impossible. Thus, the structure of the 1A1D-2:virus complex might be a trapped form of a breathing mode rather than a dead-end conformation.
If it is assumed that the particle will tend to conserve its icosahedral symmetry during breathing, then as soon as one antibody has bound, the rest of the virus alters its structure to the antibody-bound conformation. Thus, the binding of one or only a few 1A1D-2 mAbs will make all other E proteins more accessible for antibody binding. Hence, a low concentration of antibody would be sufficient to alter the surface structure of the virus. This cascade mechanism is supported by the observation that some particles seen on micrographs of DENV incubated with Fab 1A1D-2 at room temperature were covered by Fab molecules, whereas others had none (Fig. 2).
The mAb 1A1D-2 probably inhibits DENV attachment by several different mechanisms. One block to infection could be the result of the antibody altering the spatial distances between the glycans on the E proteins and, therefore, inhibiting the interaction of the virus with its ancillary attachment receptor, DC-SIGN13,34. Another block to infection may be that the antibody binding to DIII of the E glycoproteins prevents binding of the virus to its primary entry receptor9,12.
An understanding of the mechanism of neutralization of an antibody could elucidate its likelihood for promoting ADE at a given concentration. All neutralizing antibodies can promote ADE in vitro at subneutralizing concentrations35,36,37,38. Recent stoichiometric analysis of flavivirus antibody binding to virus suggests that there is a threshold occupancy required for neutralization38. Concentrations of antibody that fall below this threshold or antibodies that never reach this threshold, even at maximal binding, will enhance infection in vitro in cells expressing Fc-γ receptors. The mechanism of antibody neutralization may determine the occupancy requirement for inhibition of infection and, therefore, influence the range of concentration that promotes ADE. Antibodies that neutralize solely by sterically blocking receptor attachment may require higher concentrations for complete neutralization and, therefore, have a greater range of concentration for sustaining ADE. Indeed, this was recently observed with DII-specific mAbs against WNV14. In contrast, mAbs such as 1A1D-2 that promote a cascade of E-protein rearrangements on DENV may have lower occupancy requirements for neutralization. Vaccines that consist of an epitope recognized by mAb 1A1D-2 may thus elicit an antibody response with greater inhibitory activity and less possibility of enhancing infection over a wider range of antibody concentration.
Methods
Neutralization assay.
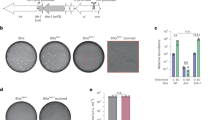
To determine the concentration of mAb required to reduce the number of plaques on BHK-21 cells, increasing concentrations of mAb 1A1D-2 were added to 50 plaque-forming units (p.f.u.) of DENV and incubated at 37 °C for 1 h. We then added 300 μl of the mixture to a monolayer of BHK-21 cells in a 6-well plate and incubated for 1 h at 37 °C. Supernatant was removed and 3 ml of 1.0% (w/v) carboxyl methyl cellulose in MEM plus 5% (v/v) FCS was layered onto the infected cells. After further incubation at 34 °C for 8 d, the wells were stained with 0.5% (w/v) crystal violet dissolved in 25% (v/v) formaldehyde to visualize the plaques. Percentage of plaque reduction was calculated as:

1A1D-2 neutralized DENV serotypes 1, 2 and 3, although DENV3 was least sensitive to this antibody (Supplementary Fig. 1).
Crystallization of the 1A1D-2 Fab:E-DIII complex.
A two-fold molar excess of E-DIII (Supplementary Methods online) was added to 1A1D-2 Fab (Supplementary Methods) and incubated at room temperature for 2 h. The complex was purified with a Superdex 75 column (GE Healthcare) in 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl and 0.01% (w/v) sodium azide, and concentrated to 2 mg ml−1. Successful crystallization conditions were 0.1 M MES pH 5.8, 12% (w/v) PEG 3350 and 0.1 M MES, pH 5.4 and 11–13% (w/v) PEG 2000. Both kinds of crystals were needle-shaped with maximum dimensions of 100 × 30 × 30 μm. The crystals were frozen using 25–28% (w/v) PEG 400 as a cryoprotectant in addition to the mother liquor.
