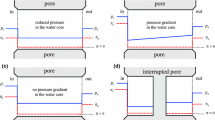
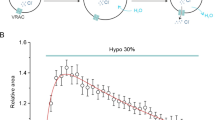
Abstract
Osmotic perturbations, occurring frequently under physiological and pathological conditions, alter cell size/volume and function. To protect cellular homeostasis, cell osmo- and volume-sensing mechanisms activate volume compensatory processes. The plasma membrane plays a prominent role in cell volume regulation by mediating the selective transport of extra- and intracellular osmolytes. The function of the membrane-enclosed cytoplasm in osmosensing and cell volume homeostasis is much less appreciated. We present current concepts and discuss evidence of cell volume sensors with emphasis on the hydrogel nature of the mammalian cytoplasm and its intrinsic osmosensitivity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akimova OA, Poirier M, Kotelevtsev SV, Hamet P, Orlov SN (2008) The death of ouabain-treated renal epithelial cells: evidence against anoikis occurrence. Apoptosis 13:670–680
Alenghat FJ, Ingber DE (2002) Mechanotransduction: all signals point to cytoskeleton, matrix, and integrins. Sci STKE 2002:E6
Bagriantsev SN, Gracheva EO, Gallagher PG (2014) Piezo proteins: regulators of mechanosensation and other cellular processes. J Biol Chem 289:31673–31681
Boudreault F, Grygorczyk R (2004) Evaluation of rapid volume changes of substrate-adherent cells by conventional microscopy 3D imaging. J Microsc 215:302–312
Brandts JF, Taverna RD, Sadasivan E, Lysko KA (1978) Calorimetric studies of the structural transitions of the human erythrocyte membrane. Studies of the B and C transitions. Biochim Biophys Acta 512:566–578
Brown A, Lasek RJ (1993) Neurofilaments move apart freely when released from the circumferential constraint of the axonal plasma membrane. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 26:313–324
Cameron IL, Hardman WE, Fullerton GD, Miseta A, Koszegi T, Ludany A, Kellermayer M (1996) Maintenance of ions, proteins and water in lens fiber cells before and after treatment with non-ionic detergents. Cell Biol Int 20:127–137
Cameron IL, Short NJ, Fullerton GD (2008) Characterization of water of hydration fractions in rabbit skeletal muscle with age and time of post-mortem by centrifugal dehydration force and rehydration methods. Cell Biol Int 32:1337–1343
Chaplin M (2006) Do we underestimate the importance of water in cell biology? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:861–866
Clegg JS (1984) Intracellular water and the cytomatrix: some methods of study and current views. J Cell Biol 99:167s–171s
Colclasure GC, Parker JC (1991) Cytosolic protein concentration is the primary volume signal in dog red cells. J Gen Physiol 98:881–892
Collins KD (1995) Sticky ions in biological systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:5553–5557
Danziger J, Zeidel ML (2014) Osmotic homeostasis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. doi:10.2215/CJN.10741013
Eduardsen K, Larsen SL, Novak I, Lambert IH, Hoffmann EK, Pedersen SF (2011) Cell volume regulation and signaling in 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes and adipocytes: on the possible roles of caveolae, insulin receptors, FAK and ERK1/2. Cell Physiol Biochem 28:1231–1246
Elliott GF, Goodfellow JM, Woolgar AE (1980) Swelling studies of bovine corneal stroma without bounding membranes. J Physiol 298:453–470
Elliott GF, Hodson SA (1998) Cornea, and the swelling of polyelectrolyte gels of biological interest. Rep Prog Phys 61:1325–1365
Ellis RJ (2001) Macromolecular crowding: obvious but underappreciated. Trends Biochem Sci 26:597–604
Fels J, Orlov SN, Grygorczyk R (2009) The hydrogel nature of mammalian cytoplasm contributes to osmosensing and extracellular pH sensing. Biophys J 96:4276–4285
