Abstract
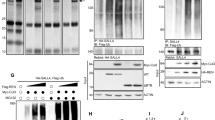
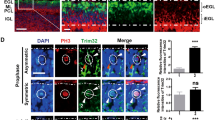
Deregulation of the Rb/E2F tumor suppressor complex and aberrantion of Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling are documented across the spectrum of human malignancies. Exaggerated de novo lipid synthesis is also found in certain highly proliferative, aggressive tumors. Here, we show that in Shh-driven medulloblastomas, Rb is inactivated and E2F1 is upregulated, promoting lipogenesis. Extensive lipid accumulation and elevated levels of the lipogenic enzyme fatty acid synthase (FASN) mark those tumors. In primary cerebellar granule neuron precursors (CGNPs), proposed Shh-associated medulloblastoma cells-of-origin, Shh signaling triggers E2F1 and FASN expression, whereas suppressing fatty acid oxidation (FAO), in a smoothened-dependent manner. In the developing cerebellum, E2F1 and FASN co-localize in proliferating CGNPs. in vivo and in vitro, E2F1 is required for FASN expression and CGNP proliferation, and E2F1 knockdown impairs Shh-mediated FAO inhibition. Pharmacological blockade of Rb inactivation and/or lipogenesis inhibits CGNP proliferation, drives medulloblastoma cell death and extends survival of medulloblastoma-bearing animals In vivo. These findings identify a novel mechanism through which Shh signaling links cell cycle progression to lipid synthesis, through E2F1-dependent regulation of lipogenic enzymes. These findings pertinent to the etiology of tumor metabolism also underscore the key role of the Shh→E2F1→FASN axis in regulating de novo lipid synthesis in cancers, and as such its value as a global therapeutic target in hedgehog-dependent and/or Rb-inactivated tumors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahamowicz M, Grodzicky T, Li Y, Panaritis C, du Berger R, Cjte R et al. (2001). APAF1 is a key transcriptional target for p53 in the regulation of neuronal cell death. Arthritis Rheum 44: 2331–2337.
Beachy PA, Karhadkar SS, Berman DM . (2004). Tissue repair and stem cell renewal in carcinogenesis. Nature 432: 324–331.
Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Hallahan AR, Pritchard JI, Eberhart CG, Watkins DN et al. (2002). Medulloblastoma growth inhibition by hedgehog pathway blockade. Science 297: 1559–1561.
Bhatia B, Northcott PA, Hambardzumyan D, Govindarajan B, Brat DJ, Arbiser JL et al. (2009). Tuberous sclerosis complex suppression in cerebellar development and medulloblastoma: separate regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin activity and p27Kip1 localization. Cancer Res 69: 7224–7234.
Chiang C, Litingtung Y, Lee E, Young KE, Corden JL, Westphal H et al. (1996). Cyclopia and defective axial patterning in mice lacking Sonic hedgehog gene function. Nature 383: 407–413.
Cooper-Kuhn CM, Vroemen M, Brown J, Ye H, Thompson MA, Winkler J et al. (2002). Impaired adult neurogenesis in mice lacking the transcription factor E2F1. Mol Cell Neurosci 21: 312–323.
Corcoran RB, Scott MP . (2006). Oxysterols stimulate Sonic hedgehog signal transduction and proliferation of medulloblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 8408–8413.
Dahmane N, Ruiz-i-Altaba A . (1999). Sonic hedgehog regulates the growth and patterning of the cerebellum. Development 126: 3089–3100.
DeBerardinis RJ, Mancuso A, Daikhin E, Nissim I, Yudkoff M, Wehrli S et al. (2007). Beyond aerobic glycolysis: transformed cells can engage in glutamine metabolism that exceeds the requirement for protein and nucleotide synthesis. Pro Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 19345–19350.
Djouadi F, Bonnefont JP, Munnich A, Bastin J . (2003). Characterization of fatty acid oxidation in human muscle mitochondria and myoblasts. Mol Genet Metab 78: 112–118.
Dowell P, Hu Z, Lane MD . (2005). Monitoring energy balance: metabolites of fatty acid synthesis as hypothalamic sensors. Annu Rev Biochem 74: 515–534.
Dynlacht BD, Moberg K, Lees JA, Harlow E, Zhu L . (1997). Specific regulation of E2F family members by cyclin-dependent kinases. Mole Cell Biol 17: 3867–3875.
Eberhart CG . (2008). Even cancers want commitment: lineage identity and medulloblastoma formation. Cancer Cell 14: 105–107.