Crystallographic structure determination.
Diffraction data of both crystal forms were collected using a wavelength of 0.979 Å at 100 K on beamline 23ID at the Advanced Photon Source. The data were indexed and scaled using HKL2000 (ref. 39; Table 1). Both crystal forms belong to space group C2, differing primarily in only a 10% change of the monoclinic b axis. The structures of both crystal forms were solved by molecular replacement using the program MOLREP40. Several immunoglobulin structures were used as search models before a good solution was attained for each of the crystal forms (PDB code 1A3R and 1BBD for crystal forms 1 and 2, respectively). The trial structures were initially refined as rigid bodies using the CNS program system41. Electron density corresponding to E-DIII was found to be adjacent to the hypervariable region, as expected. The E-DIII and Fab 1A1D-2 molecules (Supplementary Methods) were modeled into the electron density using the program O42. Coordinates were refined with the program CNS41 using reflections between 20-Å and 3.8-Å spacing for crystal form 1 and between 20-Å and 3.0-Å spacing for crystal form 2 (Table 1).
Mapping of mAb 1AID-2 epitope by yeast surface display.
We expressed DENV2 (strain 16681) E-DIII (residues 296–415) of E in yeast15 by engineering BamHI and XhoI restriction enzyme sites at the 5′ and 3′ ends of the E-DIII gene, using PCR amplification from an infectious cDNA clone43. This fragment was cloned into the BamHI and XhoI sites of the pYD1 vector (Invitrogen) and expressed in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain EBY100. Single point mutations at residues Thr303, Lys305, Lys307, Lys310 and Asn390 were made using the QuikChange mutagenesis kit (Stratagene). Yeast that expressed mutant serotype 2 DENV E proteins was incubated with 50 μl of mAb (25 μg ml−1) on ice for30 min. The yeast was washed three times with PBS supplemented with 1 mg ml−1 BSA, incubated with a 1:500 dilution of a goat anti-mouse IgG that had been conjugated to Alexa Fluor 647 (Invitrogen), and analyzed using a Becton Dickinson FACSCaliber flow cytometer.
Cryo-electron microscopy image reconstruction.
DENV2 New Guinea C strain was mixed with Fab 1A1D-2 at a concentration of one molecule of Fab for every E protein on the surface of the virus. The complex was incubated for 30 min either at room temperature or at 37 °C, followed by 2 h at 4 °C. Nearly all the particles incubated at 37 °C retained their 'spikey-rough' appearance after the temperature had been lowered to 4 °C, showing that the antibody was still bound. In contrast, only about one-third of the particles had a spikey-rough appearance when incubated at room temperature and then kept at 4 °C. Thus, the presence of antibody complexed with the virus at 37 °C on most of the particles showed that only a few or no particles had reverted to their original conformation when the temperature was lowered back to 4 °C. Preincubation at 4 °C before freezing might have improved the homogeneity of the sample by reducing the 'breathing' motion.
The virus:FAb complex suspension was flash frozen on holey carbon grids in liquid ethane. Micrographs of the frozen complex were made with a CM200 FEG transmission electron microscope (Philips) using a calibrated magnification of 51,040 and an electron dose of approximately 25 e− per Å2. The micrographs were digitized with a Zeiss SCAI scanner with a 2.74-Å separation between pixels. Particles were boxed and normalized using the program EMAN44. The micrographs were underfocused by 2.8–3.6 μm. Phases, but not amplitudes, were corrected by an appropriate calculation of the contrast transfer function. Uncomplexed West Nile virus was used as a starting model for image reconstruction. The orientations of the particles were determined using the program SPIDER45. The three-dimensional electron density map was calculated using the program XMIPP46, which had been modified to handle icosahedral symmetry. Out of a total of 2,885 boxed particles, 2,186 were used for the reconstruction of the 37 °C data to achieve a resolution of 24 Å, determined by dividing the particles into two equal sets and noting the resolution at which the Fourier shell correlation coefficient fell below 0.5 (Fig. 3a and Supplementary Table 2a, data set 3). The two leaflets of the lipid bilayers in the viral membrane were not resolved from each other, suggesting some heterogeneity in the sample.