Fullerton GD, Kanal KM, Cameron IL (2006) Osmotically unresponsive water fraction on proteins: non-ideal osmotic pressure of bovine serum albumin as a function of pH and salt concentration. Cell Biol Int 30:86–92
Fulton AB (1982) How crowded is the cytoplasm? Cell 30:345–347
Groulx N, Boudreault F, Orlov SN, Grygorczyk R (2006) Membrane reserves and hypotonic cell swelling. J Membr Biol 214:43–56
Gulak PV, Orlov SN, Pokudin NI, Postnov YV, Litvinov IS, Orlov NJ, Shnyrov VL (1984) Microcalorimetry and electrophoresis of the erythrocyte membrane of spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens 2:81–84
Hazlewood CF, Kellermayer M (1988) Ion and water retention by permeabilized cells. Scanning Microsc 2:267–273
Hoffmann EK (2000) Intracellular signalling involved in volume regulatory decrease. Cell Physiol Biochem 10:273–288
Hoffmann EK, Lambert IH, Pedersen SF (2009) Physiology of cell volume regulation in vertebrates. Physiol Rev 89:193–277
Hoffmann EK, Simonsen LO (1989) Membrane mechanisms in volume and pH regulation in vertebrate cells. Physiol Rev 69:315–382
Hortelano S, Garcia-Martin ML, Cerdan S, Castrillo A, Alvarez AM, Bosca L (2001) Intracellular water motion decreases in apoptotic macrophages after caspase activation. Cell Death Differ 8:1022–1028
Ingber DE (2003) Tensegrity I. Cell structure and hierarchical systems biology. J Cell Sci 116:1157–1173
Katchalsky A (1964) Polyelectrolytes and their biological interactions. Biophys J 4:Suppl-41
Knull H, Minton AP (1996) Structure within eukaryotic cytoplasm and its relationship to glycolytic metabolism. Cell Biochem Funct 14:237–248
Koivusalo M, Kapus A, Grinstein S (2009) Sensors, transducers, and effectors that regulate cell size and shape. J Biol Chem 284:6595–6599
Koltsova SV, Platonova A, Maksimov GV, Mongin AA, Grygorczyk R, Orlov SN (2011) Activation of P2Y receptors causes strong and persistent shrinkage of C11-MDCK renal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 301:C403–C412
Korchev YE, Bashford CL, Milovanovic M, Vodyanoy I, Lab MJ (1997) Scanning ion conductance microscopy of living cells. Biophys J 73:653–658
Korolev N, Lyubartsev AP, Rupprecht A, Nordenskiold L (1999) Competitive binding of Mg2+, Ca2+, Na+, and K+ ions to DNA in oriented DNA fibers: experimental and Monte Carlo simulation results. Biophys J 77:2736–2749
Kozera L, White E, Calaghan S (2009) Caveolae act as membrane reserves which limit mechanosensitive I(Cl, swell) channel activation during swelling in the rat ventricular myocyte. PLoS One 4:e8312
Kunz L, Stark G (1997) Photodynamic membrane damage at the level of single ion channels. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1327:1–4
Lang F (2007) Mechanisms and significance of cell volume regulation. J Am Coll Nutr 26:613S–623S
Lang F, Busch GL, Ritter M, Volkl H, Waldegger S, Gulbins E, Haussinger D (1998) Functional significance of cell volume regulatory mechanisms. Physiol Rev 78:247–306
Lehtonen JY, Kinnunen PK (1995) Phospholipase A2 as a mechanosensor. Biophys J 68:1888–1894
Leterrier JF (2001) Water and the cytoskeleton. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy -le-grand) 47:901–923
Ling GN (2006) A convergence of experimental and theoretical breakthrougs affirms the PM theory of dynamically structures cell water on the theory’s 40th birthday. In: Pollack GH, Cameron IL, Wheatley DN (eds) Water and the cell. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 1–52
Luby-Phelps K (2000) Cytoarchitecture and physical properties of cytoplasm: volume, viscosity, diffusion, intracellular surface area. Int Rev Cytol 192:189–221
Martinac B (2011) Bacterial mechanosensitive channels as a paradigm for mechanosensory transduction. Cell Physiol Biochem 28:1051–1060
