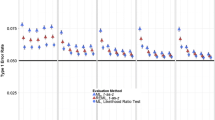
Abstract
Recent studies have shown that many physiological and behavioral processes can be characterized by long-range correlations. The Hurst exponent H of fractal analysis and the fractional-differencing parameter d of the ARFIMA methodology are useful for capturing serial correlations. In this study, we report on different estimators of H and d implemented in R, a popular and freely available software package. By means of Monte Carlo simulations, we analyzed the performance of (1) the Geweke—Porter-Hudak estimator, (2) the approximate maximum likelihood algorithm, (3) the smoothed periodogram approach, (4) the Whittle estimator, (5) rescaled range analysis, (6) a modified periodogram, (7) Higuchi’s method, and (8) detrended fluctuation analysis. The findings—confined to ARFIMA (0, d, 0) models and fractional Gaussian noise—identify the best estimators for persistent and antipersistent series. Two examples combining these results with the step-by-step procedure proposed by Delignières et al. (2006) demonstrate how this evaluation can be used as a guideline in a typical research situation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aks, D. J., & Sprott, J. C. (2003). The role of depth and 1/f dynamics in perceiving reversible figures. Nonlinear Dynamics, Psychology, & Life Sciences, 7, 161–180.
Bak, P. (1996). How nature works: The science of self-organized criticality. New York: Copernicus.
Bak, P., Tang, C., & Wiesenfeld, K. (1987). Self-organized criticality: An explanation of the 1/f noise. Physical Review Letters, 59, 381–384.
Bassingthwaighte, J. B., Liebovitch, L. S., & West, B. J. (1994). Fractal physiology. New York: Oxford University Press.
Beran, J. (1994). Statistics for long-memory processes. New York: Chapman & Hall.
Beran, J., & Feng, Y. (2002). SEMIFAR models—A semiparametric approach to modelling trends, long-range dependence and nonstationarity. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 40, 393–419.
Beran, J., & Ocker, D. (1999). SEMIFAR forecasts, with applications to foreign exchange rates. Journal of Statistical Planning & Inference, 80, 137–153.
Bloomfield, P. (2000). Fourier analysis of time series: An introduction (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Brent, R. P. (1973). Algorithms for minimization without derivatives. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Caccia, D. C., Percival, D., Cannon, M. J., Raymond, G., & Bassingthwaighte, J. B. (1997). Analyzing exact fractal time series: Evaluating dispersional analysis and rescaled range methods. Physica A, 246, 609–632.
Cannon, M. J., Percival, D. B., Caccia, D. C., Raymond, G. M., & Bassingthwaighte, J. B. (1997). Evaluating scaled windowed variance methods for estimating the Hurst coefficient of time series. Physica A, 241, 606–626.
Chen, Y., Ding, M., & Kelso, J. A. S. (1997). Long memory processes (1/fα type) in human coordination. Physical Review Letters, 79, 4501–4504.
Chen, Y., Ding, M., & Kelso, J. A. S. (2001). Origins of time errors in human sensorimotor coordination. Journal of Motor Behavior, 33, 3–8.
Craigmile, P. F. (2003). Simulating a class of stationary Gaussian processes using the Davies—Harte algorithm, with application to long memory processes. Journal of Time Series Analysis, 24, 505–511.
Davies, R. B., & Harte, D. S. (1987). Tests for Hurst effect. Biometrika, 74, 95–101.
Delignières, D., Fortes, M., & Ninot, G. (2004). The fractal dynamics of self-esteem and physical self. Nonlinear Dynamics, Psychology, & Life Sciences, 8, 479–510.
Delignières, D., Lemoine, L., & Torre, K. (2004). Time intervals production in tapping and oscillatory motion. Human Movement Science, 23, 87–103.
Delignières, D., Ramdani, S., Lemoine, L., Torre, K., Fortes, M., & Ninot, G. (2006). Fractal analyses for “short” time series: A reassessment of classical methods. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 50, 525–544.
Delignières, D., Torre, K., & Lemoine, L. (2005). Methodological issues in the application of monofractal analyses in psychological and behavioral research. Nonlinear Dynamics, Psychology, & Life Sciences, 9, 435–461.
Ding, M., Chen, Y., & Kelso, J. A. S. (2002). Statistical analysis of timing errors. Brain & Cognition, 48, 98–106.
Eke, A., Hermán, P., Bassingthwaighte, J. B., Raymond, G. M., Percival, D. B., Cannon, M., et al. (2000). Physiological time series: Distinguishing fractal noises from motions. Pflügers Archiv, 439, 403–415.
