Abstract
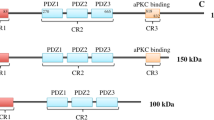
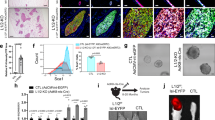
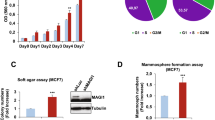
Disruption of epithelial organization and loss of growth control are universal features of carcinomas, yet how these features are linked during cancer progression remains poorly understood. Cell polarity proteins control cellular and tissue organization and are emerging as important mediators of cancer progression. The Par3 polarity protein is a molecular scaffold that functions to recruit and spatially organize signaling factors, and was recently identified as a suppressor of breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Here, we show that loss of Par3 in mammary epithelial cells promotes apoptosis, and that oncogenic Notch overcomes the apoptotic signal to reveal an unexpected pro-proliferative role for loss of Par3 in mammary tumors. In this context, loss of Par3 deregulates Rac1 activity to activate Jun N-terminal Kinase-dependent proliferation and tumor growth. Thus, we demonstrate a mechanism by which loss of Par3 promotes proliferation and tumorigenesis, which supports a tumor-suppressive function for Par3 in the mammary epithelium.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCaffrey LM, Macara IG Epithelial organization, cell polarity and tumorigenesis. Trends Cell Biol 2011; 21: 727–735.
Tepass U The apical polarity protein network in Drosophila epithelial cells: regulation of polarity, junctions, morphogenesis, cell growth, and survival. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2012; 28: 655–685.
Zhao B, Tumaneng K, Guan KL The Hippo pathway in organ size control, tissue regeneration and stem cell self-renewal. Nat Cell Biol 2011; 13: 877–883.
Huang L, Muthuswamy SK Polarity protein alterations in carcinoma: a focus on emerging roles for polarity regulators. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2010; 20: 41–50.
Hayase J, Kamakura S, Iwakiri Y, Yamaguchi Y, Izaki T, Ito T et al. The WD40 protein Morg1 facilitates Par6-aPKC binding to Crb3 for apical identity in epithelial cells. J Cell Biol 2013; 200: 635–650.
Morais-de-Sa E, Mirouse V St, Johnston D aPKC phosphorylation of Bazooka defines the apical/lateral border in Drosophila epithelial cells. Cell 2010; 141: 509–523.
Nolan ME, Aranda V, Lee S, Lakshmi B, Basu S, Allred DC et al. The polarity protein Par6 induces cell proliferation and is overexpressed in breast cancer. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 8201–8209.
Kim M, Datta A, Brakeman P, Yu W, Mostov KE . Polarity proteins PAR6 and aPKC regulate cell death through GSK-3beta in 3D epithelial morphogenesis. J Cell Sci 2007; 120: 2309–2317.
Stallings-Mann M, Jamieson L, Regala RP, Weems C, Murray NR, Fields AP A novel small-molecule inhibitor of protein kinase Ciota blocks transformed growth of non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 1767–1774.
Durgan J, Kaji N, Jin D, Hall A Par6B and atypical PKC regulate mitotic spindle orientation during epithelial morphogenesis. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 12461–12474.
Iden S, van Riel Wilhelmina E, Schäfer R, Song J-Y, Hirose T, Ohno S et al. Tumor type-dependent function of the Par3 polarity protein in skin tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2012; 22: 389–403.
McCaffrey LM, Macara IG The Par3/aPKC interaction is essential for end bud remodeling and progenitor differentiation during mammary gland morphogenesis. Genes Dev 2009; 23: 1450–1460.
Xue B, Krishnamurthy K, Allred DC, Muthuswamy SK Loss of Par3 promotes breast cancer metastasis by compromising cell-cell cohesion. Nat Cell Biol 2013; 15: 189–200.
Chen X, Macara IG Par-3 controls tight junction assembly through the Rac exchange factor Tiam1. Nat Cell Biol 2005; 7: 262–269.
Georgiou M, Baum B Polarity proteins and Rho GTPases cooperate to spatially organise epithelial actin-based protrusions. J Cell Sci 2010; 123: 1089–1098.
Nishimura T, Yamaguchi T, Kato K, Yoshizawa M, Nabeshima Y, Ohno S et al. PAR-6-PAR-3 mediates Cdc42-induced Rac activation through the Rac GEFs STEF/Tiam1. Nat Cell Biol 2005; 7: 270–277.
Pegtel DM, Ellenbroek SI, Mertens AE, van der Kammen RA, de Rooij J, Collard JG . The Par-Tiam1 complex controls persistent migration by stabilizing microtubule-dependent front-rear polarity. Curr Biol 2007; 17: 1623–1634.
Zhang H, Macara IG The polarity protein PAR-3 and TIAM1 cooperate in dendritic spine morphogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 2006; 8: 227–237.
Schnelzer A, Prechtel D, Knaus U, Dehne K, Gerhard M, Graeff H et al. Rac1 in human breast cancer: overexpression, mutation analysis, and characterization of a new isoform, Rac1b. Oncogene 2000; 19: 3013–3020.