To verify the validity of the reconstruction, a cryoEM density map generated from 532 particles using the sample incubated at room temperature (Supplementary Table 2a, data set 1) was compared with a reconstruction using a 540-particle subset of the 37 °C data (Supplementary Table 2a, data set 2). These two maps showed similar density distributions corresponding to a Fourier shell correlation greater than 0.5 at a resolution of 38 Å, similar to the resolution for both ∼500 particle data sets (Supplementary Table 2a).
Accession codes.
Coordinates for crystal forms 1 and 2 of the Fab 1A1D2:E-DIII complexes have the PDB accession codes 2R69 and 2R29, respectively. The cryoEM map of the Fab complexed with native DENV has been deposited with The European Bioinformatics Institute and has the accession code EMD-1418. The coordinate for the fitted Fab and E molecules into the cryoEM map has the PDB accession code 2R6P.
Note: Supplementary information is available on the Nature Structural & Molecular Biology website.
References
Lindenbach, B.D. & Rice, C.M. Flaviviridae: the viruses and their replication. In Fields Virology Vol. II (eds. Knipe, D.M. et al.) 991–1042 (Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, 2001).
Halstead, S.B. Pathogenesis of dengue: challenges to molecular biology. Science 239, 476–481 (1988).
Halstead, S.B., Nimmannitya, S. & Margiotta, M.R. Dengue and chikungunya virus infection in man in Thailand, 1962–1964. II Observations on disease in outpatients. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 18, 972–983 (1969).
Halstead, S.B., Chow, J.S. & Marchette, N.J. Immunological enhancement of dengue virus replication. Nat. New Biol. 243, 24–25 (1973).
Kuhn, R.J. et al. Structure of dengue virus: implications for flavivirus organization, maturation, and fusion. Cell 108, 717–725 (2002).
Modis, Y., Ogata, S., Clements, D. & Harrison, S.C. A ligand-binding pocket in the dengue virus envelope glycoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 6986–6991 (2003).
Modis, Y., Ogata, S., Clements, D. & Harrison, S.C. Variable surface epitopes in the crystal structure of dengue virus type 3 envelope glycoprotein. J. Virol. 79, 1223–1231 (2005).
Zhang, Y. et al. Conformational changes of the flavivirus E glycoprotein. Structure 12, 1607–1618 (2004).
Rey, F.A. et al. The envelope glycoprotein from tick-borne encephalitis virus at 2 Å resolution. Nature 375, 291–298 (1995).
Crill, W.D. & Roehrig, J.T. Monoclonal antibodies that bind to domain III of dengue virus E glycoprotein are the most efficient blockers of virus adsorption to Vero cells. J. Virol. 75, 7769–7773 (2001).
Bhardwaj, S. et al. Biophysical characterization and vector-specific antagonist activity of domain III of the tick-borne flavivirus envelope protein. J. Virol. 75, 4002–4007 (2001).
Hung, J.-J. et al. An external loop region of domain III of dengue virus type 2 envelope protein is involved in serotype-specific binding to mosquito but not mammalian cells. J. Virol. 78, 378–388 (2004).
Pokidysheva, E. et al. Cryo-EM reconstruction of dengue virus in complex with the carbohydrate recognition domain of DC-SIGN. Cell 124, 485–493 (2006).
Oliphant, T. et al. Antibody recognition and neutralization determinants on domains I and II of West Nile virus envelope protein. J. Virol. 80, 12149–12159 (2006).
