Abstract
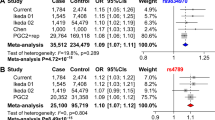
The gene encoding the transcription factor RFX4 represents an excellent neurobiological and positional candidate gene for Bipolar disorder due to the potential involvement of RFX4 proteins in the regulation of circadian rhythms and the proximity of the locus to numerous linkage signals on chromosome 12q23. In this study we have sought to identify common variants within the gene, which might confer risk to the disease in our large UK Caucasian sample of Bipolar patients (676 DSMIV Bipolar I probands, 690 controls). RFX4 was screened for sequence variants and the LD block structure across the genomic region determined using 22 biallelic polymorphisms (minor allele frequency ≥0.1). Through analysis of 10 haplotype-tagging markers and using a two-stage approach (subset I: 347 cases, 374 controls; subset II: 329 cases, 316 controls), we identified a haplotype at rs10778502 and ss24735177, which showed nominally significant disease association in our full sample (haplotype-specific P=0.002, global P=0.017; subset I: haplotype-specific P=0.0002, global P=0.0008; subset II: haplotype-specific P=0.572, global P=0.109). Evidence for potential disease association with mutations across the RFX4 region came also from the analysis of the nearby microsatellite D12S2072 (empirical P=0.009 in our full sample). Investigation of RFX4 brain cDNA tagged by rs10778502 provided evidence for significant allelic differences in expression (P<0.001), where some of the variance was accounted for by the genotype at ss24735177. Our findings thus indicate the potential functional relevance of the associated haplotype and now require replication in independent samples.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Craddock N, Jones I . Genetics of bipolar disorder. J Med Genet 1999; 36: 585–594.
McGuffin P, Owen MJ, O'Donovan MC, Thapar A, Gottesmann II . Seminars in psychiatric genetics. Gaskell: London, 1994.
Potash JB, DePaulo JR . Searching high and low: a review of the genetics of bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord 2000; 2: 8–26.
Baron M . Manic-depression genes and the new millennium: poised for discovery. Mol Psychiatry 2002; 7: 342–358.
McGuffin P, Rijsdijk F, Andrew M, Sham P, Katz R, Cardno A . The heritability of bipolar affective disorder and the genetic relationship to unipolar depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2003; 60: 497–502.
Craddock N, Owen M, Burge S, Kurian B, Thomas P, McGuffin P . Familial cosegregation of major affective-disorder and Dariers-disease (keratosis-follicularis). Br J Psychiatry 1994; 164: 355–358.
Dawson E, Parfitt E, Roberts Q, Daniels J, Lim L, Sham P et al. Linkage studies of bipolar disorder in the region of the Dariers-disease gene on chromosome 12q23–24.1. Am J Med Genet 1995; 60: 94–102.
Morissette J, Villeneuve A, Bordeleau L, Rochette D, Laberge C, Gagne B et al. Genome-wide search for linkage of bipolar affective disorders in a very large pedigree derived from a homogeneous population in quebec points to a locus of major effect on chromosome 12q23–q24. Am J Med Genet 1999; 88: 567–587.
Jones I, Jacobsen N, Green EK, Elvidge GP, Owen MJ, Craddock N . Evidence for familial cosegregation of major affective disorder and genetic markers flanking the gene for Darier's disease. Mol Psychiatry 2002; 7: 424–427.
Ewald H, Flint T, Kruse TA, Mors O . A genome-wide scan shows significant linkage between bipolar disorder and chromosome 12q24.3 and suggestive linkage to chromosomes 1p22–21, 4p16, 6q14–22, 10q26 and 16p13.3. Mol Psychiatry 2002; 7: 734–744.
Curtis D, Kalsi G, Brynjolfsson J, McInnis M, O'Neill J, Smyth C et al. Genome scan of pedigrees multiply affected with bipolar disorder provides further support for the presence of a susceptibility locus on chromosome 12q23–q24, and suggests the presence of additional loci on 1p and 1q. Psychiatr Genet 2003; 13: 77–84.
Ekholm JM, Kieseppa T, Hiekkalinna T, Partonen T, Paunio T, Perola M et al. Evidence of susceptibility loci on 4q32 and 16p12 for bipolar disorder. Hum Mol Genet 2003; 12: 1907–1915.
Abkevich V, Camp NJ, Hensel CH, Neff CD, Russell DL, Hughes DC et al. Predisposition locus for major depression at chromosome 12q22–12q23.2. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 73: 1271–1281.
Zubenko GS, Maher B, Hughes III HB, Zubenko WN, Stiffler JS, Kaplan BB et al. Genome-wide linkage survey for genetic loci that influence the development of depressive disorders in families with recurrent early-onset, major depression. Am J Med Genet 2003; 123B: 1–18.
Blacker D, Lavori PW, Faraone SV, Tsuang MT . Unipolar relatives in bipolar pedigrees: a search for indicators of underlying bipolarity. Am J Med Genet 1993; 48: 192–199.
Green E, Elvidge G, Jacobsen N, Glaser B, Jones I, O'Donovan MC et al. Localization of bipolar susceptibility locus by molecular genetic analysis of the chromosome 12q23–q24 region in two pedigrees with bipolar disorder and Darier's disease. Am J Psychiatry 2005; 162: 35–42.