Eke, A., Hermán, P., Kocsis, L., & Kozak, L. R. (2002). Fractal characterization of complexity in temporal physiological signals. Physiological Measurement, 23, R1-R38.
Farrell, S., Wagenmakers, E.-J., & Ratcliff, R. (2006). 1/f noise in human cognition: Is it ubiquitous, and what does it mean? Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 13, 737–41.
Fox, R., & Taqqu, M. S. (1986). Large-sample properties of parameter estimates for strongly dependent stationary Gaussian time series. Annals of Statistics, 14, 517–532.
Geweke, J., & Porter-Hudak, S. (1983). The estimation and application of long memory time series models. Journal of Time Series Analysis, 4, 221–238.
Gilden, D. L. (1997). Fluctuations in the time required for elementary decisions. Psychological Science, 8, 296–301.
Gilden, D. L. (2001). Cognitive emissions of 1/f noise. Psychological Review, 108, 33–56.
Gilden, D. L., & Hancock, H. (2007). Response variability in attention-deficit disorders. Psychological Science, 18, 796–802.
Gilden, D. L., Thornton, T., & Mallon, M. W. (1995). 1/f noise in human cognition. Science, 267, 1837–1839
Gilden, D. L., & Wilson, S. G. (1995a). On the nature of streaks in signal detection. Cognitive Psychology, 28, 17–64.
Gilden, D. L., & Wilson, S. G. (1995b). Streaks in skilled performance. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 2, 260–265.
Granger, C. W. J., & Joyeux, R. (1980). An introduction to long-memory time series models and fractional differencing. Journal of Time Series Analysis, 1, 15–29.
Haslett, J., & Raftery, A. E. (1989). Space-time modelling with longmemory dependence: Assessing Ireland’s wind power resource. Applied Statistics, 38, 1–50.
Hausdorff, J. M., Mitchell, S. L., Firtion, R., Peng, C. K., Cudkowicz, M. E., Wei, J. Y., & Goldberger, A. L. (1997). Altered fractal dynamics of gait: Reduced stride-interval correlations with aging and Huntington’s disease. Journal of Applied Physiology, 82, 262–269.
Hausdorff, J. M., & Peng, C. (1996). Multiscaled randomness: A possible source of 1/f noise in biology. Physical Review E, 54, 2154–2157.
Hausdorff, J. M., Zemany, L., Peng, C., & Goldberger, A. L. (1999). Maturation of gait dynamics: Stride-to-stride variability and its temporal organization in children. Journal of Applied Physiology, 86, 1040–1047.
Higuchi, T. (1988). Approach to an irregular time series on the basis of the fractal theory. Physica D, 31, 277–283.
Holden, J. G. (2005). Gauging the fractal dimension of response times from cognitive tasks. In M. A. Riley & G. C. Van Orden (Eds.), Tutorials in contemporary nonlinear methods for the behavioral sciences (pp. 268-318). [Online] Retrieved October 7, 2008, from www.nsf .gov/sbe/bcs/pac/nmbs/nmbs.jsp.
Hosking, J. R. M. (1981). Fractional differencing. Biometrika, 68, 165–176.
Hosking, J. R. M. (1984). Modeling persistence in hydrological time series using fractional differencing. Water Resources Research, 20, 1898–1908.
Hurst, H. E., Black, R. P., & Simaika, Y. M. (1965). Long-term storage, an experimental study. London: Constable.
Linkenkaer-Hansen, K. (2002). Self-organized criticality and stochastic resonance in the human brain. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Helsinki University of Technology, Helsinki, Finland.
Maddala, G. S., & Kim, I.-M. (1998). Unit roots, cointegration, and structural change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Madison, G. (2004). Fractal modeling of human isochronous serial interval production. Biological Cybernetics, 90, 105–112.
Mandelbrot, B. B. (1975). Limit theorems on the self-normalized range for weakly and strongly dependent processes. Zeitschrift für Wahrscheinlichkeitstheorie & verwandte Gebiete, 31, 271–285.
Mandelbrot, B. B., & van Ness, J. W. (1968). Fractional Brownian motion, fractional noises and applications. SIAM Review, 10, 422–437.
Mandelbrot, B. B., & Wallis, J. R. (1969). Computer experiments with fractional Gaussian noises. Water Resources Research, 5, 228–267.
Marks-Tarlow, T. (1999). The self as a dynamical system. Nonlinear Dynamics, Psychology, & Life Sciences, 3, 311–345.
Peng, C.-K., Mietus, J., Hausdorff, J. M., Havlin, S., Stanley, H. E., & Goldberger, A. L. (1993). Long-range anticorrelations and non-Gaussian behavior of the heartbeat. Physical Review Letters, 70, 1343–1346.