Oliphant, T. et al. Development of a humanized monoclonal antibody with therapeutic potential against West Nile virus. Nat. Med. 11, 522–530 (2005).
Bressanelli, S. et al. Structure of a flavivirus envelope glycoprotein in its low-pH-induced membrane fusion conformation. EMBO J. 23, 728–738 (2004).
Modis, Y., Ogata, S., Clements, D. & Harrison, S.C. Structure of the dengue virus envelope protein after membrane fusion. Nature 427, 313–319 (2004).
Stiasny, K. et al. Structural requirements for low-pH-induced rearrangements in the envelope glycoprotein of tick-borne encephalitis virus. J. Virol. 70, 8142–8147 (1996).
Kaufmann, B. et al. West Nile virus in complex with the Fab fragment of a neutralizing monoclonal antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 12400–12404 (2006).
Nybakken, G.E. et al. Structural basis of West Nile virus neutralization by a therapeutic antibody. Nature 437, 764–769 (2005).
Roehrig, J.T., Bolin, R.A. & Kelly, R.G. Monoclonal antibody mapping of the envelope glycoprotein of the dengue 2 virus, Jamaica. Virology 246, 317–328 (1998).
Harris, L.J. et al. The three-dimensional structure of an intact monoclonal antibody for canine lymphoma. Nature 360, 369–372 (1992).
Davies, D.R., Padlan, E.A. & Sheriff, S. Antibody-antigen complexes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 59, 439–473 (1990).
Sukupolvi-Petty, S. et al. Type- and subcomplex-specific neutralizing antibodies against domain III of dengue virus type 2 envelope protein recognize adjacent epitopes. J. Virol. 81, 12816–12826 (2007).
Lin, B., Parrish, C.R., Murray, J.M. & Wright, P.J. Localization of a neutralizing epitope on the envelope protein of dengue virus type 2. Virology 202, 885–890 (1994).
Lok, S.-M., Ng, M.L. & Aaskov, J.G. Amino acid and phenotypic changes in dengue 2 virus associated with escape from neutralization by IgM antibody. J. Med. Virol. 65, 315–323 (2001).
Lisova, O., Hardy, F., Petit, V. & Bedouelle, H. Mapping to completeness and transplantation of a group-specific, discontinuous, neutralizing epitope in the envelope protein of dengue virus. J. Gen. Virol. 88, 2387–2397 (2007).
Thullier, P. et al. Mapping of a dengue virus neutralizing epitope critical for the infectivity of all serotypes: insight into the neutralization mechanism. J. Gen. Virol. 82, 1885–1892 (2001).
Zhang, Y. et al. Structures of immature flavivirus particles. EMBO J. 22, 2604–2613 (2003).
Rossmann, M.G., Bernal, R. & Pletnev, S.V. Combining electron microscopic with X-ray crystallographic structures. J. Struct. Biol. 136, 190–200 (2001).
Zhang, W. et al. Visualization of membrane protein domains by cryo-electron microscopy of dengue virus. Nat. Struct. Biol. 10, 907–912 (2003).
Bothner, B. et al. Evidence of viral capsid dynamics using limited proteolysis and mass spectrometry. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 673–676 (1998).
Lewis, J.K., Bothner, B., Smith, T.J. & Siuzdak, G. Antiviral agent blocks breathing of the common cold virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 6774–6778 (1998).
Davis, C.W. et al. The location of asparagine-linked glycans on West Nile virions controls their interactions with CD209 (dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3 grabbing nonintegrin). J. Biol. Chem. 281, 37183–37194 (2006).
Morens, D.M., Larsen, L.K. & Halstead, S.B. Study of the distribution of antibody-dependent enhancement determinants on dengue 2 isolates using dengue 2-derived monoclonal antibodies. J. Med. Virol. 22, 163–167 (1987).
Morens, D.M. & Halstead, S.B. Measurement of antibody-dependent infection enhancement of four dengue virus serotypes by monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. J. Gen. Virol. 71, 2909–2914 (1990).
