Abstract
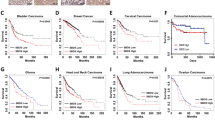
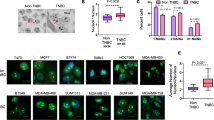
Hyperactive ribosomal biogenesis is widely observed in cancer, which has been partly attributed to the increased rDNA transcription by Pol I in cancer. However, whether small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs), a class of non-coding RNAs crucial in ribosomal RNA (rRNA) maturation and functionality, are involved in cancer remains elusive. We report that snoRNAs and fibrillarin (FBL, an enzymatic small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein, snoRNP) are frequently overexpressed in both murine and human breast cancer as well as in prostate cancers, and significantly, that this overexpression is essential for tumorigenicity in vitro and in vivo. We demonstrate that when the elevated snoRNA pathway is suppressed, the tumor suppressor p53 can act as a sentinel of snoRNP perturbation, the activation of which mediates the growth inhibitory effect. On the other hand, high level of FBL interferes with the activation of p53 by stress. We further show that p53 activation by FBL knockdown is not only regulated by the ribosomal protein-MDM2-mediated protein stabilization pathway, but also by enhanced PTB-dependent, cap-independent translation. Together, our data uncover an essential role of deregulated snoRNA biogenesis in tumors and a new mechanism of nucleolar modulation of p53.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barna M, Pusic A, Zollo O, Costa M, Kondrashov N, Rego E et al. Suppression of Myc oncogenic activity by ribosomal protein haploinsufficiency. Nature 2008; 456: 971–975.
Ruggero D, Pandolfi PP . Does the ribosome translate cancer? Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 179–192.
Kondrashov AV, Kiefmann M, Ebnet K, Khanam T, Muddashetty RS, Brosius J . Inhibitory effect of naked neural BC1 RNA or BC200 RNA on eukaryotic in vitro translation systems is reversed by poly(A)-binding protein (PABP). J Mol Biol 2005; 353: 88–103.
White RJ . RNA polymerases I and III, growth control and cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2005; 6: 69–78.
Derenzini M, Montanaro L, Trere D . What the nucleolus says to a tumour pathologist. Histopathology 2009; 54: 753–762.
Montanaro L, Trere D, Derenzini M . Nucleolus, ribosomes, and cancer. Am J Pathol. 2008; 173: 301–310.
Derenzini M, Ploton D . Interphase nucleolar organizer regions in cancer cells. Int Rev Exp Pathol 1991; 32: 149–192.
Williams GT, Farzaneh F . Are snoRNAs and snoRNA host genes new players in cancer? Nat Rev Cancer 2012; 12: 84–88.
Mei YP, Liao JP, Shen J, Yu L, Liu BL, Liu L et al. Small nucleolar RNA 42 acts as an oncogene in lung tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2012; 31: 2794–2804.
Cavanaugh AH, Hempel WM, Taylor LJ, Rogalsky V, Todorov G, Rothblum LI . Activity of RNA polymerase I transcription factor UBF blocked by Rb gene product. Nature 1995; 374: 177–180.
Coller HA, Grandori C, Tamayo P, Colbert T, Lander ES, Eisenman RN et al. Expression analysis with oligonucleotide microarrays reveals that MYC regulates genes involved in growth, cell cycle, signaling, and adhesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 3260–3265.
Boon K, Caron HN, van Asperen R, Valentijn L, Hermus MC, van Sluis P et al. N-myc enhances the expression of a large set of genes functioning in ribosome biogenesis and protein synthesis. EMBO J 2001; 20: 1383–1393.
Vogt PKPI . 3-kinase, mTOR, protein synthesis and cancer. Trends Mol Med 2001; 7: 482–484.
Krastev DB, Slabicki M, Paszkowski-Rogacz M, Hubner NC, Junqueira M, Shevchenko A et al. A systematic RNAi synthetic interaction screen reveals a link between p53 and snoRNP assembly. Nat Cell Biol 2011; 13: 809–818.
Dai MS, Lu H . Inhibition of MDM2-mediated p53 ubiquitination and degradation by ribosomal protein L5. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 44475–44482.
Lohrum MA, Ludwig RL, Kubbutat MH, Hanlon M, Vousden KH . Regulation of HDM2 activity by the ribosomal protein L11. Cancer Cell 2003; 3: 577–587.