Minton AP (1980) Excluded volume as a determinant of protein structure and stability. Biophys J 32:77–79
Minton AP (2001) The influence of macromolecular crowding and macromolecular confinement on biochemical reactions in physiological media. J Biol Chem 276:10577–10580
Minton AP, Colclasure GC, Parker JC (1992) Model for the role of macromolecular crowding in regulation of cellular volume. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:10504–10506
Mongin AA, Orlov SN (2001) Mechanism of cell volume regulation and possible nature of the cell volume sensor. Pathophysiology 8:77–88
Munakata S, Hatori K (2013) The excluded volume effect induced by poly(ethylene glycol) modulates the motility of actin filaments interacting with myosin. FEBS J 280:5875–5883
O’Neil RG, Heller S (2005) The mechanosensitive nature of TRPV channels. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 451:193–203
Okada Y (1997) Volume expansion-sensing outward-rectifier Cl− channel: fresh start to the molecular identity and volume sensor. Am J Physiol 273:C755–C789
Orlov SN, Kolosova IA, Cragoe EJ, Gurlo TG, Mongin AA, Aksentsev SL, Konev SV (1993) Kinetics and peculiarities of thermal inactivation of volume-induced Na+/H+ exchange, Na+, K+,2Cl− cotransport and K+, Cl− cotransport in rat erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1151:186–192
Orlov SN, Kuznetsov SR, Kolosova IA, Aksentsev SL, Konev SV (1997) Volume-dependent regulation of ion carriers in human and rat erythrocytes: role of cytoskeleton and protein phosphorylation. Ross Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova 83:119–147
Parker JC (1993) Urea alters set point volume for K-Cl cotransport, Na-H exchange, and Ca-Na exchange in dog red blood cells. Am J Physiol 265:C447–C452
Parshina EY, Yusipovich AI, Platonova AA, Grygorczyk R, Maksimov GV, Orlov SN (2013) Thermal inactivation of volume-sensitive K(+), Cl(−) cotransport and plasma membrane relief changes in human erythrocytes. Pflugers Arch 465:977–983
Pedersen SF, Hoffmann EK, Mills JW (2001) The cytoskeleton and cell volume regulation. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 130:385–399
Pedersen SF, Kapus A, Hoffmann EK (2011) Osmosensory mechanisms in cellular and systemic volume regulation. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:1587–1597
Pedersen SF, Nilius B (2007) Transient receptor potential channels in mechanosensing and cell volume regulation. Methods Enzymol 428:183–207
Peppas NA, Huang Y, Torres-Lugo M, Ward JH, Zhang J (2000) Physicochemical foundations and structural design of hydrogels in medicine and biology. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 2:9–29
Platonova A, Boudreault F, Kapilevich LV, Maksimov GV, Ponomarchuk O, Grygorczyk R, Orlov SN (2014) Temperature-induced inactivation of cytoplasmic biogel osmosensing properties is associated with suppression of regulatory volume decrease in A549 cells. J Membr Biol 247:571–579
Platonova AA, Orlov SN, Grygorczyk R (2013) Volume changes triggered by aniosmotic media in intact and permeabilized A549 cells: role of cytoskeleton network. Bull Sib Med 12(4):60, Ref Type: Abstract
Ricka J, Tanaka T (1984) Swelling of ionic gels—quantitative performance of the donnan theory. Macromolecules 17:2916–2921
Sachs F (2010) Stretch-activated ion channels: what are they? Physiology (Bethesda) 25:50–56
Sachs JR (1998) How red blood cells know how big they are? In: Okada Y (ed) Cell volume regulation: the molecular mechanism and volume sensing machinery. Elsevier Science, Tokyo, pp 3–13
Shepherd VA (2006) Coherent domains in the streaming cytoplasm of a giant algal cell. In: Pollack GH, Cameron IL, Wheatley DN (eds) Water and the cell. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 71–92