Fernandez LA, Northcott PA, Dalton J, Fraga C, Ellison D, Angers S et al. (2009). YAP1 is amplified and up-regulated in hedgehog-associated medulloblastomas and mediates Sonic hedgehog-driven neural precursor proliferation. Genes Dev 23: 2729–2741.
Ferretti E, Di Marcotullio L, Gessi M, Mattei T, Greco A, Po A et al. (2006). Alternative splicing of the ErbB-4 cytoplasmic domain and its regulation by hedgehog signaling identify distinct medulloblastoma subsets. Oncogene 25: 7267–7273.
Gao P, Tchernyshyov I, Chang TC, Lee YS, Kita K, Ochi T et al. (2009). c-Myc suppression of miR-23a/b enhances mitochondrial glutaminase expression and glutamine metabolism. Nature 458: 762–765.
Guo D, Hildebrandt IJ, Prins RM, Soto H, Mazzotta MM, Dang J et al. (2009a). The AMPK agonist AICAR inhibits the growth of EGFRvIII-expressing glioblastomas by inhibiting lipogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 12932–12937.
Guo D, Prins RM, Dang J, Kuga D, Iwanami A, Soto H et al. (2009b). EGFR signaling through an Akt-SREBP-1-dependent, rapamycin-resistant pathway sensitizes glioblastomas to antilipogenic therapy. Sci Signal 2: ra82.
Hahn H, Wicking C, Zaphiropoulous PG, Gailani MR, Shanley S, Chidambaram A et al. (1996). Mutations of the human homolog of Drosophila patched in the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Cell 85: 841–851.
Hammerschmidt M, Bitgood MJ, McMahon AP . (1996). Protein kinase A is a common negative regulator of Hedgehog signaling in the vertebrate embryo. Genes Dev 10: 647–658.
Hatton BA, Villavicencio EH, Tsuchiya KD, Pritchard JI, Ditzler S, Pullar B et al. (2008). The Smo/Smo model: hedgehog-induced medulloblastoma with 90% incidence and leptomeningeal spread. Cancer Res 68: 1768–1776.
Helin K, Wu CL, Fattaey AR, Lees JA, Dynlacht BD, Ngwu C et al. (1993). Heterodimerization of the transcription factors E2F-1 and DP-1 leads to cooperative trans-activation. Genes Dev 7: 1850–1861.
Hepker J, Wang QT, Motzny CK, Holmgren R, Orenic TV . (1997). Drosophila cubitus interruptus forms a negative feedback loop with patched and regulates expression of Hedgehog target genes. Development 124: 549–558.
Hernando E, Nahle Z, Juan G, Diaz-Rodriguez E, Alaminos M, Hemann M et al. (2004). Rb inactivation promotes genomic instability by uncoupling cell cycle progression from mitotic control. Nature 430: 797–802.
Ho KS, Scott MP . (2002). Sonic hedgehog in the nervous system: functions, modifications and mechanisms. Curr Opin Neurobiol 12: 57–63.
Hsieh MCF, Das D, Sambandam N, Zhang MQ, Nahle Z . (2008). Regulation of the PDK4 isozyme by the Rb-E2F1 complex. J Biol Chem 283: 27410–27417.
Incardona JP, Eaton S . (2000). Cholesterol in signal transduction. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12: 193–203.
Johnson DG, Ohtani K, Nevins JR . (1994). Autoregulatory control of E2F1 expression in response to positive and negative regulators of cell cycle progression. Genes Dev 8: 1514–1525.
Johnson RL, Rothman AL, Xie J, Goodrich LV, Bare JW, Bonifas JM et al. (1996). Human homolog of patched, a candidate gene for the basal cell nevus syndrome. Science 272: 1668–1671.
Jones RG, Thompson CB . (2009). Tumor suppressors and cell metabolism: a recipe for cancer growth. Genes Dev 23: 537–548.
Karpen HE, Bukowski JT, Hughes T, Gratton JP, Sessa WC, Gailani MR . (2001). The sonic hedgehog receptor patched associates with caveolin-1 in cholesterol-rich microdomains of the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem 276: 19503–19511.
Kenney AM, Cole MD, Rowitch DH . (2003). Nmyc upregulation by sonic hedgehog signaling promotes proliferation in developing cerebellar granule neuron precursors. Development 130: 15–28.
Kenney AM, Rowitch DH . (2000). Sonic hedgehog promotes G(1) cyclin expression and sustained cell cycle progression in mammalian neuronal precursors. Mol Cell Biol 20: 9055–9067.
