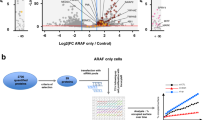
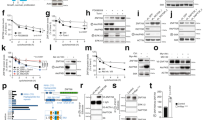
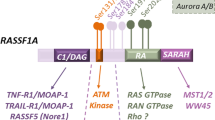
Abstract
The Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signalling cascade regulates various biological functions, including cell growth, proliferation and survival. As such, this pathway is often deregulated in cancer, including melanomas, which frequently harbour activating mutations in the NRAS and BRAF oncogenes. Hyperactive MAPK signalling is known to promote protein synthesis, but the mechanisms by which this occurs remain poorly understood. Here, we show that expression of oncogenic forms of Ras and Raf promotes the constitutive activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). Using pharmacological inhibitors and RNA interference, we find that the MAPK-activated protein kinase RSK (p90 ribosomal S6 kinase) is partly required for these effects. Using melanoma cell lines carrying activating BRAF mutations, we show that ERK/RSK signalling regulates assembly of the translation initiation complex and polysome formation, as well as the translation of growth-related messenger RNAs containing a 5′-terminal oligopyrimidine (TOP) motif. Accordingly, we find that RSK inhibition abrogates tumour growth in mice. Our findings indicate that RSK may be a valuable therapeutic target for the treatment of tumours characterized by deregulated MAPK signalling, such as melanoma.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murphy LO, Blenis J . MAPK signal specificity: the right place at the right time. Trends Biochem Sci 2006; 31: 268–275.
Ballif BA, Blenis J . Molecular mechanisms mediating mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase (MEK)-MAPK cell survival signals. Cell Growth Differ 2001; 12: 397–408.
Schubbert S, Shannon K, Bollag G . Hyperactive Ras in developmental disorders and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2007; 7: 295–308.
Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P, Edkins S, Clegg S et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature 2002; 417: 949–954.
Fecher LA, Amaravadi RK, Flaherty KT . The MAPK pathway in melanoma. Curr Opin Oncol 2008; 20: 183–189.
Gray-Schopfer VC, da Rocha Dias S, Marais R . The role of B-RAF in melanoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2005; 24: 165–183.
Miller AJ, Mihm MC . Melanoma. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 51–65.
Scheier B, Amaria R, Lewis K, Gonzalez R . Novel therapies in melanoma. Immunotherapy 2011; 3: 1461–1469.
Meloche S, Pouyssegur J . The ERK1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway as a master regulator of the G1- to S-phase transition. Oncogene 2007; 26: 3227–3239.
Servant MJ, Giasson E, Meloche S . Inhibition of growth factor-induced protein synthesis by a selective MEK inhibitor in aortic smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 16047–16052.
Rajalingam K, Schreck R, Rapp UR, Albert S . Ras oncogenes and their downstream targets. Biochim Biophys Acta 2007; 1773: 1177–1195.
Waskiewicz AJ, Flynn A, Proud CG, Cooper JA . Mitogen-activated protein kinases activate the serine/threonine kinases Mnk1 and Mnk2. Embo J 1997; 16: 1909–1920.
Waskiewicz AJ, Johnson JC, Penn B, Mahalingam M, Kimball SR, Cooper JA . Phosphorylation of the cap-binding protein eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E by protein kinase Mnk1 in vivo. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19: 1871–1880.
Cargnello M, Roux PP . Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2011; 75: 50–83.
Buxade M, Parra-Palau JL, Proud CG . The Mnks: MAP kinase-interacting kinases (MAP kinase signal-integrating kinases). Front Biosci 2008; 13: 5359–5373.
Ueda T, Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Fukuyama H, Nagata S, Fukunaga R . Mnk2 and Mnk1 are essential for constitutive and inducible phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E but not for cell growth or development. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 6539–6549.
Furic L, Rong L, Larsson O, Koumakpayi IH, Yoshida K, Brueschke A et al. eIF4E phosphorylation promotes tumorigenesis and is associated with prostate cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 14134–14139.
Gaestel M . Specificity of signaling from MAPKs to MAPKAPKs: kinases' tango nuevo. Front Biosci 2008; 13: 6050–6059.
Romeo Y, Zhang X, Roux PP . Regulation and function of the RSK family of protein kinases. Biochem J 2012; 441: 553–569.
Carriere A, Ray H, Blenis J, Roux PP . The RSK factors of activating the Ras/MAPK signaling cascade. Front Biosci 2008; 13: 4258–4275.
Anjum R, Blenis J . The RSK family of kinases: emerging roles in cellular signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008; 9: 747–758.
Romeo Y, Roux PP . Paving the way for targeting RSK in cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2011; 15: 5–9.
Old WM, Shabb JB, Houel S, Wang H, Couts KL, Yen CY et al. Functional proteomics identifies targets of phosphorylation by B-Raf signaling in melanoma. Mol Cell 2009; 34: 115–131.
Ma L, Chen Z, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Pandolfi PP . Phosphorylation and functional inactivation of TSC2 by Erk implications for tuberous sclerosis and cancer pathogenesis. Cell 2005; 121: 179–193.
Roux PP, Ballif BA, Anjum R, Gygi SP, Blenis J . Tumor-promoting phorbol esters and activated Ras inactivate the tuberous sclerosis tumor suppressor complex via p90 ribosomal S6 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 13489–13494.
Sengupta S, Peterson TR, Sabatini DM . Regulation of the mTOR complex 1 pathway by nutrients, growth factors, and stress. Mol Cell 2010; 40: 310–322.
Caron E, Ghosh S, Matsuoka Y, Ashton-Beaucage D, Therrien M, Lemieux S et al. A comprehensive map of the mTOR signaling network. Mol Syst Biol 2011; 6: 453.