Shepherd VA (2006) The cytomatrix as a cooperative system of macromolecular and water networks. Curr Top Dev Biol 75:171–223
Shnyrov VL, Orlov SN, Zhadan GG, Pokudin NI (1990) Thermal inactivation of membrane proteins, volume-dependent Na+, K(+)-cotransport, and protein kinase C activator-induced changes of the shape of human and rat erythrocytes. Biomed Biochim Acta 49:445–453
Sinha B, Koster D, Ruez R, Gonnord P, Bastiani M, Abankwa D, Stan RV, Butler-Browne G, Vedie B, Johannes L, Morone N et al (2011) Cells respond to mechanical stress by rapid disassembly of caveolae. Cell 144:402–413
Solenov E, Watanabe H, Manley GT, Verkman AS (2004) Sevenfold-reduced osmotic water permeability in primary astrocyte cultures from AQP-4-deficient mice, measured by a fluorescence quenching method. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 286:C426–C432
Sowa G (2012) Caveolae, caveolins, cavins, and endothelial cell function: new insights. Front Physiol 2:120
Spagnoli C, Beyder A, Besch S, Sachs F (2008) Atomic force microscopy analysis of cell volume regulation. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys 78:031916
Strange K (1989) Ouabain-induced cell swelling in rabbit cortical collecting tubule: NaCl transport by principal cells. J Membr Biol 107:249–261
Strange K (2004) Cellular volume homeostasis. Adv Physiol Educ 28:155–159
Strotmann R, Harteneck C, Nunnenmacher K, Schultz G, Plant TD (2000) OTRPC4, a nonselective cation channel that confers sensitivity to extracellular osmolarity. Nat Cell Biol 2:695–702
Summers JC, Trais L, Lajvardi R, Hergan D, Buechler R, Chang H, Pena-Rasgado C, Rasgado-Flores H (1997) Role of concentration and size of intracellular macromolecules in cell volume regulation. Am J Physiol 273:C360–C370
Thirone AC, Speight P, Zulys M, Rotstein OD, Szaszi K, Pedersen SF, Kapus A (2009) Hyperosmotic stress induces Rho/Rho kinase/LIM kinase-mediated cofilin phosphorylation in tubular cells: key role in the osmotically triggered F-actin response. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 296:C463–C475
Trouet D, Hermans D, Droogmans G, Nilius B, Eggermont J (2001) Inhibition of volume-regulated anion channels by dominant-negative caveolin-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 284:461–465
Volkers L, Mechioukhi Y, Coste B (2014) Piezo channels: from structure to function. Pflugers Arch. doi:10.1007/s00424-014-1578-z
Wheatley DN (2003) Diffusion, perfusion and the exclusion principles in the structural and functional organization of the living cell: reappraisal of the properties of the ‘ground substance’. J Exp Biol 206:1955–1961
Yusipovich AI, Zagubizhenko MV, Levin GG, Platonova A, Parshina EY, Grygorzcyk R, Maksimov GV, Rubin AB, Orlov SN (2011) Laser interference microscopy of amphibian erythrocytes: impact of cell volume and refractive index. J Microsc 244:223–229
Zhou HX, Rivas G, Minton AP (2008) Macromolecular crowding and confinement: biochemical, biophysical, and potential physiological consequences. Annu Rev Biophys 37:375–397
Zimmerman SB, Harrison B (1987) Macromolecular crowding increases binding of DNA polymerase to DNA: an adaptive effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84:1871–1875
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This article is published as part of a Special Issue on Salt and Osmosensing.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grygorczyk, R., Boudreault, F., Platonova, A. et al. Salt and osmosensing: role of cytoplasmic hydrogel. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 467, 475–487 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-014-1680-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-014-1680-2