Kim EK, Miller I, Aja S, Landree LE, Pinn M, McFadden J et al. (2004). C75, a fatty acid synthase inhibitor, reduces food intake via hypothalamic AMP-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 279: 19970–19976.
Kim JW, Tchernyshyov I, Semenza GL, Dang CV . (2006). HIF-1-mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase: a metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Cell Metab 3: 177–185.
Kimura H, Ng JM, Curran T . (2008). Transient inhibition of the Hedgehog pathway in young mice causes permanent defects in bone structure. Cancer Cell 13: 249–260.
Kolf-Clauw M, Chevy F, Wolf C, Siliart B, Citadelle D, Roux C . (1996). Inhibition of 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase by the teratogen AY9944: a rat model for Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. Teratology 54: 115–125.
Landree LE, Hanlon AL, Strong DW, Rumbaugh G, Miller IM, Thupari JN et al. (2004). C75, a fatty acid synthase inhibitor, modulates AMP-activated protein kinase to alter neuronal energy metabolism. J Biol Chem 279: 3817–3827.
Lees JA, Saito M, Vidal M, Valentine M, Look T, Harlow E et al. (1993). The retinoblastoma protein binds to a family of E2F transcription factors. Mole Cell Biol 13: 7813–7825.
Leung C, Lingbeek M, Shakhova O, Liu J, Tanger E, Saremaslani P et al. (2004). Bmi1 is essential for cerebellar development and is overexpressed in human medulloblastomas. Nature 428: 337–341.
Loftus TM, Jaworsky DE, Frehywot GL, Townsend CA, Ronnett GV, Lane MD et al. (2000). Reduced food intake and body weight in mice treated with fatty acid synthase inhibitors. Science 288: 2379–2381.
Marino S, Vooijs M, van Der Gulden H, Jonkers J, Berns A . (2000). Induction of medulloblastomas in p53-null mutant mice by somatic inactivation of Rb in the external granular layer cells of the cerebellum. Genes Dev 14: 994–1004.
McCullough LD, Zeng Z, Li H, Landree LE, McFadden J, Ronnett GV . (2005). Pharmacological inhibition of AMP-activated protein kinase provides neuroprotection in stroke. J Biol Chem 280: 20493–20502.
Menendez JA . (2009). Fine-tuning the lipogenic/lipolytic balance to optimize the metabolic requirements of cancer cell growth: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Biochim Biophys Acta.
Menendez JA, Lupu R . (2007). Fatty acid synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 7: 763–777.
Nahle Z, Polakoff J, Davuluri RV, McCurrach ME, Jacobson MD, Narita M et al. (2002). Direct coupling of the cell cycle and cell death machinery by E2F. Nat Cell Biol 4: 859–864.
Northcott PA, Fernandez LA, Hagan JP, Ellison DW, Grajkowska W, Gillespie Y et al. (2009). The miR-17/92 polycistron is up-regulated in sonic hedgehog-driven medulloblastomas and induced by N-myc in sonic hedgehog-treated cerebellar neural precursors. Cancer Res 69: 3249–3255.
Nowak K, Kerl K, Fehr D, Kramps C, Gessner C, Killmer K et al. (2006). BMI1 is a target gene of E2F-1 and is strongly expressed in primary neuroblastomas. Nucleic Acids Res 34: 1745–1754.
Oliver TG, Grasfeder LL, Carroll AL, Kaiser C, Gillingham CL, Lin SM et al. (2003). Transcriptional profiling of the Sonic hedgehog response: a critical role for N-myc in proliferation of neuronal precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 7331–7336.
Olson MV, Johnson DG, Jiang H, Xu J, Alonso MM, Aldape KD et al. (2007). Transgenic E2F1 expression in the mouse brain induces a human-like bimodal pattern of tumors. Cancer Res 67: 4005–4009.
Orita H, Coulter J, Lemmon C, Tully E, Vadlamudi A, Medghalchi SM et al. (2007). Selective inhibition of fatty acid synthase for lung cancer treatment. Clin Cancer Res 13: 7139–7145.
Orita H, Coulter J, Tully E, Kuhajda FP, Gabrielson E . (2008). Inhibiting fatty acid synthase for chemoprevention of chemically induced lung tumors. Clin Cancer Res 14: 2458–2464.
Parathath SR, Mainwaring LA, Fernandez LA, Campbell DO, Kenney AM . (2008). Insulin receptor substrate 1 is an effector of sonic hedgehog mitogenic signaling in cerebellar neural precursors. Development 135: 3291–3300.