Zhang Y, Wolf GW, Bhat K, Jin A, Allio T, Burkhart WA et al. Ribosomal protein L11 negatively regulates oncoprotein MDM2 and mediates a p53-dependent ribosomal-stress checkpoint pathway. Mol Cell Biol 2003; 23: 8902–8912.
Dai MS, Zeng SX, Jin Y, Sun XX, David L, Lu H . Ribosomal protein L23 activates p53 by inhibiting MDM2 function in response to ribosomal perturbation but not to translation inhibition. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 7654–7668.
Jin A, Itahana K, O'Keefe K, Zhang Y . Inhibition of HDM2 and activation of p53 by ribosomal protein L23. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 7669–7680.
Zhang Y, Lu H . Signaling to p53: ribosomal proteins find their way. Cancer Cell 2009; 16: 369–377.
Guy CT, Webster MA, Schaller M, Parsons TJ, Cardiff RD, Muller WJ . Expression of the neu protooncogene in the mammary epithelium of transgenic mice induces metastatic disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992; 89: 10578–10582.
Muller WJ, Sinn E, Pattengale PK, Wallace R, Leder P . Single-step induction of mammary adenocarcinoma in transgenic mice bearing the activated c-neu oncogene. Cell 1988; 54: 105–115.
Watkins NJ, Lemm I, Ingelfinger D, Schneider C, Hossbach M, Urlaub H et al. Assembly and maturation of the U3 snoRNP in the nucleoplasm in a large dynamic multiprotein complex. Mol Cell 2004; 16: 789–798.
Takagi M, Absalon MJ, McLure KG, Kastan MB . Regulation of p53 translation and induction after DNA damage by ribosomal protein L26 and nucleolin. Cell 2005; 123: 49–63.
Ray PS, Grover R, Das S . Two internal ribosome entry sites mediate the translation of p53 isoforms. EMBO Rep 2006; 7: 404–410.
Grover R, Ray PS, Das S . Polypyrimidine tract binding protein regulates IRES-mediated translation of p53 isoforms. Cell Cycle 2008; 7: 2189–2198.
Macias E, Jin A, Deisenroth C, Bhat K, Mao H, Lindstrom MS et al. An ARF-independent c-MYC-activated tumor suppression pathway mediated by ribosomal protein-Mdm2 Interaction. Cancer Cell 2010; 18: 231–243.
Gasco M, Shami S, Crook T . The p53 pathway in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 2002; 4: 70–76.
Mahata B, Sundqvist A, Xirodimas DP . Recruitment of RPL11 at promoter sites of p53-regulated genes upon nucleolar stress through NEDD8 and in an Mdm2-dependent manner. Oncogene 2012; 31: 3060–3071.
Debnath J, Muthuswamy SK, Brugge JS . Morphogenesis and oncogenesis of MCF-10A mammary epithelial acini grown in three-dimensional basement membrane cultures. Methods 2003; 30: 256–268.
Wang WZ, Cheng J, Luo J, Zhuang SM . Abrogation of G2/M arrest sensitizes curcumin-resistant hepatoma cells to apoptosis. FEBS Lett 2008; 582: 2689–2695.
Su H, Yang JR, Xu T, Huang J, Xu L, Yuan Y et al. MicroRNA-101, down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, promotes apoptosis and suppresses tumorigenicity. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 1135–1142.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by NIH/NCI. 2 R01 CA85679-10; R01 CA125144 for Zhi-Min Yuan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, H., Xu, T., Ganapathy, S. et al. Elevated snoRNA biogenesis is essential in breast cancer. Oncogene 33, 1348–1358 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.89
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.89
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Identification of four snoRNAs (SNORD16, SNORA73B, SCARNA4, and SNORD49B) as novel non-invasive biomarkers for diagnosis of breast cancer
Cancer Cell International (2024)
-
snoRNAs: functions and mechanisms in biological processes, and roles in tumor pathophysiology
Cell Death Discovery (2022)
-
Small non-coding RNAs in human cancer: function, clinical utility, and characterization
Oncogene (2021)
-
Location, location, location: subcellular protein partitioning in proteostasis and aging
Biophysical Reviews (2021)
-
Overexpression of NOP58 as a Prognostic Marker in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A TCGA Data-Based Analysis
Advances in Therapy (2021)