Morens, D.M. Antibody-dependent enhancement of infection and the pathogenesis viral disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 19, 500–512 (1994).
Pierson, T.C. et al. The stoichiometry of antibody-mediated neutralization and enhancement of West Nile virus infection. Cell Host Microbe 1, 135–145 (2007).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326 (1997).
Vagin, A. & Teplyakov, A. MOLREP: an automated program for molecular replacement. J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 1022–1025 (1997).
Brünger, A.T. et al. Crystallography and NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. 54, 905–921 (1998).
Jones, T.A., Zou, J.Y., Cowan, S.W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr. A 47, 110–119 (1991).
Kinney, R.M. et al. Construction of infectious cDNA clones for dengue 2 virus: strain 16681 and its attenuated vaccine derivative, strain PDK-53. Virology 230, 300–308 (1997).
Ludtke, S.J., Baldwin, P.R. & Chiu, W. EMAN: semiautomated software for high-resolution single-particle reconstructions. J. Struct. Biol. 128, 82–97 (1999).
Frank, J. et al. SPIDER and WEB: processing and visualization of images in 3D electron microscopy and related fields. J. Struct. Biol. 116, 190–199 (1996).
Sorzano, C.O.S. et al. XMIPP: a new generation of an open-source image processing package for electron microscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 148, 194–204 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Choi for help with the crystallography, W. Zhang for advice concerning the cryoEM reconstruction and P.G. Leiman for help in data collection. We also thank Argonne National Laboratory and the Advanced Photon Source (Argonne, Illinois, USA) staff at beamline GM/CA 23 for help and encouragement with diffraction data collection. Use of the Advanced Photon Source was supported by the US Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357. The GM/CA CAT is funded by the US National Institute of General Medical Science (Y1-GM-1104) and the US National Cancer Institute (Y1-CO-1020). We thank S. Johnson for help with the sequencing of the 1A1D-2 VH and VL domains. The work was supported by the Pediatric Dengue Vaccine Initiative (TR-17) to R.J.K. and M.G.R. and a US National Institutes of Health (NIH) National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases program project grant (AI055672) awarded to R.J.K., M.G.R. and others. M.S.D. and D.H.F. were supported by the Midwest Regional Center of Excellence for Biodefense and Emerging Infectious Disease Research (V54 A1057160). R.J.K. and M.G.R. also had support from Region V Great Lakes Regional Center of Excellence (NIH award U54 AI057153).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.-M.L. prepared Fab fragments and viruses, conducted the neutralization and temperature experiments and solved both the crystal and cryoEM structures of the Fab complex. V.K. developed software for the cryoEM reconstruction. G.E.N. and D.H.F. provided E-DIII. H.A.H., A.J.B. and P.R.C. took the cryoEM images. J.T.R. and D.S. provided the hybridomas and produced antibodies, respectively. S.S.-P. and M.S.D. mapped Fab 1A1D-2 epitope on E-DIII by yeast expression system. R.J.K. initiated the project, established collaborations and advised on writing of the paper. M.G.R. supervised the project and, together with S.-M.L., wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–5, Supplementary Tables 1 and 2, and Supplementary Methods (PDF 837 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lok, SM., Kostyuchenko, V., Nybakken, G. et al. Binding of a neutralizing antibody to dengue virus alters the arrangement of surface glycoproteins. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15, 312–317 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1382
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1382
This article is cited by
-
The dengue-specific immune response and antibody identification with machine learning
npj Vaccines (2024)
-
Antiviral neutralizing antibodies: from in vitro to in vivo activity
Nature Reviews Immunology (2023)
-
Designer DNA nanostructures for viral inhibition
Nature Protocols (2022)
-
Discovery of B-cell epitopes for development of dengue vaccines and antibody therapeutics
Medical Microbiology and Immunology (2022)
-
Fever as an evolutionary agent to select immune complexes interfaces
Immunogenetics (2022)