Press, W. H., Teukolsky, S. A., Vetterling, W. T., & Flannery, B. P. (1992). Numerical recipes in C: The art of scientific computing (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Pressing, J. (1999). Sources for 1/f noise effects in human cognition and performance. In R. Heath, B. Hayes, A. Heathcote, & C. Hooker (Eds.), Proceedings of the Fourth Conference of the Australian Cognitive Science Society. Newcastle, NSW: University of Newcastle, Department of Psychology.
Rangarajan, G., & Ding, M. (2000). First passage time distribution for anomalous diffusion. Physics Letters A, 273, 322–330.
R Development Core Team (2008). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Available at www.R-project.org.
Reisen, V. A. (1994). Estimation of the fractional difference parameter in the ARIMA(p, d, q) model using the smoothed periodogram. Journal of Time Series Analysis, 15, 335–350.
Reisen, V. A., Abraham, B., & Toscano, E. M. (2000). Parametric and semiparametric estimations of stationary univariate ARFIMA models. Brazilian Journal of Probability & Statistics, 14, 185–206.
Riley, M. A., & Van Orden, G. C. (Eds.) (2005). Tutorials in contemporary nonlinear methods for the behavioral sciences [Online]. Retrieved October 7, 2008, from www.nsf.gov/sbe/bcs/pac/nmbs/nmbs.jsp.
Shumway, R. H., & Stoffer, D. S. (2006). Time series analysis and its applications: With R examples. New York: Springer.
Sowell, F. (1992). Maximum likelihood estimation of stationary univariate fractionally integrated time series models. Journal of Econometrics, 53, 165–188.
Stadnytska, T., & Werner, J. (2006). Sample size and accuracy of estimation of the fractional differencing parameter. Methodology, 4, 135–144.
Stroe-Kunold, E., & Werner, J. (2008). Modeling human dynamics by means of cointegration methodology. Methodology, 4, 113–131.
Taqqu, M. S., & Teverovsky, V. (1998). On estimating the intensity of long-range dependence in finite and infinite variance time series. In R. J. Adler, R. E. Feldman, & M. S. Taqqu (Eds.), A practical guide to heavy tails: Statistical techniques and applications (pp. 177–217). Boston: Birkhäuser.
Taqqu, M. S., Teverovsky, V., & Willinger, W. (1995). Estimators for long-range dependence: An empirical study. Fractals, 3, 785–798.
Thornton, T. L., & Gilden, D. L. (2005). Provenance of correlations in psychological data. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 12, 409–441.
Torre, K., Delignières, D., & Lemoine, L. (2007a). Detection of long-range dependence and estimation of fractal exponents through ARFIMA modelling. British Journal of Mathematical & Statistical Psychology, 60, 85–106.
Torre, K., Delignières, D., & Lemoine, L. (2007b). 1/fβ fluctuations in bimanual coordination: An additional challenge for modeling. Experimental Brain Research, 183, 225–234.
Van Orden, G. C., Holden, J. G., & Turvey, M. T. (2003). Self-organization of cognitive performance. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 132, 331–350.
Van Orden, G. C., Kello, C. T., & Holden, J. G. (in press). Situated behavior and the place of measurement in psychological theory. Ecological Psychology.
Wagenmakers, E.-J., Farrell, S., & Ratcliff, R. (2004). Estimation and interpretation of 1/fα noise in human cognition. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 11, 579–615.
Wagenmakers, E.-J., Farrell, S., & Ratcliff, R. (2005). Human cognition and a pile of sand: A discussion on serial correlations and selforganized criticality. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 134, 108–116.
Ward, L. M., & Richard, C. M. (2001). 1/fα noise and decision complexity. Unpublished manuscript, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada.
West, B. J., & Shlesinger, M. F. (1990). The noise in natural phenomena. American Scientist, 78, 40–45.
Zbilut, J. P., & Marwan, N. (2008). The Wiener—Khinchin theorem and recurrence quantification. Physics Letters A, 372, 6622–6626.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The research for this article was supported by a scholarship awarded the first author by the German National Academic Foundation. Part of this work was done while the first author was a visiting scholar with Eric-Jan Wagenmakers at the University of Amsterdam.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stroe-Kunold, E., Stadnytska, T., Werner, J. et al. Estimating long-range dependence in time series: An evaluation of estimators implemented in R. Behavior Research Methods 41, 909–923 (2009). https://doi.org/10.3758/BRM.41.3.909
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3758/BRM.41.3.909