Zhou C, Licciulli S, Avila JL, Cho M, Troutman S, Jiang P et al. The Rac1 splice form Rac1b promotes K-ras-induced lung tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2013; 32: 903–909.
Kawazu M, Ueno T, Kontani K, Ogita Y, Ando M, Fukumura K et al. Transforming mutations of RAC guanosine triphosphatases in human cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: 3029–3034.
Wertheimer E, Gutierrez-Uzquiza A, Rosemblit C, Lopez-Haber C, Sosa MS, Kazanietz MG Rac signaling in breast cancer: a tale of GEFs and GAPs. Cell Signal 2012; 24: 353–362.
Strumane K, Rygiel T, van der Valk M, Collard JG . Tiam1-deficiency impairs mammary tumor formation in MMTV-c-neu but not in MMTV-c-myc mice. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2009; 135: 69–80.
McCaffrey Luke M, Montalbano J, Mihai C, Macara Ian G Loss of the Par3 polarity protein promotes breast tumorigenesis and metastasis. Cancer Cell 2012; 22: 601–614.
Hu C, Dievart A, Lupien M, Calvo E, Tremblay G, Jolicoeur P Overexpression of activated murine Notch1 and Notch3 in transgenic mice blocks mammary gland development and induces mammary tumors. Am J Pathol 2006; 168: 973–990.
Al-Hussaini H, Subramanyam D, Reedijk M, Sridhar SS Notch signaling pathway as a therapeutic target in breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 2011; 10: 9–15.
Simmons MJ, Serra R, Hermance N, Kelliher MA NOTCH1 inhibition in vivo results in mammary tumor regression and reduced mammary tumorsphere-forming activity in vitro. Breast Cancer Res 2012; 14: R126.
Herschkowitz JI, Simin K, Weigman VJ, Mikaelian I, Usary J, Hu Z et al. Identification of conserved gene expression features between murine mammary carcinoma models and human breast tumors. Genome Biol 2007; 8: R76.
Bosco EE, Mulloy JC, Zheng Y Rac1 GTPase: a "Rac" of all trades. Cell Mol Life Sci 2009; 66: 370–374.
Gao Y, Dickerson JB, Guo F, Zheng J, Zheng Y Rational design and characterization of a Rac GTPase-specific small molecule inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 7618–7623.
Olson MF, Ashworth A, Hall A An essential role for Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 GTPases in cell cycle progression through G1. Science 1995; 269: 1270–1272.
Warner SJ, Yashiro H, Longmore GD The Cdc42/Par6/aPKC polarity complex regulates apoptosis-induced compensatory proliferation in epithelia. Curr Biol 2010; 20: 677–686.
Cellurale C, Girnius N, Jiang F, Cavanagh-Kyros J, Lu S, Garlick DS et al. Role of JNK in mammary gland development and breast cancer. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 472–481.
Brumby AM, Richardson HE scribble mutants cooperate with oncogenic Ras or Notch to cause neoplastic overgrowth in Drosophila. Embo J 2003; 22: 5769–5779.
Uhlirova M, Jasper H, Bohmann D Non-cell-autonomous induction of tissue overgrowth by JNK/Ras cooperation in a Drosophila tumor model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 13123–13128.
Fereshteh MP, Tilli MT, Kim SE, Xu J, O'Malley BW, Wellstein A et al. The nuclear receptor coactivator amplified in breast cancer-1 is required for Neu (ErbB2/HER2) activation, signaling, and mammary tumorigenesis in mice. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 3697–3706.
Han JS, Crowe DL Jun amino-terminal kinase 1 activation promotes cell survival in ErbB2-positive breast cancer. Anticancer Res 2010; 30: 3407–3412.
Acknowledgements
We thank Didier Trono (Lausanne, Switzerland) for lentivectors. K8 hybridoma, developed by Philippe Brulet and Rolf Kemler, was obtained from the Universtiy of Iowa Developmental Hybridoma Bank. This work was supported by grants from TFRI (Project #1009) and CIHR (MOP-119482) to LM. LM is a FRQS Research Scholar.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Archibald, A., Mihai, C., Macara, I. et al. Oncogenic suppression of apoptosis uncovers a Rac1/JNK proliferation pathway activated by loss of Par3. Oncogene 34, 3199–3206 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.242
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.242
This article is cited by
-
The polarity protein PARD3 and cancer
Oncogene (2021)
-
MicroRNA 483-3p targets Pard3 to potentiate TGF-β1-induced cell migration, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition in anaplastic thyroid cancer cells
Oncogene (2019)
-
Intersectin-1s deficiency in pulmonary pathogenesis
Respiratory Research (2017)
-
The Par3 polarity protein is an exocyst receptor essential for mammary cell survival
Nature Communications (2017)
-
Expression of Par3 polarity protein correlates with poor prognosis in ovarian cancer
BMC Cancer (2016)