Gajiwala KS, Chen H, Cornille F, Roques BP, Reith W, Mach B et al. Structure of the winged-helix protein hRFX1 reveals a new mode of DNA binding. Nature 2000; 403: 916–921.
Emery P, Durand B, Mach B, Reith W . RFX proteins, a novel family of DNA binding proteins conserved in the eukaryotic kingdom. Nucl Acids Res 1996; 24: 803–807.
Morotami-Yano K, Yano K, Saito H, Sun Z, Iwama A, Miki Y . Human regulatory factor X 4 (RFX4) is a testis-specific dimeric DNA-binding protein that cooperates with other human RFX members. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 836–842.
Araki R, Takahashi H, Fukumura R, Sun F, Umeda N, Sujino M et al. Restricted expression and photic induction of a novel mouse regulatory factor X4 transcript in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 10237–10242.
Dotzlaw H, Alkhalaf M, Murphy LC . Characterization of estrogen receptor variant mRNAs from human breast cancers. Mol Endocrinol 1992; 6: 773–785.
Blackshear PJ, Graves JP, Stumpo DJ, Cobos I, Rubenstein JL, Zeldin DC . Graded phenotypic response to partial and complete deficiency of a brain-specific transcript variant of the winged helix transcription factor RFX4. Development 2003; 130: 4539–4552.
Klein D, Moore R, Reppert S (eds). Suprachiasmatic Nucleus. The Mind's Clock. Oxford University Press: Oxford, 1991.
Wehr TA, Sack D, Rosenthal N, Duncan W, Gillin JC . Circadian rhythm disturbances in manic-depressive illness. Fed Proc 1983; 42: 2809–2814.
Klemfuss H . Rhythms and the pharmacology of lithium. Pharmacol Ther 1992; 56: 53–78.
Abe M, Herzog ED, Block GD . Lithium lengthens the circadian period of individual suprachiasmatic nucleus neurons. Neuroreport 2000; 11: 3261–3264.
APA. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, 1994.
Endicott J, Spitzer RL . A diagnostic interview. The schedule for affective disorder and schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatr 1978; 35: 837–844.
Wing JK, Babor T, Brugha T, Burke J, Cooper JE, Giel R et al. SCAN. Schedules for clinical assessment in neuropsychiatry. Arch Gen Psychiatr 1990; 47: 589–593.
Owen MJ, Holmans P, McGuffin P . Association studies in psychiatric genetics. Mol Psychiatr 1997; 2: 270–273.
Jacobsen NJO, Elvidge G, Franks EKE, O'Donovan MC, Craddock N, Owen MJ . CUX2, a potential regulator of NCAM expression: genomic characterization and analysis as a positional candidate susceptibility gene for bipolar disorder. Am J Med Genet 2001; 105: 295–300.
Abecasis GR, Cookson WOC . GOLD—graphical overview of linkage disequilibrium. Bioinformatics 2000; 16: 182–183.
Dudbridge F . Pedigree disequilibrium tests for multilocus haplotypes. Genet Epidemiol 2003; 25: 115–121.
Bray NJ, Buckland PR, Owen MJ, O'Donovan MC . Cis-acting variation in the expression of a high proportion of genes in human brain. Hum Genet 2003; 113: 149–153.
Sham P, Curtis D . Monte Carlo tests for associations between disease and alleles at highly polymorphic loci. Ann Hum Genet 1995; 59: 97–105.
Green EK, Elvidge GP, Owen MJ, Craddock N . Mutational analysis of two positional candidate susceptibility genes for bipolar disorder on chromosome 12q23–q24: phenylalanine hydroxylase and human LIM-homeobox LHX5. Psychiatr Genet 2003; 13: 97–101.
Glaser B, Kirov G, Green E, Craddock N, Owen MJ . Linkage disequilibrium mapping of bipolar affective disorder at 12q23–q24 provides evidence for association at CUX2 and FLJ32356. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2005; 132: 38–45.
Jacobsen NJO, Lyons I, Hoogendoorn B, Burge S, Kwok PY, O'Donovan MC et al. ATP2A2 mutations in Darier's disease and their relationship to neuropsychiatric phenotypes. Hum Mol Genet 1999; 8: 1631–1636.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Wellcome Trust (Grant Ref: 054305/B/98) and the Medical Research Council, London, UK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Molecular Psychiatry website (http://www.nature.com/mp)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glaser, B., Kirov, G., Bray, N. et al. Identification of a potential Bipolar risk haplotype in the gene encoding the winged-helix transcription factor RFX4. Mol Psychiatry 10, 920–927 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001689
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001689
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
T cell reactivity to regulatory factor X4 in type 1 narcolepsy
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Integrative approach for inference of gene regulatory networks using lasso-based random featuring and application to psychiatric disorders
BMC Medical Genomics (2016)
-
RNA-sequencing of the brain transcriptome implicates dysregulation of neuroplasticity, circadian rhythms and GTPase binding in bipolar disorder
Molecular Psychiatry (2014)
-
Polymorphisms in ABLIM1 are Associated with Personality Traits and Alcohol Dependence
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2012)
-
Case–control studies show that a non-conservative amino-acid change from a glutamine to arginine in the P2RX7 purinergic receptor protein is associated with both bipolar- and unipolar-affective disorders
Molecular Psychiatry (2009)