Wullschleger S, Loewith R, Hall MN . TOR signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell 2006; 124: 471–484.
Jacinto E . What controls TOR? IUBMB Life 2008; 60: 483–496.
Foster KG, Fingar DC . Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR): conducting the cellular signaling symphony. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 14071–14077.
Ma XM, Blenis J . Molecular mechanisms of mTOR-mediated translational control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009; 10: 307–318.
Sonenberg N, Hinnebusch AG . Regulation of translation initiation in eukaryotes: mechanisms and biological targets. Cell 2009; 136: 731–745.
Ma XM, Yoon SO, Richardson CJ, Julich K, Blenis J . SKAR links pre-mRNA splicing to mTOR/S6K1-mediated enhanced translation efficiency of spliced mRNAs. Cell 2008; 133: 303–313.
Menon S, Manning BD . Common corruption of the mTOR signaling network in human tumors. Oncogene 2008; 27 (Suppl 2): S43–S51.
Karbowniczek M, Spittle CS, Morrison T, Wu H, Henske EP . mTOR is activated in the majority of malignant melanomas. J Invest Dermatol 2008; 128: 980–987.
Guertin DA, Sabatini DM . The pharmacology of mTOR inhibition. Sci Signal 2009; 2: pe24.
Meyuhas O, Dreazen A . Chapter 3 Ribosomal protein S6 kinase from TOP mRNAs to cell size. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 2009; 90: 109–153.
Yamashita R, Suzuki Y, Takeuchi N, Wakaguri H, Ueda T, Sugano S et al. Comprehensive detection of human terminal oligo-pyrimidine (TOP) genes and analysis of their characteristics. Nucleic Acids Res 2008; 36: 3707–3715.
Bilanges B, Argonza-Barrett R, Kolesnichenko M, Skinner C, Nair M, Chen M et al. Tuberous sclerosis complex proteins 1 and 2 control serum-dependent translation in a TOP-dependent and -independent manner. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 5746–5764.
Eisenmann KM, VanBrocklin MW, Staffend NA, Kitchen SM, Koo HM . Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway-dependent tumor-specific survival signaling in melanoma cells through inactivation of the proapoptotic protein bad. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 8330–8337.
Bilanges B, Stokoe D . Mechanisms of translational deregulation in human tumors and therapeutic intervention strategies. Oncogene 2007; 26: 5973–5990.
Mamane Y, Petroulakis E, LeBacquer O, Sonenberg N . mTOR translation initiation and cancer. Oncogene 2006; 25: 6416–6422.
O'Reilly KE, Warycha M, Davies MA, Rodrik V, Zhou XK, Yee H et al. Phosphorylated 4E-BP1 is associated with poor survival in melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 2872–2878.
She QB, Halilovic E, Ye Q, Zhen W, Shirasawa S, Sasazuki T et al. 4E-BP1 is a key effector of the oncogenic activation of the AKT and ERK signaling pathways that integrates their function in tumors. Cancer Cell 2010; 18: 39–51.
Dowling RJ, Topisirovic I, Alain T, Bidinosti M, Fonseca BD, Petroulakis E et al. mTORC1-mediated cell proliferation, but not cell growth, controlled by the 4E-BPs. Science 2010; 328: 1172–1176.
Shahbazian D, Roux PP, Mieulet V, Cohen MS, Raught B, Taunton J et al. The mTOR/PI3K and MAPK pathways converge on eIF4B to control its phosphorylation and activity. Embo J 2006; 25: 2781–2791.
Roux PP, Shahbazian D, Vu H, Holz MK, Cohen MS, Taunton J et al. RAS/ERK signaling promotes site-specific ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation via RSK and stimulates cap-dependent translation. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 14056–14064.
Zheng B, Jeong JH, Asara JM, Yuan YY, Granter SR, Chin L et al. Oncogenic B-RAF negatively regulates the tumor suppressor LKB1 to promote melanoma cell proliferation. Mol Cell 2009; 33: 237–247.
Engelman JA, Chen L, Tan X, Crosby K, Guimaraes AR, Upadhyay R et al. Effective use of PI3K and MEK inhibitors to treat mutant Kras G12D and PIK3CA H1047R murine lung cancers. Nat Med 2008; 14: 1351–1356.
Carriere A, Cargnello M, Julien LA, Gao H, Bonneil E, Thibault P et al. Oncogenic MAPK signalling stimulates mTORC1 activity by promoting RSK-mediated raptor phosphorylation. Curr Biol 2008; 18: 1269–1277.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Canadian Cancer Society Research Institute (PPR), the Cancer Research Society (PPR and SM), and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (PPR). We thank Dr Nahum Sonenberg for the phospho-4E-BP1 antibody. PP Roux holds a Canada Research Chair in Signal Transduction and Proteomics and a Career Development Award from the Human Frontier Science Programme (HFSP). K Borden and S Meloche hold Canada Research Chairs in Molecular Biology of the Cell Nucleus, and in Cellular Signalling, respectively. IRIC core facilities are supported by the FRSQ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romeo, Y., Moreau, J., Zindy, PJ. et al. RSK regulates activated BRAF signalling to mTORC1 and promotes melanoma growth. Oncogene 32, 2917–2926 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.312
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.312
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The role of the p90 ribosomal S6 kinase family in prostate cancer progression and therapy resistance
Oncogene (2021)
-
Expression of transgenes enriched in rare codons is enhanced by the MAPK pathway
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Cisplatin based therapy: the role of the mitogen activated protein kinase signaling pathway
Journal of Translational Medicine (2018)
-
The unfolded protein response impacts melanoma progression by enhancing FGF expression and can be antagonized by a chemical chaperone
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Feedback activation of neurofibromin terminates growth factor-induced Ras activation
Cell Communication and Signaling (2016)