Platt KA, Michaud J, Joyner AL . (1997). Expression of the mouse Gli and Ptc genes is adjacent to embryonic sources of hedgehog signals suggesting a conservation of pathways between flies and mice. Mech Dev 62: 121–135.
Ren B, Cam H, Takahashi Y, Volkert T, Terragni J, Young RA et al. (2002). E2F integrates cell cycle progression with DNA repair, replication, and G(2)/M checkpoints. Genes Dev 16: 245–256.
Sakamaki T, Casimiro MC, Ju X, Quong AA, Katiyar S, Liu M et al. (2006). Cyclin D1 determines mitochondrial function in vivo. Mol Cell Biol 26: 5449–5469.
Sjostrom SK, Finn G, Hahn WC, Rowitch DH, Kenney AM . (2005). The cdk1 complex plays a prime role in regulating N-myc phosphorylation and turnover in neural precursors. Dev Cell 9: 327–338.
Suh JM, Gao X, McKay J, McKay R, Salo Z, Graff JM . (2006). Hedgehog signaling plays a conserved role in inhibiting fat formation. Cell Metab 3: 25–34.
Teglund S, Toftgard R . (2010). Hedgehog beyond medulloblastoma and basal cell carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta 1805: 181–208.
Thupari JN, Kim E-K, Moran TH, Ronnett GV, Kuhajda FP . (2004). Chronic C75 treatment of diet-induced obese mice increases fat oxidation and reduces food intake to reduce adipose mass. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 287: E97–E104.
Thupari JN, Landree LE, Ronnett GV, Kuhajda FP . (2002). C75 increases peripheral energy utilization and fatty acid oxidation in diet-induced obesity. Pro Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 9498–9502.
Tong X, Zhao F, Thompson CB . (2009). The molecular determinants of de novo nucleotide biosynthesis in cancer cells. Curr Opin Genet Dev 19: 32–37.
Uziel T, Karginov FV, Xie S, Parker JS, Wang YD, Gajjar A et al. (2009). The miR-17∼92 cluster collaborates with the Sonic Hedgehog pathway in medulloblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 2812–2817.
Wechsler-Reya R, Scott MP . (2001). The developmental biology of brain tumors. Annu Rev Neurosci 24: 385–428.
Wechsler-Reya RJ, Scott MP . (1999). Control of neuronal precursor proliferation in the cerebellum by Sonic Hedgehog [see comments]. Neuron 22: 103–114.
Wetmore C . (2003). Sonic hedgehog in normal and neoplastic proliferation: insight gained from human tumors and animal models. Curr Opin Genet Dev 13: 34–42.
Wise DR, DeBerardinis RJ, Mancuso A, Sayed N, Zhang XY, Pfeiffer HK et al. (2008). Myc regulates a transcriptional program that stimulates mitochondrial glutaminolysis and leads to glutamine addiction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 18782–18787.
Yauch RL, Dijkgraaf GJ, Alicke B, Januario T, Ahn CP, Holcomb T et al. (2009). Smoothened mutation confers resistance to a hedgehog pathway inhibitor in medulloblastoma. Science 326: 572–574.
Zhu L, Enders G, Lees JA, Beijersbergen RL, Bernards R, Harlow E . (1995). The pRB-related protein p107 contains two growth suppression domains: independent interactions with E2F and cyclin/cdk complexes. EMBO J 14: 1904–1913.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Michael J Klein and the Pathology and Laboratory Medicine group at the Hospital for Special Surgery and MSKCC microcyteometry facility. We also thank Lori A Mainwaring, Cedric Dray, Cemille Guldal, Elisa DeStanchina and Fajun Yang for helpful discussions. These studies were funded by the Lung Cancer Center and the division of thoracic surgery at Weill Cornell Medical College (ZN), the NIH (NINDS R01NS061070) (AMK) and the Memorial Sloan–Kettering Brain Tumor Center (BB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatia, B., Hsieh, M., Kenney, A. et al. Mitogenic Sonic hedgehog signaling drives E2F1-dependent lipogenesis in progenitor cells and medulloblastoma. Oncogene 30, 410–422 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.454
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.454
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Low blood levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol are positively associated with cancer
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2022)
-
Metabolic reprogramming in cervical cancer and metabolomics perspectives
Nutrition & Metabolism (2021)
-
Lipid profile and risk of ovarian tumours: a meta-analysis
BMC Cancer (2020)
-
The regulation of IMF deposition in pectoralis major of fast- and slow- growing chickens at hatching
Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology (2017)
-
A distinct function of the retinoblastoma protein in the control of lipid composition identified by lipidomic profiling
Oncogenesis (2017)